前言
在之前写程序的时候并没有考虑到关于程序的性能方面的问题,随后到了公司工作之后老板叫我优化一个程序的链接,那个时候我才知道性能对一个程序的后面发展有多的重要。没有了性能,那这个程序的也就没有了生命力。
线程池功能
应用程序可以有多个线程,这些线程在休眠状态中需要耗费大量时间来等待事件发生。其他线程可能进入睡眠状态,并且仅定期被唤醒以轮循更改或更新状态信息,然后再次进入休眠状态。为了简化对这些线程的管理,.NET框架为每个进程提供了一个线程池,一个线程池有若干个等待操作状态,当一个等待操作完成时,线程池中的辅助线程会执行回调函数。线程池中的线程由系统管理,程序员不需要费力于线程管理,可以集中精力处理应用程序任务。
线程池是一种多线程处理形式,处理过程中将任务添加到队列,然后在创建线程后自动启动这些任务。线程池线程都是后台线程.每个线程都使用默认的堆栈大小,以默认的优先级运行,并处于多线程单元中.如果某个线程在托管代码中空闲(如正在等待某个事件),则线程池将插入另一个辅助线程来使所有处理器保持繁忙.如果所有线程池线程都始终保持繁忙,但队列中包含挂起的工作,则线程池将在一段时间后创建另一个辅助线程但线程的数目永远不会超过最大值.超过最大值的线程可以排队,但他们要等到其他线程完成后才启动
代码
案例是一个多组闹钟的定时器
开发环境是:Jdk1.6 、Tomcat6、 Eclipse3.7
采用的是Quartz1.6版本的包
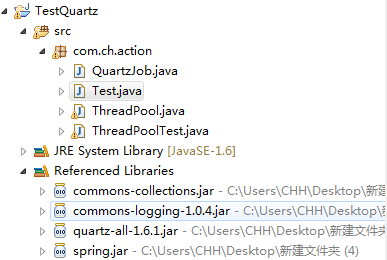
项目所需要的jar以及项目目录结构:
/*=======ThreadPool==========*/
 ThreadPool Code
ThreadPool Code
1 package com.ch.action;
2
3 import java.util.LinkedList;
4
5 /**
6 * 线程池
7 * @author CHH
8 * @since 2012-08-12
9 */
10 public class ThreadPool extends ThreadGroup {
11
12 // 线程池是否关闭
13 private boolean isClosed = false;
14 // 工作队列
15 private LinkedList workQueue;
16 // 线程池的id
17 private static int threadPoolID = 1;
18
19 // poolSize 表示线程池中的工作线程的数量
20 public ThreadPool(int poolSize) {
21
22 // 指定ThreadGroup的名称
23 super(threadPoolID + "");
24 // 继承到的方法,设置是否守护线程池
25 setDaemon(true);
26 // 创建工作队列
27 workQueue = new LinkedList();
28 for (int i = 0; i < poolSize; i++) {
29 // 创建并启动工作线程,线程池数量是多少就创建多少个工作线程
30 new WorkThread(i).start();
31 }
32 }
33
34 /** 向工作队列中加入一个新任务,由工作线程去执行该任务 */
35 public synchronized void execute(Runnable task) {
36 if (isClosed) {
37 throw new IllegalStateException();
38 }
39 if (task != null) {
40 // 向队列中加入一个任务
41 workQueue.add(task);
42 // 唤醒一个正在getTask()方法中带任务的工作线程
43 notify();
44 }
45 }
46
47 /** 从工作队列中取出一个任务,工作线程会调用此方法 */
48 private synchronized Runnable getTask(int threadid)
49 throws InterruptedException {
50 while (workQueue.size() == 0) {
51 if (isClosed)
52 return null;
53 System.out.println("工作线程" + threadid + "等待任务...");
54 // 如果工作队列中没有任务,就等待任务
55 wait();
56 }
57 System.out.println("工作线程" + threadid + "开始执行任务...");
58 // 反回队列中第一个元素,并从队列中删除
59 return (Runnable) workQueue.removeFirst();
60 }
61
62 /** 关闭线程池 */
63 public synchronized void closePool() {
64 if (!isClosed) {
65 // 等待工作线程执行完毕
66 waitFinish();
67 isClosed = true;
68 // 清空工作队列
69 workQueue.clear();
70 // 中断线程池中的所有的工作线程,此方法继承自ThreadGroup类
71 interrupt();
72 }
73 }
74
75 /** 等待工作线程把所有任务执行完毕 */
76 public void waitFinish() {
77 synchronized (this) {
78 isClosed = true;
79 // 唤醒所有还在getTask()方法中等待任务的工作线程
80 notifyAll();
81 }
82 // activeCount()
83 Thread[] threads = new Thread[activeCount()];
84 // 返回该线程组中活动线程的估计值。
85 // enumerate()方法继承自ThreadGroup类,根据活动线程的估计值获得线程组中当前所有活动的工作线程
86 int count = enumerate(threads);
87 // 等待所有工作线程结束
88 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
89 try {
90 // 等待工作线程结束
91 threads[i].join();
92 } catch (InterruptedException ex) {
93 ex.printStackTrace();
