一 教材学习总结
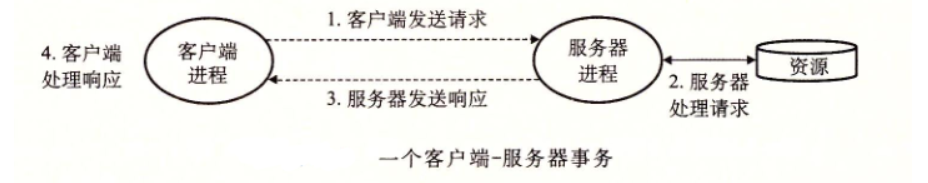
每一个网络应用都是基于客户端-服务器模型
客户端和服务器都是进程
客户端和服务器通常运行在不同主机上
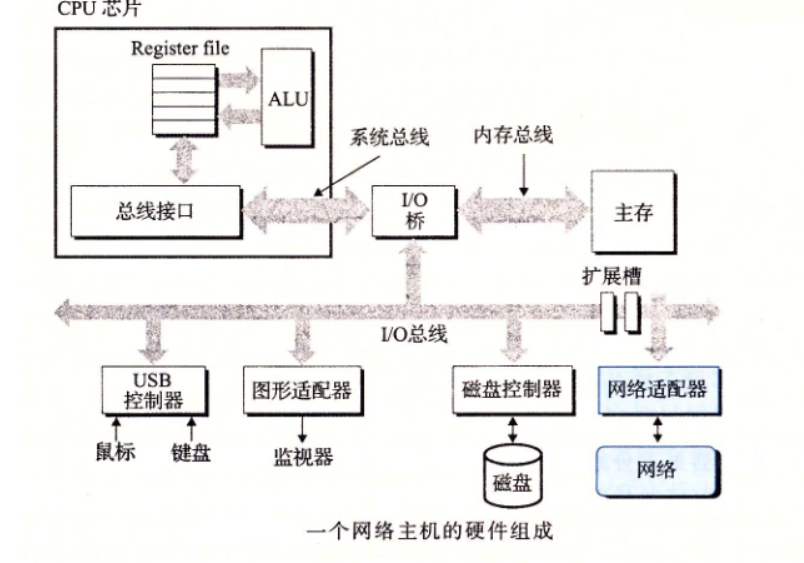
通过计算机网络实现主机通信
网桥比集线器更充分利用电缆宽带
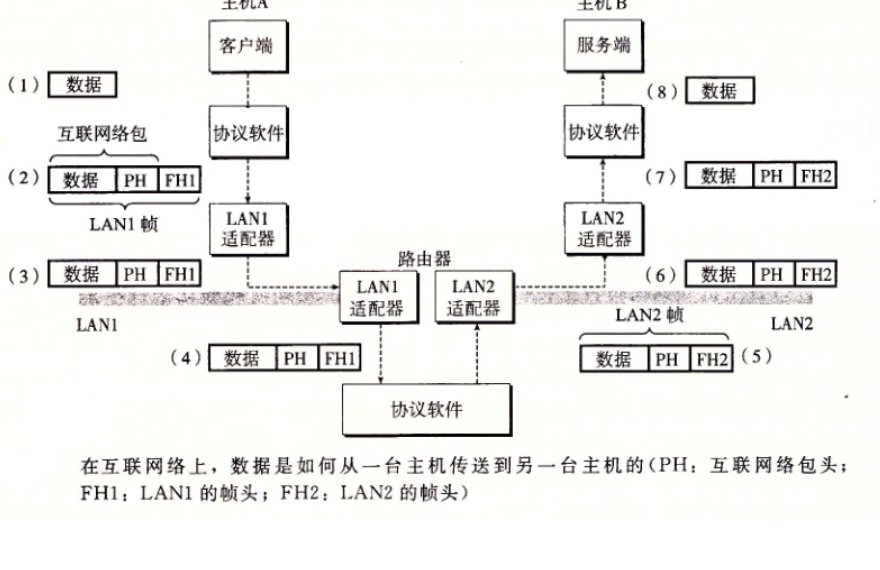
多个不兼容的局域网可以通过
互联网由各种局域网和广域网先连接
全球IP就是互联网的实现
每一台主机都实现TCPIP协议
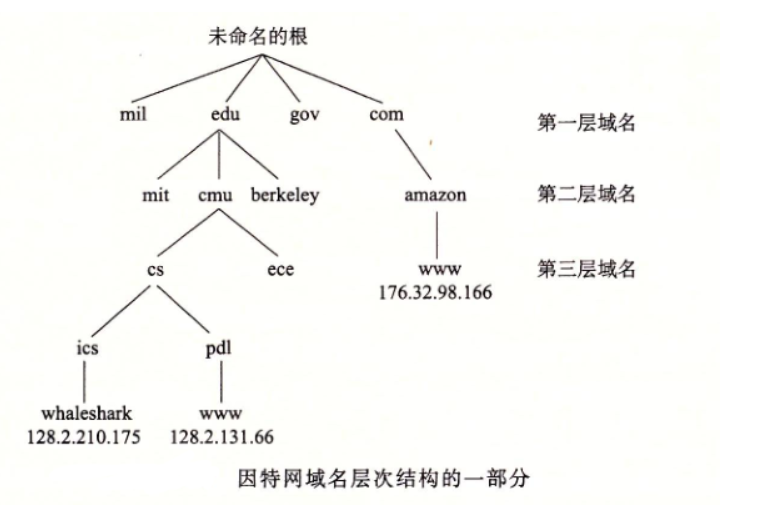
IP地址通常是点分十进制表示
客户端和服务器是点对点的通信
套接字接口就是一组函数
一个套接字就是一个通信端点

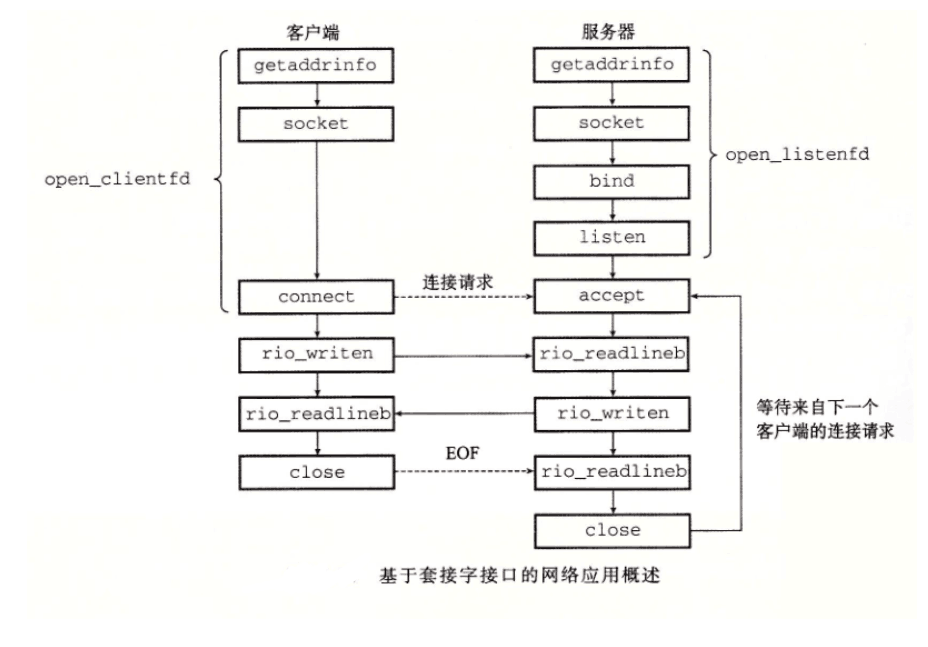
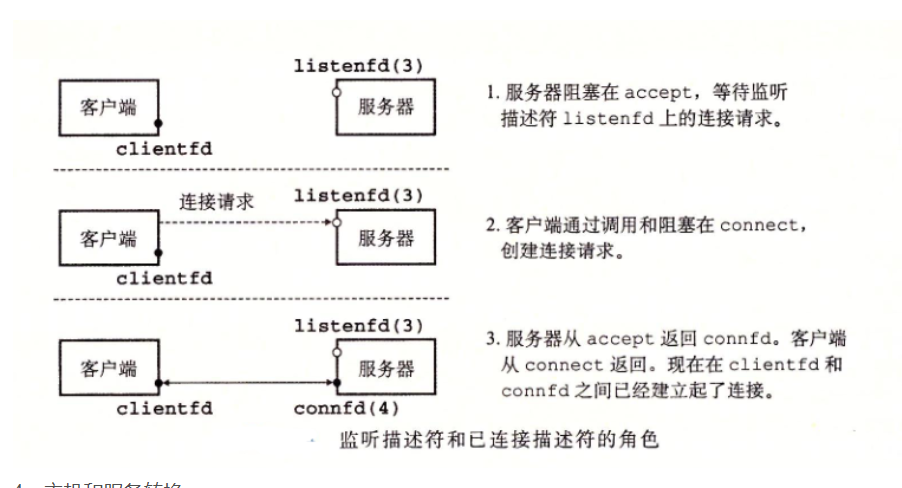
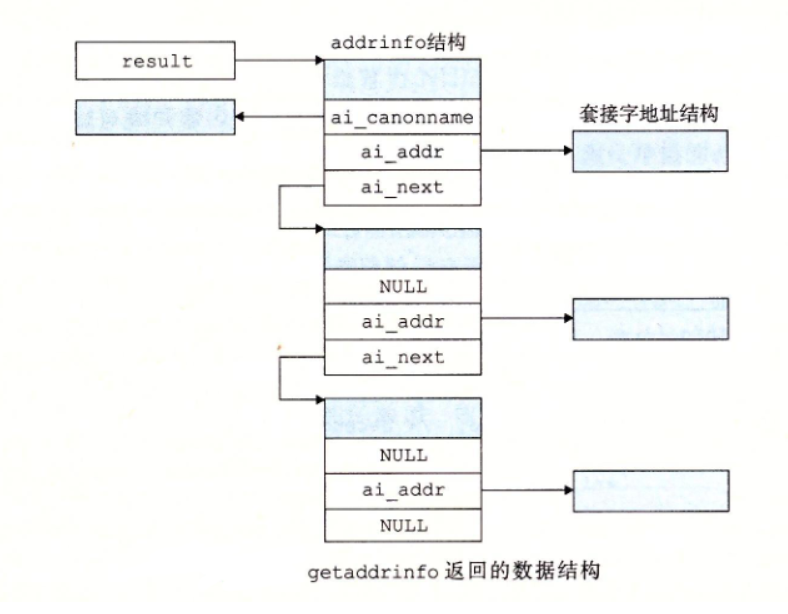
实现函数:
/* IP socket address structure */
struct sockaddr_in {
uint16_t sin_family; /* Protocol family (always AF_INET) */
uint16_t sin_port; /* Port number in network byte order */
struct in_addr sin_addr; /* IP address in network byte order */
unsigned char sin_zero[8]; /* Pad to sizeof(struct sockaddr) */
};#include <sys/types #include <sys/socket.h int socket(int dimain, int type, int protocol)
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netdb.h>
int getaddrinfo(const char *host, const char * service, struct addrinfo **result);
返回:成功则为0,错位则为非0的错误代码。
void freeaddrinfo(struct addrinfo **result);
const char *gai_strerror(int errcode);
返回错误信息。
//
struct addrinfo {
int ai_flags; /* Hints argument flags */
int ai_family; /* First arg to socket function */
int ai_socktype; /* Second arg to socket function */
int ai_protocol; /* Third arg to socket function */
