先上图。
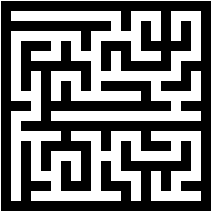
随机生成迷宫要求任意两点都能够找到相同的路径,也就是说,迷宫是一个连通图。随机生成迷宫可以使用普里姆算法、广度优先算法、深度优先算法等实现。这里将使用普里姆算法通过生成最小数的方法,实现迷宫图。
初始迷宫
迷宫有路和墙,白色表示路,黑色表示墙。每一个格子代表一个顶点,这里一共有100个顶点,需要找出99条边,使顶点连接起来,也就是要打通99块墙。
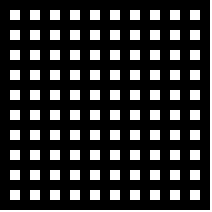
迷宫使用二位数组保存,为迷宫指定路的行数和列数,生成初始数组。
普利姆算法不了解的话,可以参考这篇博客的解析。
/*
* this.r 路的行数
* this.c 路的列数
* this.arr 保存迷宫的二维数组
*/
initArray() { for(let i = 0; i < 2 * this.r + 1; ++i) { this.arr[i] = []; for(let n = 0; n < 2 * this.c + 1; ++n) { if((n ^ (n - 1)) === 1 && (i ^ (i - 1)) === 1) { this.arr[i][n] = 0; // 0 表示路 this.notAccessed.push(0); }else { this.arr[i][n] = 1; // 1 表示墙 } } } }
生成迷宫
这里需要使用两个数组,分别保存已访问和未访问的顶点。
this.accessed = []; this.notAccessed = [...];
(1)初始状态下,notAccessed包含所有顶点,状态为0表示未访问,accessed为空。
(2)随机从notAccessed中抽取一个顶点cur,放入accessed中,cur在notAccessed中的状态改为1,表示已访问。
(3)忽略墙,遍历cur上下左右的顶点。若其中一顶点没有超出边界,且未访问过的,则将顶点加入accessed中,修改notAccessed中的状态,cur指向该顶点.
(4)循环步骤3,直到accessed.length等于顶点数。generate() {
let count = this.r * this.c; let cur = MathUtil.randomInt(0, count); let offs = [-this.c, this.c, -1, 1], // 四周顶点在notAccessed的偏移量
offr = [-1, 1, 0, 0], // 四周顶点在arr的纵向偏移量 offc = [0, 0, -1, 1]; // 四周顶点在arr的横向偏移量 this.accessed.push(cur); this.notAccessed[cur] = 1; while(this.accessed.length < count) { let tr = Math.floor(cur / this.c), tc = cur % this.c; let num = 0, off = -1;
// 遍历上下左右顶点 while(++num < 5) { let around = MathUtil.randomInt(0, 4), nr = tr + offr[around], nc = tc + offc[around]; if(nr >= 0 && nc >= 0 && nr < this.r && nc < this.c && this.notAccessed[cur + offs[around]] === 0) { off = around; break; } } // 四周顶点均被访问,则从已访问的顶点中随机抽取一个为cur if(off < 0) { cur = this.accessed[MathUtil.randomInt(0, this.accessed.length)]; }else { tr = 2 * tr + 1; tc = 2 * tc + 1; this.arr[tr + offr[off]][tc + offc[off]] = 0; cur = cur + offs[off]; this.notAccessed[cur] = 1; this.accessed.push(cur); } } }
渲染
最后,利用canvas,根据this.arr中的值,就可以生成迷宫啦。
好像少了入口和出口,直接将this.arr中这两个位置的值改成0就好了。
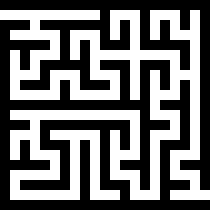
迷宫生成之后,可以对指定两个点生成路径哦。







 本文介绍了一种使用普里姆算法生成可通行迷宫的方法。通过确保迷宫中的每个点都能相互连接,实现了迷宫的完全连通性。文章详细解释了算法流程,并提供了具体的实现代码。
本文介绍了一种使用普里姆算法生成可通行迷宫的方法。通过确保迷宫中的每个点都能相互连接,实现了迷宫的完全连通性。文章详细解释了算法流程,并提供了具体的实现代码。
















 611
611

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








