项目地址:https://github.com/yogurt1998/WordCount
要求
- 基本要求
- -c 统计文件字符数(实现)
- -w 统计文件单词数(实现)
- -l 统计文件行数(实现)
- 扩展功能
- 递归处理目录下符合条件的文件。(实现)
- 返回更复杂的数据(代码行 / 空行 / 注释行)(实现)
- 高级功能
实现图形化界面(未实现)
PSP
PSP2.1 Personal Software Process Stages 预估耗时(分钟) 实际耗时(分钟) Planning 计划 40 65 · Estimate · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 30 45 Development 开发 450 600 · Analysis · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) 60 90 · Design Spec · 生成设计文档 60 60 · Design Review · 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) 30 30 · Coding Standard · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) 30 30 · Design · 具体设计 30 30 · Coding · 具体编码 150 150 · Code Review · 代码复审 150 150 · Test · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) 60 60 Reporting 报告 100 100 · Test Report · 测试报告 60 60 · Size Measurement · 计算工作量 30 30 · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 30 30 合计 1310 1530 设计
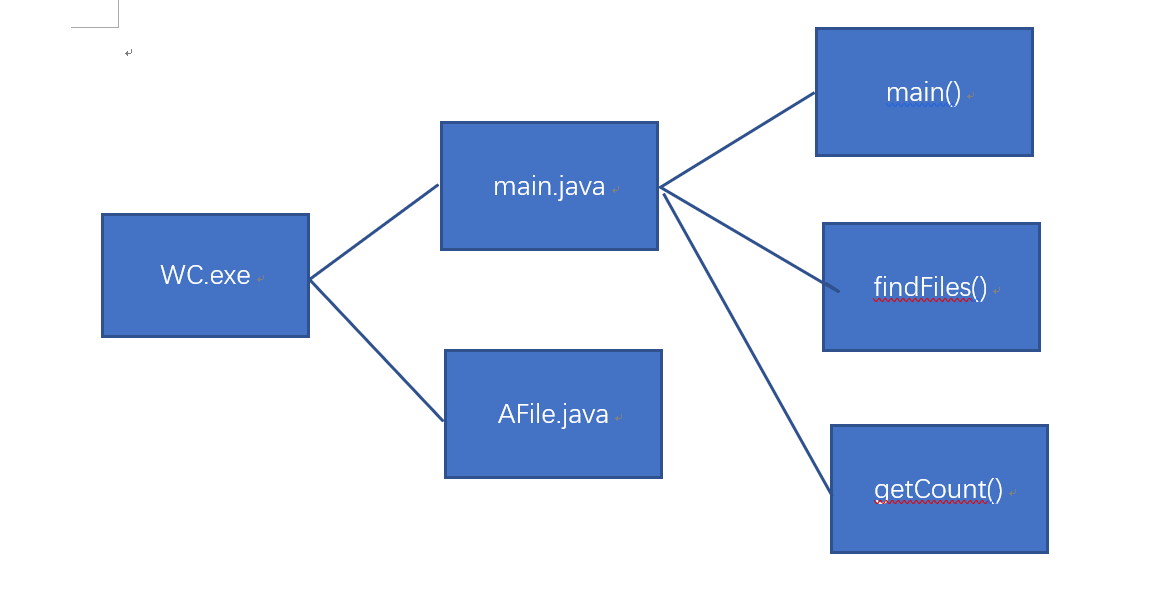
main.java
主函数:一个循环获取输入命令并分隔出指令和文件路径。
统计函数:通过IO流获取文件内容并统计字符数、行数、单词数等。
文件判断函数:判断是否为文件夹或者文件以实现递归处理功能AFile.java
代表着字符数等六个属性。
代码
main()函数
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub do { String filename = null; String bString = null; System.out.println("请输入命令(格式:[parameter] [file_name])"); while (true) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); // 获取键盘输入 if (scanner.hasNext()) { bString = scanner.next(); } if (bString.equals("-c") || bString.equals("-w") || bString.equals("-l") || bString.equals("-s") || bString.equals("-a")) { if (scanner.hasNextLine()) { filename = scanner.next(); } break; } else { System.out.println("错误!请重新输入!"); } } String filepath = "D:\\test\\" + filename; // 在绝对路径中打开 File file = new File(filepath); if (!file.exists()) { System.out.println("文件不存在"); continue; } AFile aFile = new AFile(); aFile = findFiles(filepath); if (bString.equals("-c")) System.out.println("字符数为" + aFile.charNumb); else if (bString.equals("-w")) System.out.println("单词数为" + aFile.wordNumb); else if (bString.equals("-l")) System.out.println("行数为" + aFile.lineNumb); else if (bString.equals("-a")) System.out.println("空行数为:" + aFile.empleLine + " 代码行数为:" + aFile.codeLine + " 注释行数为:" + aFile.nodeLine); } while(true); }findFiles()函数:通过递归处理文件