94 }
95 }
96 }
97
98 /**
99 * 内部类,工作线程,负责从工作队列中取出任务,并执行
100 *
101 * @author CHH
102 */
103 private class WorkThread extends Thread {
104 private int id;
105
106 public WorkThread(int id) {
107 // 父类构造方法,将线程加入到当前ThreadPool线程组中
108 super(ThreadPool.this, id + "");
109 this.id = id;
110 }
111
112 public void run() {
113 while (!isInterrupted()) {
114 // isInterrupted()方法继承自Thread类,判断线程是否被中断
115 Runnable task = null;
116 try {
117 // 取出任务
118 task = getTask(id);
119 } catch (InterruptedException ex) {
120 ex.printStackTrace();
121 }
122 // 如果getTask()返回null或者线程执行getTask()时被中断,则结束此线程
123 if (task == null)
124 return;
125 try {
126 // 运行任务
127 task.run();
128 } catch (Throwable t) {
129 t.printStackTrace();
130 }
131 }
132 }
133 }
134
135 }/*=======QuartzJob==========*/

 QuartzJob Code
QuartzJob Code
1 package com.ch.action;
2
3 import org.quartz.Job;
4 import org.quartz.JobExecutionContext;
5 import org.quartz.JobExecutionException;
6
7 /**
8 * Spring Quartz调度的任务
9 * @author CHH
10 * @since 2012-08-12
11 */
12 public class QuartzJob implements Job{
13 @Override
14 public void execute(JobExecutionContext arg0) throws JobExecutionException {
15 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
16 System.out.println("懒虫,闹钟响了该起床了!");
17 }
18 }/*=======ThreadPoolTest==========*/

 ThreadPoolTest Code
ThreadPoolTest Code
1 package com.ch.action;
2
3 import java.util.Calendar;
4 import java.util.Date;
5 import java.util.GregorianCalendar;
6 import java.util.Properties;
7 import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
8
9 import org.quartz.CronTrigger;
10 import org.quartz.JobDetail;
11 import org.quartz.Scheduler;
12 import org.quartz.SchedulerFactory;
13 import org.quartz.impl.StdSchedulerFactory;
14
15 /**
16 * Java版多组闹钟模拟程序实现
17 * 实现技术:线程池、Quartz定时器
18 * 还未实现的部分:
19 * 1、例如设定两个线程来定时两组闹钟,但是突然有一组闹钟不想用了想关掉,这该怎么实现。
20 * 2、可以尝试用配置未见去配置定时任务,提示一下当用配置文件配置定时的时间时,要用代码
21 * 去生成xml文件。这样才可以让时间动态。
22 * @author CHH
23 * @since 2012-08-12
24 */
25 public class ThreadPoolTest {
26
27 private static Scheduler sched = null;
28
29 public static ThreadPoolTest t = new ThreadPoolTest();
30
31 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
32 String time = null;
33
34 // 创建一个有个3工作线程的线程池
35 ThreadPool threadPool = new ThreadPool(3);
36 // 休眠500毫秒,以便让线程池中的工作线程全部运行
37 Thread.sleep(500);
38 // 运行任务
39 for (int i = 0; i <= 1; i++) {
40 //实例化GregorianCalendar
41 Calendar calendar = new GregorianCalendar();
42 calendar.setTime(new Date());
43 //获得当前时间的年、月、日、时、分
44 int year = calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR);
45 int month = calendar.get(Calendar.MONTH) + 1;
46 int day = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
47 int hh = calendar.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY);
48 int mi = calendar.get(Calendar.MINUTE)+i+1;
49 //time里面放的内容是一个cron表达式
