下面是网上的一张流程图
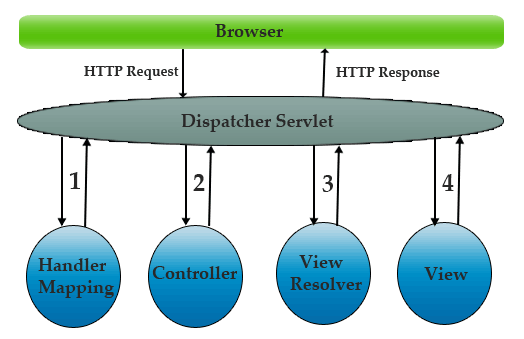
所有请求经过Dispatcher Servlet再经过HandlerMapping寻找指定的Controller
我们看看DispatcherServlet的部分源码
...
private List<HandlerMapping> handlerMappings;
...
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
Iterator var2 = this.handlerMappings.iterator();
HandlerExecutionChain handler;
do {
if(!var2.hasNext()) {
return null;
}
HandlerMapping hm = (HandlerMapping)var2.next();
if(this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("Testing handler map [" + hm + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + this.getServletName() + "'");
}
handler = hm.getHandler(request);
} while(handler == null);
return handler;
}关键就是handler = hm.getHandler(request);这句根据request取得对应的Handler。我们接下来再看看HandlerMapping里是如何实现request的注册与查找的。
先看一张继承图
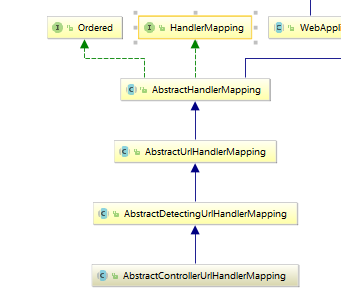
1.我们先从顶层的HandlerMapping看起
以下是它的源码:
public interface HandlerMapping {
String PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".pathWithinHandlerMapping" ;
String BEST_MATCHING_PATTERN_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".bestMatchingPattern";
String INTROSPECT_TYPE_LEVEL_MAPPING = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".introspectTypeLevelMapping" ;
String URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".uriTemplateVariables";
String MATRIX_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".matrixVariables";
String PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".producibleMediaTypes";
/**
* Return a handler and any interceptors for this request. The choice may be made
* on request URL, session state, or any factor the implementing class chooses.
* <p>The returned HandlerExecutionChain contains a handler Object, rather than
* even a tag interface, so that handlers are not constrained in any way.
* For example, a HandlerAdapter could be written to allow another framework's
* handler objects to be used.
* <p>Returns <code> null</code> if no match was found. This is not an error.
* The DispatcherServlet will query all registered HandlerMapping beans to find
* a match, and only decide there is an error if none can find a handler.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @return a HandlerExecutionChain instance containing handler object and
* any interceptors, or <code>null</code> if no mapping found
* @throws Exception if there is an internal error
*/
HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception;
}
着重看注释中的这两段话
- The DispatcherServlet will query all registered HandlerMapping beans to find a match, and only decide there is an error if none can find a handler.
Dispatcher会在HandlerMapping里注册的每个Beans里去找与之匹配的,若没有就返回error. - Return a handler and any interceptors for this request. The choice may be made on request URL, session state, or any factor the implementing class chooses.
getHandler方法会根据request的一些因素去决定返回interceptor还是handler.
我们再看看具体的实现类(AbstractUrlHandlerMapping)里是如何注册request与获取handler的
...
...
private final Map<String, Object> handlerMap = new LinkedHashMap();
...
...
protected void registerHandler(String urlPath, Object handler) throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
Assert.notNull(urlPath, "URL path must not be null");
Assert.notNull(handler, "Handler object must not be null");
Object resolvedHandler = handler;
if(!this.lazyInitHandlers && handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String)handler;
if(this.getApplicationContext().isSingleton(handlerName)) {
resolvedHandler = this.getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
}
Object mappedHandler = this.handlerMap.get(urlPath);
if(mappedHandler != null) {
if(mappedHandler != resolvedHandler) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot map " + this.getHandlerDescription(handler) + " to URL path [" + urlPath + "]: There is already " + this.getHandlerDescription(mappedHandler) + " mapped.");
}
} else if(urlPath.equals("/")) {
if(this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("Root mapping to " + this.getHandlerDescription(handler));
}
this.setRootHandler(resolvedHandler);
} else if(urlPath.equals("/*")) {
if(this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("Default mapping to " + this.getHandlerDescription(handler));
}
this.setDefaultHandler(resolvedHandler);
} else {
this.handlerMap.put(urlPath, resolvedHandler);
if(this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("Mapped URL path [" + urlPath + "] onto " + this.getHandlerDescription(handler));
}
}
}
...
...
protected Object getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
String lookupPath = this.getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
Object handler = this.lookupHandler(lookupPath, request);
...
...
protected Object lookupHandler(String urlPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
Object handler = this.handlerMap.get(urlPath);
if(handler != null) {
if(handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String)handler;
handler = this.getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
...
...注册的关键代码是如下两行
- resolvedHandler = this.getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
- this.handlerMap.put(urlPath, resolvedHandler);
从上下问中获取相应的Bean,然后以url为key,handler为value添加到Map中。
获取handler也很简单,直接再Map里根据查找。
完




















 475
475

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