private static AFile findFiles(String file_path) { File file = new File(file_path); AFile aFile = new AFile(); if (file.isDirectory()) { // 判断为文件夹 File[] files = file.listFiles(); // 获取文件列表 if (files == null) { System.err.println("找不到"); } else if (files.length == 0) { System.out.println("目录为空"); } else { for (File f : files) { // 循环处理文件 if (f.isDirectory()) // 判断为文件夹 findFiles(f.getPath()); else if (f.isFile()) { // 判断为文件 System.out.println("文件名为:" + f.getName() + "\n字符数为" + getCount(f.getPath()).charNumb + "\n单词数为" + getCount(f.getPath()).wordNumb + "\n行数为" + getCount(f.getPath()).lineNumb + "\n空行数为:" + getCount(f.getPath()).empleLine + "\n代码行数为:" + getCount(f.getPath()).codeLine + "\n注释行数为:" + getCount(f.getPath()).nodeLine); } } } } else if (file.isFile() && file.exists()) { // 判断为文件 aFile = getCount(file.getPath()); } return aFile; }getCount()函数:通过BufferedReader获取文件内容并判断
private static AFile getCount(String filepath) { AFile aFile = new AFile(); try { BufferedReader brin = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filepath)); String s; int state = 0; // 判断是否在单词内 // 使用正则表达式判断注释行 String regxNodeBegin = "(\\S?)\\s*/\\*.*"; String regxNodeEnd = "(.*\\*/\\s*)\\S?"; String regxNode = "(\\s*)(\\S?)(//+).*"; while ((s = brin.readLine()) != null) { ++ aFile.lineNumb; int countLetter = 0; // 判断非空格字符数量 for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { ++aFile.charNumb; Character c = s.charAt(i); ++countLetter; if (c == ' ' || c == '\n' || c == '\t') { state = 0; --countLetter; } else if (state == 0) { state = 1; ++aFile.wordNumb; } } if (s.matches(regxNodeBegin) || s.matches(regxNodeEnd) || s.matches(regxNode)) ++aFile.nodeLine; else if (countLetter > 1) // 如果非空格字符数多于1 ++aFile.codeLine; else ++aFile.empleLine; } } catch (IOException e) { // TODO: handle exception System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } return aFile; }测试运行
测试文件:

测试结果: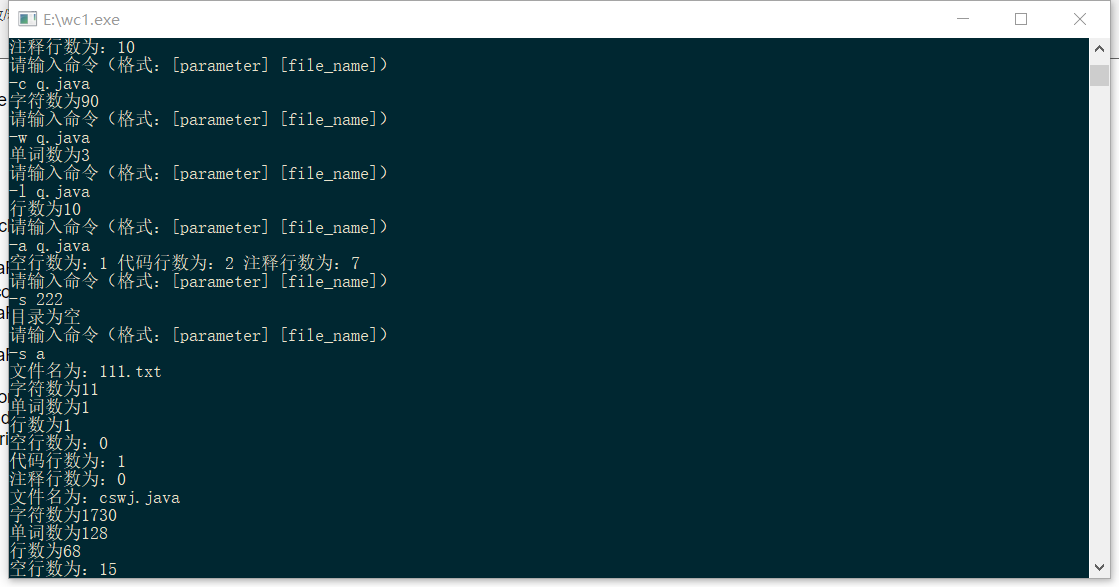
总结
- 根据在软件工程课堂上得到的知识进行分析,但没有细心分析导致递归功能一开始写错。
- 程序的思路一开始并不是很清晰导致后面很多修改以及代码繁杂。
- 学习了Git和GitHub的使用以及exe4j的使用。
- 对程序设计很不熟悉需要更多的练习。




 该项目通过命令行接收参数,统计文件的字符数、单词数、行数,并具备处理目录下所有文件的能力,支持统计代码行、空行和注释行。项目使用Java编写,涉及IO流操作、递归算法及正则表达式。
该项目通过命令行接收参数,统计文件的字符数、单词数、行数,并具备处理目录下所有文件的能力,支持统计代码行、空行和注释行。项目使用Java编写,涉及IO流操作、递归算法及正则表达式。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