50 //例如"0 10 23 14 08 ? 2012" 表示:在2012年8月14号23点10分开始启动任务
51 time = "0 "+ mi +" "+ hh +" "+ day +" "+ month +" ? "+ year +"";
52 System.out.println("time"+ i +"----->" + time);
53 // 创建任务,每次调用任务的时候time的值不要重复。因为每次
54 threadPool.execute(createTask(i,time));
55 }
56 // 等待所有任务执行完毕
57 threadPool.waitFinish();
58 // 关闭线程池
59 threadPool.closePool();
60 }
61
62 private static Runnable createTask(final int taskID,final String str) {
63 return new Runnable() {
64 public void run() {
65 Scheduler sched = null;
66 // 创建LzstoneTimeTask的定时任务
67 JobDetail jobDetail = new JobDetail("lzstoneJob"+taskID,sched.DEFAULT_GROUP, QuartzJob.class);
68 // 目标 创建任务计划
69 CronTrigger trigger;
70 try {
71 System.out.println(str);
72 System.out.println("taskID"+taskID);
73 trigger = new CronTrigger("lzstoneTrigger"+taskID, "lzstone",str);
74
75 //new org.quartz.impl.StdScheduler(sched, schedCtxt);
76
77 //实例化StdSchedulerFactory,通过动态的修改instanceName属性的值
78 StdSchedulerFactory factory = new StdSchedulerFactory();
79 //动态
80 Properties properties = new Properties();
81 //实例化线程名
82 properties.put("org.quartz.scheduler.instanceName","DefaultQuartzScheduler"+taskID);
83 //
84 properties.put("org.quartz.scheduler.rmi.export","false");
85 //是否设置代理
86 properties.put("org.quartz.scheduler.rmi.proxy","false");
87 //
88 properties.put("org.quartz.scheduler.wrapJobExecutionInUserTransaction","false");
89 //
90 properties.put("org.quartz.threadPool.class","org.quartz.simpl.SimpleThreadPool");
91 //设置线程数量为20
92 properties.put("org.quartz.threadPool.threadCount","20");
93 //
94 properties.put("org.quartz.threadPool.threadPriority","5");
95 //
96 properties.put("org.quartz.threadPool.threadsInheritContextClassLoaderOfInitializingThread","true");
97 //
98 properties.put("org.quartz.jobStore.misfireThreshold","60000");
99 //
100 properties.put("org.quartz.jobStore.class","org.quartz.simpl.RAMJobStore");
101 factory.initialize(properties);
102 SchedulerFactory sf = (StdSchedulerFactory)factory;
103 sched = sf.getScheduler();
104 sched.scheduleJob(jobDetail, trigger);
105 sched.start();
106 } catch (Exception e) {
107 // TODO Auto-generated catch block
108 e.printStackTrace();
109 }
110 }
111 };
112 }
113
114 // 停止
115 public static void stop() throws Exception {
116 sched.shutdown();
117 }
118
119 }至于后面的那个Test类是没有用的
以下情况是不建议采用线程池
●如果需要使一个任务具有特定优先级
●如果具有可能会长时间运行(并因此阻塞其他任务)的任务
●如果需要将线程放置到单线程单元中(线程池中的线程均处于多线程单元中)
●如果需要永久标识来标识和控制线程,比如想使用专用线程来终止该线程,将其挂起或按名称发现它
System.ThreadingPool类实现了线程池,这是一个静态类,它提供了管理线程的一系列方法
Threading.QueueUserItem方法在线程池中创建一个线程池线程来执行指定方法(用委托WaitCallBack表示),并将该线程排入线程池的队列等待执行。
public static Boolean QueueUserWorkItem(WaitCallback wc,Object state);
最后
写这样的一篇博客主要是为记录自己所学到的东西,同时也共享给大家一起学习。如果对于代码有什么不明白的地方或者有什么好的建议,在Q里面搜索“鼠标CHH”,我们一起讨论。
 深入探讨线程池与定时任务实现
深入探讨线程池与定时任务实现
























 3072
3072

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