char *ai_canonname; /* Canonical hostname */
size_t ai_addrlen; /* Size of ai_addr struct */
struct sockaddr *ai_addr; /* Ptr to socket address structure */
struct addrinfo *ai_next; /* Ptr to next item in linked list */
};
nt open_clientfd(char *hostname, char *port)
{
int clientfd;
struct addrinfo hints, *listp, *p;
/* Get a list of potential server addresses */
memset(&hints, 0, sizeof(struct addrinfo));
hints.ai_socktype = SOCK_STREAM; /* Open a connection */
hints.ai_flags = AI_NUMERICSERV; /* ...using a numeric port arg. */
hints.ai_flags |= AI_ADDRCONFIG; /* Recommended for connection */
Getaddrinfo(hostnamem, port, &hints, &listp);
/* Walk the list for one that we can successfully connect to */
for (p = listp; p; p = p->ai_next) {
/* Create a socket descriptor */
if ((clientfd = socket(p->ai_family, p->ai_socktype, p->ai_protocol))
< 0) continue; /* Socket failed, try the next */
/* Connect to the server */
if (connect(clientfd, p->ai_addr, p->ai_addrlen) != -1)
break; /* Success */
Close(clientfd); /* Connect failed, try another */
}
/* Clean up */
Freeaddrinfo(listp);
if (!p) /* All last connects failed */
return -1;
else /* The last connect succeeded */
return clientfd;
}
int open_listenfd(char *port)
{
struct addrinfo hints, *listp, *p;
int listenfd, optval = 1;
/* Get a list of potential server addresses */
memset(&hints, 0, sizeof(struct addrinfo));
