LINUX系统学习一(进程、MMU,环境变量、getenv、fork、getpid/ge
LINUX系统学习一(进程、MMU,环境变量、getenv、fork、getpid/getppid、ps、kill)
1、进程的概念
编译好的二进制文件叫程序
进行是运行起来的程序
站在程序员的角度:运行一系列指令的过程
站在操作系统角度:分配系统资源的基本单位
区别:
程序占用磁盘,不占用系统资源
进程占用系统资源
一个程序对应多个进程,可以同时运行多个,一个进程对应一个程序
程序没有生命周期,进程有生命周期
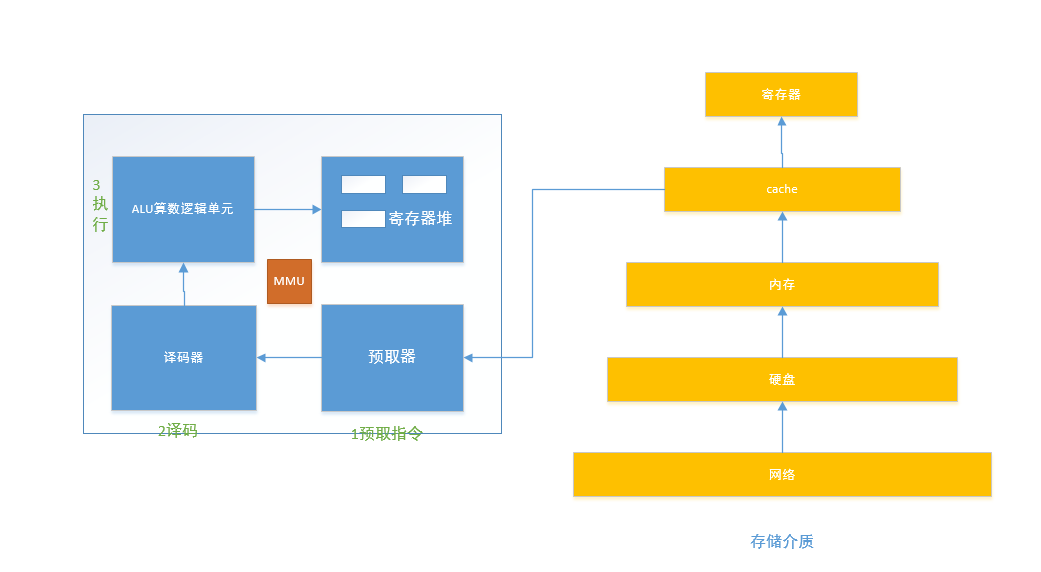
2、进程的过程
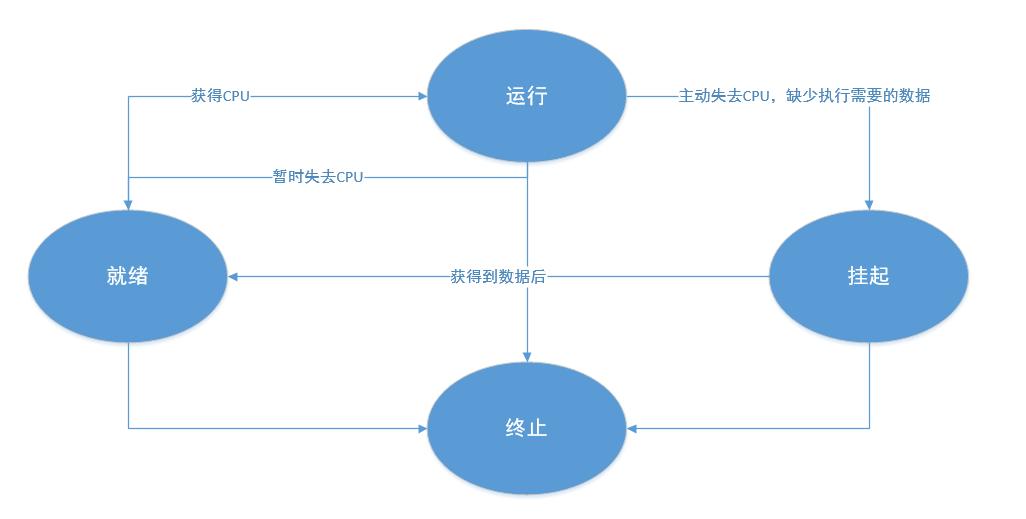
3、进程的状态
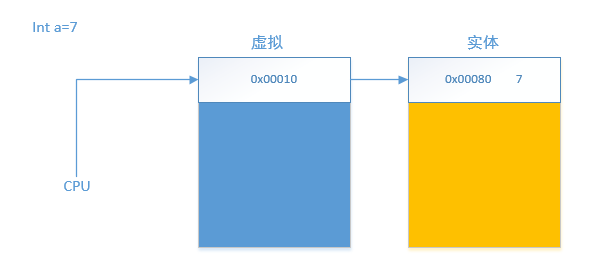
4、MMU的作用
1、虚拟内存和物理内存的映射
2、修改内存访问级别
3、用户空间映射到物理内在是独立的
5、进程控制块PCB
[email protected]:~# grep -rn "struct task_struct {" /usr/ 查找进程控制块代码
/usr/share/systemtap/tapset/linux/signal.stp:837:// struct task_struct {
/usr/share/systemtap/tapset/linux/signal.stp:876:// struct task_struct {
/usr/src/linux-headers-4.4.0-148/include/linux/sched.h:1391:struct task_struct {
/usr/src/linux-headers-4.4.0-31/include/linux/sched.h:1380:struct task_struct {
/usr/src/linux-headers-4.4.0-93/include/linux/sched.h:1380:struct task_struct {
[email protected]:/usr/src/linux-headers-4.4.0-31/include/linux# pwd
/usr/src/linux-headers-4.4.0-31/include/linux
[email protected]:/usr/src/linux-headers-4.4.0-31/include/linux# ls sched.h
sched.h
6、环境变量
查看所有环境变量
[email protected]:/usr/src/linux-headers-4.4.0-31/include/linux# env
查看某个环境变量
[email protected]:~# echo $PATH
