For histograms, the following statistics are calculated:
| Mean | The average of all the values. |
| Minimum | The smallest value. |
| Maximum | The biggest value. |
| Std Dev | An expression of how widely spread the values are around the mean. |
| Class Width | The x-axis distance between the left and right edges of each bar in the histogram. |
| Number of Classes | The number of bars (including zero height bars) in the histograms. |
| Skewness | Is the histogram symmetrical? If so, Skewness is zero. If the left hand tail is longer, skewness will be negative. If the right hand tail is longer, skewness will be positive. Where skewness exists, process capability indices are suspect. For process improvement, a good rule of thumb is to look at the long tail of your distribution; that is usually where quality problems lie. |
| Kurtosis | Kurtosis is a measure of the pointiness of a distribution. The standard normal curve has a kurtosis of zero. The Matterhorn, has negative kurtosis, while a flatter curve would have positive kurtosis. Positive kurtosis is usually more of a problem for quality control, since, with "big" tails, the process may well be wider than the spec limits. |
Distributions you may encounter
- The standard normal distribution, with its zero skewness and zero kurtosis.
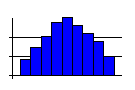
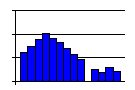
- A skewed distribution, with one tail longer than the other.
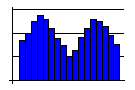
- A double-peaked curve often means that the data actually reflects two distinct processes with different centers. You will need to distinguish between the two processes to get a clear view of what is really happening in either individual process.
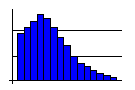
- A truncated curve, with the peak at or near the edge while trailing gently off to the other side, often means that part of the distribution has been removed through screening, 100% inspection, or review. These efforts are usually costly and make good candidates for improvement efforts.
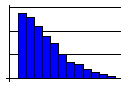
- A plateau-like curve often means that the process is ill-defined to those doing the work, which leaves everyone on their own. Since everyone handles the process differently, there are many different measurements with none standing out. The solution here is to clearly define an efficient process.
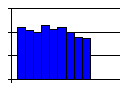
- Outliers in a histogram – bars that are removed from the others by at least the width of one bar – sometimes indicate that perhaps a separate process is included, but one that doesn't happen all the time. It may also indicate that special causes of variation are present in the process and should be investigated, though if the process is in control before the histogram is made as it should be, this latter option is unlikely.







 本文介绍了直方图中各项统计指标的含义,包括平均值、最小值、最大值、标准差等,并解释了偏斜度和峰度的概念及其对质量控制的影响。此外,还讨论了几种常见的分布形态及其背后可能的原因。
本文介绍了直方图中各项统计指标的含义,包括平均值、最小值、最大值、标准差等,并解释了偏斜度和峰度的概念及其对质量控制的影响。此外,还讨论了几种常见的分布形态及其背后可能的原因。
















 1553
1553

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








