一般来说cast是转型的意思,但是学java的时间也不短了,class类居然还有cast这个方法,这里来学习一下这个cast有何用。
第一次看到这个cast是在Spring的源码中,
spring-framework/spring-beans/src/main/java/org/springframework/beans/factory/xml/XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java:517处有这样的一段代码:
1 /** 2 * Create the {@link BeanDefinitionDocumentReader} to use for actually 3 * reading bean definitions from an XML document. 4 * <p>The default implementation instantiates the specified "documentReaderClass". 5 * @see #setDocumentReaderClass 6 */ 7 protected BeanDefinitionDocumentReader createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader() { 8 return BeanDefinitionDocumentReader.class.cast(BeanUtils.instantiateClass(this.documentReaderClass)); 9 }
当时我就好奇了,还有这个。
一、Java api
public T cast(Object obj);
Casts an object to the class or interface represented
解释的比较笼统,意思就是将一个对象装换为类或者接口。
二、代码示例
A.java
1 public class A { 2 public static void show() { 3 System.out.println("Class A show() function"); 4 } 5 }
B.java
1 public class B extends A { 2 public static void show() { 3 System.out.println("Class B show() function"); 4 } 5 }
TestCast.java
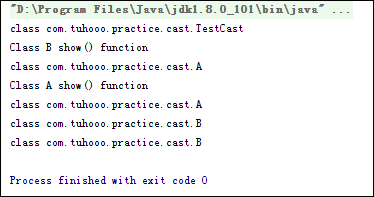
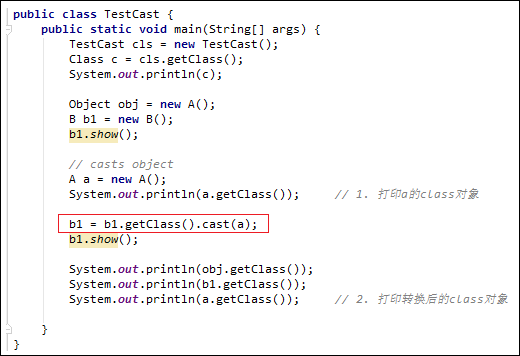
1 public class TestCast { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 TestCast cls = new TestCast(); 4 Class c = cls.getClass(); 5 System.out.println(c); 6 7 Object obj = new A(); 8 B b1 = new B(); 9 b1.show(); 10 11 // casts object 12 A a = new A(); 13 System.out.println(a.getClass()); // 1. 打印a的class对象 14 a = A.class.cast(b1); 15 a.show(); 16 17 System.out.println(obj.getClass()); 18 System.out.println(b1.getClass()); 19 System.out.println(a.getClass()); // 2. 打印a转换后的class对象 20 } 21 }
执行结果如下图:
这个例子是网上给出来的,核心为:a = A.class.cast(b1); 把a转化为了B类型,此处容易产生把b1转成A类型误解。
但是我很不满意啊,这个例子说明了啥??没看出来有卵用。
cast方法的源码
这个方法属于Class.java的
1 /** 2 * Casts an object to the class or interface represented 3 * by this {@code Class} object. 4 * 5 * @param obj the object to be cast 6 * @return the object after casting, or null if obj is null 7 * 8 * @throws ClassCastException if the object is not 9 * null and is not assignable to the type T. 10 * 11 * @since 1.5 12 */ 13 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 14 public T cast(Object obj) { 15 if (obj != null && !isInstance(obj)) 16 throw new ClassCastException(cannotCastMsg(obj)); 17 return (T) obj; 18 }
有点晕,这个T是Class的泛型。这个方法只能转换当前类型或其子类下的对象。再来看一下这个isInstance方法
1 /** 2 * Determines if the specified {@code Object} is assignment-compatible 3 * with the object represented by this {@code Class}. This method is 4 * the dynamic equivalent of the Java language {@code instanceof} 5 * operator. The method returns {@code true} if the specified 6 * {@code Object} argument is non-null and can be cast to the 7 * reference type represented by this {@code Class} object without 8 * raising a {@code ClassCastException.} It returns {@code false} 9 * otherwise. 