/usr/java/jdk1.8.0_181/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games
PATH可执行文件搜索路径
SHELL当前使用的shell,通常是/bin/bash
TERM当前终端类型,图形界面终端下的值通常是xterm
LANG语言与locale,决定了字符编码以及时间,货币等信息的显示式
HOME当前用户主目标录的路径
7、getenv获取环境变量
char *getenv(const char *name);
[[email protected]_0_5_centos test3]# more getenv.c
#include
#include
int main()
{
printf("homepath is [%s]\n",getenv("HOME"));
return 0;
}
[[email protected]_0_5_centos test3]# gcc getenv.c
[[email protected]_0_5_centos test3]# ./a.out
homepath is [/root]
8、fork创建一个新的进程
pid_t fork(void);
返回值:
失败:-1
成功,两次返回
父进程返回子进程的id
子进程返回0
9、getpid和getppid
获得pid,进程id,获得当前进程的
pid_t getpid(void);
获得当前进程的父进程的id
pid_t getppid(void);
代码示例
[[email protected]_0_5_centos test3]# more fork.c
#include
#include
#include
int main(){
printf("begin...\n");
pid_t pid =fork();
if(pid<0){
perror("fork err");
exit(1);
}
if(pid==0){
//子进程
printf("I am child,pid=%d,ppid=%d\n",getpid(),getppid());
}
else if(pid>0){
//父进程
printf("childpid=%d,self=%d,ppid=%d\n",pid,getpid(),getppid());
sleep(1);
}
printf("end...\n");
return 0;
}
[[email protected]_0_5_centos test3]# gcc fork.c
[[email protected]_0_5_centos test3]# ./a.out
begin...
childpid=19741,self=19740,ppid=18132
I am child,pid=19741,ppid=19740
end...
end...