hints.ai_socktype = SOCK_STREAM; /* Accept a connection */
hints.ai_flags = AI_PASSIVE | AI_ADDRCONFIG; /* ...on any IP addresses */
hints.ai_flags |= AI_NUMERICSERV; /* ...using port number */
Getaddrinfo(NULL, port, &hints, &listp);
/* Walk the list for one that we can bind to */
for (p = listp; p; p = p->ai_next) {
/* Create a socket descriptor */
if ((listenfd = socket(p->ai_family, p->ai_socktype, p->ai_protocol))
< 0) continue; /* Socket failed, try the next */
/* Eliminates "Address already in use" error from bind */
Setsockopt(listenfd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR,
(const void *)&optval, sizeof(int));
/* Bind the descriptor to the address */
if (bind(listenfd, p->ai_addr, p->ai_addrlen) == 0)
break; /* Success */
Close(clientfd); /* Bind failed, try the next */
}
/* Clean up */
Freeaddrinfo(listp);
if (!p) /* All last connects failed */
return -1;
/* Make it a listening socket ready to accept connection requests */
if (listen(listenfd, LISTENQ) < 0) {
Close(listenfd);
return -1;
}
return listenfd;
}




 本文深入讲解了网络编程的基础概念,包括客户端-服务器模型、TCP/IP协议、IP地址、套接字接口及其实现函数,详细解释了如何使用getaddrinfo、socket、connect和bind等函数进行网络通信,并提供了打开客户端和监听端口的具体代码示例。
本文深入讲解了网络编程的基础概念,包括客户端-服务器模型、TCP/IP协议、IP地址、套接字接口及其实现函数,详细解释了如何使用getaddrinfo、socket、connect和bind等函数进行网络通信,并提供了打开客户端和监听端口的具体代码示例。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