10 * 11 * <p> Specifically, if this {@code Class} object represents a 12 * declared class, this method returns {@code true} if the specified 13 * {@code Object} argument is an instance of the represented class (or 14 * of any of its subclasses); it returns {@code false} otherwise. If 15 * this {@code Class} object represents an array class, this method 16 * returns {@code true} if the specified {@code Object} argument 17 * can be converted to an object of the array class by an identity 18 * conversion or by a widening reference conversion; it returns 19 * {@code false} otherwise. If this {@code Class} object 20 * represents an interface, this method returns {@code true} if the 21 * class or any superclass of the specified {@code Object} argument 22 * implements this interface; it returns {@code false} otherwise. If 23 * this {@code Class} object represents a primitive type, this method 24 * returns {@code false}. 25 * 26 * @param obj the object to check 27 * @return true if {@code obj} is an instance of this class 28 * 29 * @since JDK1.1 30 */ 31 public native boolean isInstance(Object obj);
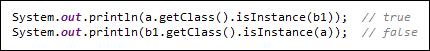
这个isInstance(Object obj)的意思是,obj这个对象是不是与这个Class对象兼容的类。
前面一句是,b1这个对象是不是a.getClass()的实例,后面一个是a是不是a.getClass()的实例。
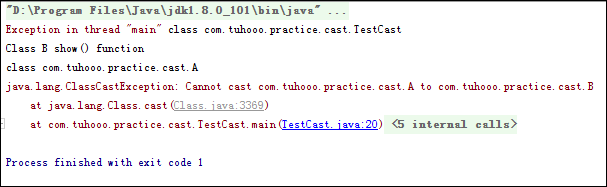
我想了下,把上面cast所在的那句话反过来一下:
执行结果,报错了:
不能把A转成B,A是父类,B是子类,也就是cast括号中的是源对象,前面的getClass()是待转换成为的目标对象。
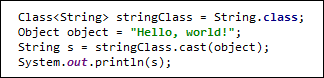
或者还有这种用法:
asSubclass方法
1 /** 2 * Casts this {@code Class} object to represent a subclass of the class 3 * represented by the specified class object. Checks that the cast 4 * is valid, and throws a {@code ClassCastException} if it is not. If 5 * this method succeeds, it always returns a reference to this class object. 6 * 7 * <p>This method is useful when a client needs to "narrow" the type of 8 * a {@code Class} object to pass it to an API that restricts the 9 * {@code Class} objects that it is willing to accept. A cast would 10 * generate a compile-time warning, as the correctness of the cast 11 * could not be checked at runtime (because generic types are implemented 12 * by erasure). 13 * 14 * @param <U> the type to cast this class object to 15 * @param clazz the class of the type to cast this class object to 16 * @return this {@code Class} object, cast to represent a subclass of 17 * the specified class object. 18 * @throws ClassCastException if this {@code Class} object does not 19 * represent a subclass of the specified class (here "subclass" includes 20 * the class itself). 21 * @since 1.5 22 */ 23 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 24 public <U> Class<? extends U> asSubclass(Class<U> clazz) { 25 if (clazz.isAssignableFrom(this)) 26 return (Class<? extends U>) this; 27 else 28 throw new ClassCastException(this.toString()); 29 }
翻译一下方法上面的注释:将这个类强制转为另一个类的子类。当需要使类的类型窄化的时候,这个方法特别有用。
这是java.lang.Class中的一个方法,作用是将调用这个方法的class对象转换成由clazz参数所表示的class对象的某个子类。
上面的代码将strList.getClass()获取的class对象转换成Class<? extends List>,这么做似乎没有什么意义,因为我们很清楚strList.getClass()获取的class对象就是ArrayList,它当然是List.class的一个子类;但有些情况下,我们并不能确知一个class对象的类型,典型的情况是Class.forName()获取的class对象:Class.forName()的返回类型是Class<?>,但这显然太宽泛了,假设我们需要List.class类型的class对象,但我们传递给Class.forName的参数是未知的(可能是"java.lang.String",也可能是"java.util.ArrayList"),这时我们就可以用到asSubclass()这个方法了,如下:
asSubclass用于窄化未知的Class类型的范围,而instanceof用于判断一个对象引用是否是一个超类或者接口的子类/实现类,如果试图将instanceof用于Class类型的判断会引起编译错误。
通常在向某些参数严格限制的API传递参数时,为了避免产生编译警告,这个方法比较有用!
下次对asSubclass和cast这两个方法找一个好的例子,这里先了解一下。





















 8060
8060

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








