摘要
直接插入排序(Insertion Sort)序是一种最简单的插入排序。为简化问题,我们下面只讨论升序排序。

一、前言
直接插入排序(Insertion Sort)序是一种最简单的插入排序。为简化问题,我们下面只讨论升序排序。
二、算法思想
插入排序:每一趟将一个待排序的记录,按照其关键字的大小插入到有序队列的合适位置里,知道全部插入完成。
动态效果示意图:

以上的过程,其实就是典型的直接插入排序,每次将一个新数据插入到有序队列中的合适位置里。
很简单吧,接下来,我们要将这个算法转化为编程语言。
假设有一组无序序列 R0, R1, ... , RN-1。
(1) 我们先将这个序列中下标为 0 的元素视为元素个数为 1 的有序序列。
(2) 然后,我们要依次把 R1, R2, ... , RN-1 插入到这个有序序列中。所以,我们需要一个外部循环,从下标 1 扫描到 N-1 。
(3) 接下来描述插入过程。假设这是要将 Ri 插入到前面有序的序列中。由前面所述,我们可知,插入Ri时,前 i-1 个数肯定已经是有序了。
所以我们需要将Ri 和R0 ~ Ri-1 进行比较,确定要插入的合适位置。这就需要一个内部循环,我们一般是从后往前比较,即从下标 i-1 开始向 0 进行扫描。
1、代码
C++:
C++
#include
#include
using namespace std;
vector insertSort(vector list){
vector result;
if (list.empty()){
return result;
}
result = list;
// 第1个数肯定是有序的,从第2个数开始遍历,依次插入有序序列
for (int i = 1; i < result.size(); i++){
// 取出第i个数,和前i-1个数比较后,插入合适位置
int temp = result[i];
// 因为前i-1个数都是从小到大的有序序列,所以只要当前比较的数(list[j])比temp大,就把这个数后移一位
int j = i - 1;
for (j; j >= 0 && result[j] > temp; j--){
result[j + 1] = result[j];
}
result[j + 1] = temp;
}
return result;
}
void main(){
int arr[] = { 6, 4, 8, 9, 2, 3, 1 };
vector test(arr, arr + sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]));
cout << "排序前" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < test.size(); i++){
cout << test[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
vector result;
result = insertSort(test);
cout << "排序后" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++){
cout << result[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
system("pause");
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42#include
#include
usingnamespacestd;
vectorinsertSort(vectorlist){
vectorresult;
if(list.empty()){
returnresult;
}
result=list;
// 第1个数肯定是有序的,从第2个数开始遍历,依次插入有序序列
for(inti=1;i
// 取出第i个数,和前i-1个数比较后,插入合适位置
inttemp=result[i];
// 因为前i-1个数都是从小到大的有序序列,所以只要当前比较的数(list[j])比temp大,就把这个数后移一位
intj=i-1;
for(j;j>=0&&result[j]>temp;j--){
result[j+1]=result[j];
}
result[j+1]=temp;
}
returnresult;
}
voidmain(){
intarr[]={6,4,8,9,2,3,1};
vectortest(arr,arr+sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]));
cout<
for(inti=0;i
cout<
}
cout<
vectorresult;
result=insertSort(test);
cout<
for(inti=0;i
cout<
}
cout<
system("pause");
}
运行结果:
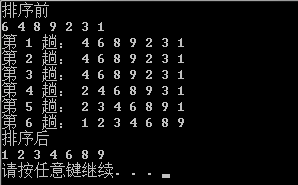
Python:
Python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
def insertSort(input_list):
if len(input_list) == 0:
return []
sorted_list = input_list
for i in range(1, len(sorted_list)):
temp = sorted_list[i]
j = i - 1
while j >=0 and temp < sorted_list[j]:
sorted_list[j + 1] = sorted_list[j]
j -= 1
sorted_list[j + 1] = temp
return sorted_list
if __name__ == '__main__':
input_list = [6, 4, 8, 9, 2, 3, 1]
print('排序前:', input_list)
sorted_list = insertSort(input_list)
print('排序后:', sorted_list)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
definsertSort(input_list):
iflen(input_list)==0:
return[]
sorted_list=input_list
foriinrange(1,len(sorted_list)):
temp=sorted_list[i]
j=i-1
whilej>=0andtemp
sorted_list[j+1]=sorted_list[j]
j-=1
sorted_list[j+1]=temp
returnsorted_list
if__name__=='__main__':
input_list=[6,4,8,9,2,3,1]
print('排序前:',input_list)
sorted_list=insertSort(input_list)
print('排序后:',sorted_list)
三、算法分析
1、直接插入排序的算法性能

