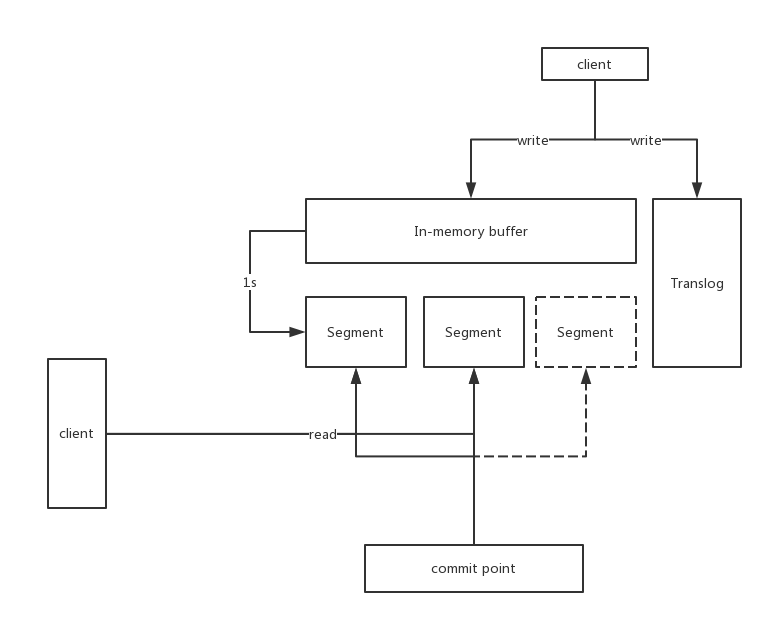
准实时索引的实现
如果对mysql的innodb有了解的话,es的实现原理相似
- client只能搜索到commit point指向的segment
- 写入到memory buffer和translog之后,即写入成功
- memory buffer中的内容,每隔1s(可以通过/_refresh控制),异步刷新到磁盘
- 刷新到磁盘后,flush掉translog
- 很过个segment由单独merge线程处理segment的merge操作
上图:
routing和replica
- 每个对象都有routing字段,默认是_id值
计算对象所在的shard通过以下方式:
shard = hash(routing) % number_of_primary_shards
所以创建索引,指定的分片数不能变,一旦变化,所有的索引数据都会读取失败
- replica一致性
默认写完一半以上即为成功。
int((primary + number_of_replicas) / 2) + 1
也可以设置为one或者all
如何提升写入性能
参见:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/tune-for-indexing-speed.html
- 使用bulk request
- 使用多线程发送数据
- 增加refresh interval
- 在批量数据加载初始化的时候,可以关闭refresh
- 禁用交换空间
- 给文件系统较大的memory
- 使用自生成的id
- 使用更高效的硬件,例如:SSD
- 如果索引比较大,调大indices.memory.index_buffer_size
如何提升读取性能
参见:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/tune-for-search-speed.html
- 给文件系统缓存更大的内存
- 使用更高效的硬件,例如:SSD
- 优化查询条件:避免join操作、nested操作和parent-child关系
- 数据预处理
- 一些情况下mapping使用keyword而不是integer或者long
- 强制merge read-only索引
- 文件系统缓存预热
如何减少磁盘使用空间
参见:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/tune-for-disk-usage.html
- 禁用不必要的feature
- 不要使用默认的string mapping
- 禁用_all
- 使用best_compression
其他建议
参见:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/general-recommendations.html
- 避免返回大的结果集,使用scroll代替
- 避免索引大文档,默认最大是100MB,(http.max_context_length)
- 避免在同一个索引下加入不相关的数据
- 避免过多的types,使用单独的index代替







 本文介绍了Elasticsearch的写入及读取性能优化方法,包括调整refresh interval、使用bulk request等提升写入速度;增大文件系统缓存、优化查询条件等提高读取速度。同时,也提供了减少磁盘空间使用的技巧。
本文介绍了Elasticsearch的写入及读取性能优化方法,包括调整refresh interval、使用bulk request等提升写入速度;增大文件系统缓存、优化查询条件等提高读取速度。同时,也提供了减少磁盘空间使用的技巧。

















 2192
2192

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








