一、主键约束的三种方式
1.在字段后加primary key 约束 id varchar(32) primary key
2.在表创建好之后添加外键约束 alter table student add constraints pk_student_id PRIMARY key(id);
3.在创建表的语句的最后面使用 constraints pk_表名_字段名 primary key(字段名)
4.删除主键约束alter table student drop constraints pk_student_id;
验证流程:
1-1.创建一张表,在id后加上主键约束 primary key
create table student(
id varchar(32) primary key,
name varchar(32) not null
)1-2.插入两条数据
insert into student(id,name) values('1','张三');
insert into student(id,name) values('1','李四');1-3.报错如下
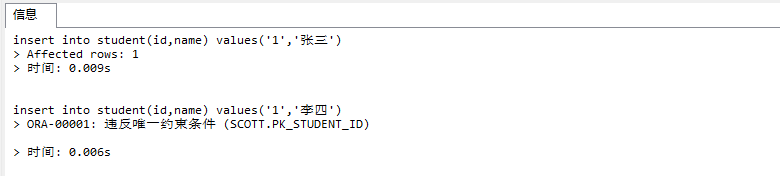
1-4.删除表,然后重新创建
-- 删除表
drop table student;
-- 重新创建
create table student(
id varchar(32),
name varchar(32) not null,
constraints pk_student_id PRIMARY key(id)
)1-5.插入原来的两条数据
1-6.报错如下

1-7.删除表,然后重新创建
drop table student;
create table student(
id varchar(32),
name varchar(32) not null
)1-8.修改表的外键约束
alter table student add constraints pk_student_id PRIMARY key(id);1-9.插入原来的两条数据,报同样的错误
二、检查约束的三种方式
1.直接在创建表的字段后使用 check(条件) 例如 sage number(3) check(sage<150 and sage>0),
2.在创建表的语句的最后面使用 constraints ck_表名_字段名 check(条件)
3.在创建表后使用 alter table 表名 add constraints ck_表名_字段名 check(条件);
4.删除检查约束 alter table student drop constraints 检查约束名;
三、非空约束的三种方式
1.直接在创建表的字段后使用 not null 关键字
2.在创建表的语句的最后面使用 constraints ck_表名_字段名 check(字段名 is not null)
3.在创建表后使用 alter table 表名 add constraints ck_表名_字段名 check(字段名 is not null);
4.删除非空约束 alter table student drop constraints 非空约束名;
四、唯一约束的三种方式
1.直接在创建表的字段后使用 unique
2.在创建表的语句后面使用 constraints un_表名_字段名 unique(字段名);
3.在创建表后使用 alter table 表名 add constraints un_表名_字段名 unique(字段名);
4.删除约束:alter table 表名 drop constraints 唯一约束名;
五、外键约束
--二维表创建 外键约束学习:
--创建学生表
create table student(
sno number(10) primary key,
sname varchar2(100) not null,
sage number(3) check(sage>0 and sage<150),
ssex char(4) check(ssex='男' or ssex='女'),
sfav varchar2(500),
sqq varchar2(30) unique,
cid number(10) --references clazz(cno)
--constraints fk_student_cid foreign key(cid) references clazz(cno)--外键
)
--添加外键
alter table student add constraints fk_student_cid foreign key(cid) references clazz(cno) on delete set null
alter table student drop constraints fk_student_cid
drop table student
--添加测试数据
insert into student values(1,'张三001',18,'男','唱歌','657889900',1);
insert into student values(2,'张三002',18,'男','唱歌','657889901',1);
insert into student values(3,'李四001',18,'男','唱歌','657889903',2);
insert into student values(4,'李四002',18,'男','唱歌','657889904',2);
--创建班级表
create table clazz(
cno number(10) primary key,
cname varchar2(100) not null,
cdesc varchar2(300)
)
--添加测试数据
insert into clazz values(1,'java','6666');
insert into clazz values(2,'python','33333');
--查询学生及其班级信息
select * from student s
inner join clazz c
on s.cno=c.cno
--问题:竟然可以在学生表中插入一个不存在班级
insert into student values(5,'李四003',18,'男','唱歌','657889905',3);
--使用外键:
--作用:当在子表中插入的数据在父表中不存在,则会自动报错。
--概念:当一张表的某个字段的值需要依赖另外一张表的某个字段的值,则使用外键约束。
--其中主动依赖的表称为子表,被依赖的表称为父表。外键加在子表中。
--使用:
--在子表中的字段后直接使用 references 父表名(字段) 例如: cid number(10) references clazz(cno)
--在创建表语句的最后面使用 constraints fk_子表名_字段名 foreign key(字段名) references 父表名(字段名)
--在创建表后使用:alter table 表名 add constraints fk_子表名_字段名 foreign key(字段名) references 父表名(字段名)
--删除外键:alter table 表名 drop constraints 外键约束名
--外键选取:
--一般选取父表的主键作为子表的外键。
--外键的缺点:
--无法直接删除父表数据,除非级联删除
--级联删除:在添加外键约束时,使用关键字 on delete cascade
--使用:当删除父表数据时,自动删除子表相关所有数据。
--缺点:无法保留子表历史数据。
--使用关键字 on delete set null
--删除父表数据时,将子表中的依赖字段的值设置为null。
--注意:子表依赖字段不能添加非空约束。
--删除班级1的信息
select * from student
delete from clazz where cno=1




 本文详细介绍了SQL中的五种约束类型:主键约束、检查约束、非空约束、唯一约束及外键约束。通过实例展示了每种约束的应用场景及实现方法。
本文详细介绍了SQL中的五种约束类型:主键约束、检查约束、非空约束、唯一约束及外键约束。通过实例展示了每种约束的应用场景及实现方法。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