2、时间复杂度
当数据正序时,执行效率最好,每次插入都不用移动前面的元素,时间复杂度为O(N)。
当数据反序时,执行效率最差,每次插入都要前面的元素后移,时间复杂度为O(N^2)。
所以,数据越接近正序,直接插入排序的算法性能越好。
3、空间复杂度
由直接插入排序算法可知,我们在排序过程中,需要一个临时变量存储要插入的值,所以空间复杂度为 1 。
4、算法稳定性
直接插入排序的过程中,不需要改变相等数值元素的位置,所以它是稳定的算法。
四、优化
因为在一个有序序列中查找一个插入位置,以保证有序序列的序列不变,所以可以使用二分查找,减少元素比较次数提高效率。
二分查找是对于有序数组而言的,假设如果数组是升序排序的。那么,二分查找算法就是不断对数组进行对半分割,每次拿中间元素和目标数字进行比较,如果中间元素小于目标数字,则说明目标数字应该在右侧被分割的数组中,如果中间元素大于目标数字,则说明目标数字应该在左侧被分割的数组中。
1、代码
C++:
C++
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// 给定一个有序的数组,查找第一个大于等于value的下标,不存在返回-1
int BinarySearch(vector list, int n, int value){
int left = 0;
int right = n - 1;
while (left <= right){
int middle = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
if (list[middle] > value){
right = middle - 1;
}
else{
left = middle + 1;
}
}
return (left < n) ? left : -1;
}
vector BinaryInsertSort(vector list){
vector result = list;
for (int i = 1; i < result.size(); i++){
int insert_index = BinarySearch(result, i, result[i]);
if (insert_index != -1){
int temp = result[i];
int j = i - 1;
while (j >= insert_index){
result[j + 1] = result[j];
j--;
}
result[j + 1] = temp;
}
printf("第 %d 趟: ", i);
for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++){
cout << result[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return result;
}
void main(){
int arr[] = { 6, 4, 8, 9, 2, 3, 1 };
vector test(arr, arr + sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]));
cout << "排序前" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < test.size(); i++){
cout << test[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
vector result;
result = BinaryInsertSort(test);
cout << "排序后" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++){
cout << result[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
system("pause");
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62#include
#include
usingnamespacestd;
// 给定一个有序的数组,查找第一个大于等于value的下标,不存在返回-1
intBinarySearch(vectorlist,intn,intvalue){
intleft=0;
intright=n-1;
while(left<=right){
intmiddle=left+((right-left)>>1);
if(list[middle]>value){
right=middle-1;
}
else{
left=middle+1;
}
}
return(left
}
vectorBinaryInsertSort(vectorlist){
vectorresult=list;
for(inti=1;i
intinsert_index=BinarySearch(result,i,result[i]);
if(insert_index!=-1){
inttemp=result[i];
intj=i-1;
while(j>=insert_index){
result[j+1]=result[j];
j--;
}
result[j+1]=temp;
}
printf("第 %d 趟: ",i);
for(inti=0;i
cout<
}
cout<
}
returnresult;
}
voidmain(){
intarr[]={6,4,8,9,2,3,1};
vectortest(arr,arr+sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]));
cout<
for(inti=0;i
cout<
}
cout<
vectorresult;
result=BinaryInsertSort(test);
cout<
for(inti=0;i
cout<
}
cout<
system("pause");
}
运行结果没有改变,只是在查找插入位置的次数减少了,提高了算法的效率。
Python:
Python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
def BinarySearch(input_list, end, value):
left = 0
right = end - 1
while left <= right:
middle = left + (right - left) // 2
if input_list[middle] > value:
right = middle - 1
else:
left = middle + 1
return left if left < end else -1
def BinaryInsertSort(input_list):
if len(input_list) == 0:
return []
result = input_list
for i in range(1, len(input_list)):
j = i - 1
temp = result[i]
insert_index = BinarySearch(result, i, result[i])
if insert_index != -1:
while j >= insert_index:
result[j + 1] = result[j]
j -= 1
result[j + 1] = temp
return result
if __name__ == '__main__':
input_list = [6, 4, 8, 9, 2, 3, 1]
print('排序前:', input_list)
sorted_list = BinaryInsertSort(input_list)
print('排序后:', sorted_list)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
defBinarySearch(input_list,end,value):
left=0
right=end-1
whileleft<=right:
middle=left+(right-left)//2
ifinput_list[middle]>value:
right=middle-1
else:
left=middle+1
returnleftifleft
defBinaryInsertSort(input_list):
iflen(input_list)==0:
return[]
result=input_list
foriinrange(1,len(input_list)):
j=i-1
temp=result[i]
insert_index=BinarySearch(result,i,result[i])
ifinsert_index!=-1:
whilej>=insert_index:
result[j+1]=result[j]
j-=1
result[j+1]=temp
returnresult
if__name__=='__main__':
input_list=[6,4,8,9,2,3,1]
print('排序前:',input_list)
sorted_list=BinaryInsertSort(input_list)
print('排序后:',sorted_list)
本站整理自:























 859
859

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