10、ps aux查看进程 ps ajx还能查到父进程
[[email protected]_0_5_centos test3]# ps aux
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
root 1 0.0 0.0 41096 3412 ? Ss 2019 32:06 /usr/lib/system
root 2 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 2019 0:01 [kthreadd]
root 3 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 2019 0:26 [ksoftirqd/0]
root 5 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 2019 0:00 [kworker/0:0H]
root 7 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 2019 1:57 [migration/0]
[[email protected]_0_5_centos test3]# ps ajx ---可以追述进程之间的血缘关系
PPID PID PGID SID TTY TPGID STAT UID TIME COMMAND
0 1 1 1 ? -1 Ss 0 32:06 /usr/lib/systemd/system
0 2 0 0 ? -1 S 0 0:01 [kthreadd]
2 3 0 0 ? -1 S 0 0:26 [ksoftirqd/0]
2 5 0 0 ? -1 S< 0 0:00 [kworker/0:0H]
2 7 0 0 ? -1 S 0 1:57 [migration/0]
11、kill 进程ID 杀进程
[[email protected]_0_5_centos test3]#kill 2898
12、创建n个子进程
父进程创建5个子进程示例
[[email protected]_0_5_centos test3]# more fork_five.c
#include
#include
#include
int main(){
int i=0;
pid_t pid=0;
for(i=0;i<5;i++){ //父进程结束循环
pid=fork();
if(pid==0){ //子进程
printf("I am child,pid=%d,ppid=%d\n",getpid(),getppid());
break;//子进程退出循环
}
else if(pid>0){//父进程
printf("I am fatcher,pid=%d,ppid=%d\n",getpid(),getppid(
));
sleep(1);
}
}
sleep(i);
//If(i<5){
//printf("I am child,pid=%d,ppid=%d\n",getpid(),getppid());
//}else{
// printf("I am fatcher,pid=%d,ppid=%d\n",getpid(),getppid());
//}
while(1){
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
[[email protected]_0_5_centos test3]# gcc fork_five.c
[[email protected]_0_5_centos test3]# ./a.out
I am fatcher,pid=23907,ppid=18132
I am child,pid=23908,ppid=23907
I am fatcher,pid=23907,ppid=18132
I am child,pid=23917,ppid=23907
I am fatcher,pid=23907,ppid=18132
I am child,pid=23923,ppid=23907
I am fatcher,pid=23907,ppid=18132
I am child,pid=23924,ppid=23907
I am fatcher,pid=23907,ppid=18132
I am child,pid=23926,ppid=23907
[[email protected]_0_5_centos ~]# ps ajx|grep a.out
18132 23907 23907 18132 pts/2 23907 S+ 0 0:00 ./a.out
23907 23908 23907 18132 pts/2 23907 S+ 0 0:00 ./a.out
23907 23917 23907 18132 pts/2 23907 S+ 0 0:00 ./a.out
23907 23923 23907 18132 pts/2 23907 S+ 0 0:00 ./a.out
23907 23924 23907 18132 pts/2 23907 S+ 0 0:00 ./a.out
23907 23926 23907 18132 pts/2 23907 S+ 0 0:00 ./a.out
23943 24045 24044 23943 pts/0 24044 R+ 0 0:00 grep --color=auto a.out
LINUX系统学习一(进程、MMU,环境变量、getenv、fork、getpid/ge相关教程




 本文深入讲解了Linux系统中进程的概念、状态及控制方法,包括MMU的作用、环境变量的使用、getenv函数、fork和getpid函数的应用,以及如何通过ps和kill命令管理进程。
本文深入讲解了Linux系统中进程的概念、状态及控制方法,包括MMU的作用、环境变量的使用、getenv函数、fork和getpid函数的应用,以及如何通过ps和kill命令管理进程。

















 2100
2100

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








