1. 定义一个工具类
其中提供了对于×××数组和double类型数组的一些工具方法。
方法分别有:
1.求数组值的和.
2.求数组中的最大值
3.对数组进行升序排序.
4.对数组进行倒序排序(也就是反转数组)
工具类要求:
a.私有化构造方法
b.不希望被继承
public class ArraysDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
int arr[]=new int[]{34,54,243,65,7867,23,4,355,252,98};
double arr1[]=new double[]{22.3,465.7,65.4,43.3,544.4,23.9,78.9};
write(arr);//调用×××数组的输出方法
write(arr1);//调用double类型数组输出方法
}
//×××数组的输出
static void write(int arr[]){
System.out.print("×××数组开始的序列:");
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
System.out.print(+arr[i]+",");
}
System.out.println("");
Arrays arrays=new Arrays();
arrays.getSum(arr);
arrays.getMax(arr);
arrays.UpSort(arr);
arrays.DownSort(arr);
}
//double类型数组输出
static void write(double arr1[]){
System.out.print("double类型数组开始的序列:");
for(int i=0;i<arr1.length;i++){
System.out.print(+arr1[i]+",");
}
System.out.println("");
Arrays arrays=new Arrays();
arrays.getSum(arr1);
arrays.getMax(arr1);
arrays.UpSort(arr1);
arrays.DownSort(arr1);
}
}
//final修饰拒绝继承
final class Arrays{
Arrays(){
}
//求和方法
void getSum(int arr[]){
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
sum+=arr[i];
}
System.out.println("×××数组序列的和为:"+sum);
}
//求最大值方法
void getMax(int arr[]){
int temp=0;
for(int i=0;i<arr.length-1;i++){
for(int j=(i+1);j<arr.length;j++){
if(arr[i]<arr[j]){
temp=arr[i];
arr[i]=arr[j];
arr[j]=temp;
}
}
}
System.out.println("×××数组序列的最大值是:"+arr[0]);
}
//排序方法
void UpSort(int []arr){
int temp=0;
System.out.print("×××数组序列的和升序排列:");
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
for(int j=(i+1);j<arr.length;j++){
if(arr[i]>arr[j]){
temp=arr[i];
arr[i]=arr[j];
arr[j]=temp;
}
}
System.out.print(arr[i]+",");
}
System.out.println("");
}
void DownSort(int []arr){
System.out.print("×××数组序列的翻转序列是:");
for(int i=arr.length-1;i>=0;i--){
System.out.print(arr[i]+",");
}
System.out.println("");
}
//double类型的处理方法
void getSum(double []arr1){
double sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<arr1.length;i++){
sum+=arr1[i];
}
System.out.println("double类型数组序列的和为:"+sum);
}
void getMax(double []arr1){
double temp=0;
for(int i=0;i<arr1.length-1;i++){
for(int j=(i+1);j<arr1.length;j++){
if(arr1[i]<arr1[j]){
temp=arr1[i];
arr1[i]=arr1[j];
arr1[j]=temp;
}
}
}
System.out.println("double类型数组序列的最大值是:"+arr1[0]);
}
void UpSort(double []arr1){
double temp=0;
System.out.print("double类型数组序列的和升序排列:");
for(int i=0;i<arr1.length;i++){
for(int j=(i+1);j<arr1.length;j++){
if(arr1[i]>arr1[j]){
temp=arr1[i];
arr1[i]=arr1[j];
arr1[j]=temp;
}
}
System.out.print(arr1[i]+",");
}
System.out.println("");
}
void DownSort(double []arr1){
System.out.print("double类型数组序列的翻转序列是:");
for(int i=arr1.length-1;i>=0;i--){
System.out.print(arr1[i]+",");
}
}
}2. a.定义一个英雄类 Hero
属性:(全部私有,提供公共方法让外部访问)
年龄, 血量 ,***力,防御力
方法:
释放技能,加血.
必须至少包含一个构造方法,且该构造方法可以初始化所有四个成员变量
b.定义一个类BatMan继承Hero类
方法:
飞行(方法中输出一行打印"飞行")
c.定义一个SuperBatMan类继承 BatMan类
方法:
重写飞行方法(方法中输出一行打印"超级飞行")
最终分别创建BatMan对象和SuperBatMan对象,并调用飞行方法.
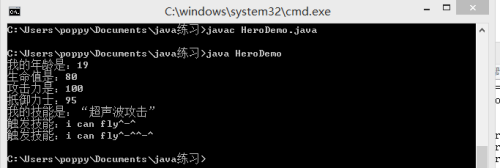
public class HeroDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
BatMan batMan=new BatMan(19,80,95,100);
SuperBatMan superbatman=new SuperBatMan(19,80,95,100);
batMan.skill();
batMan.fly();
superbatman.fly();
}
}
class Hero{
private int hp,age,protect,power;
Hero(){
}
Hero(int age,int hp,int protect,int power){
this.age=age;
this.hp=hp;
this.protect=protect;
this.power=power;
}
void skill(){
System.out.println("我的年龄是:"+age);
System.out.println("生命值是:"+hp+'\n'+"***力是:"+power+'\n'+"抵御力士:"+protect);
System.out.println("我的技能是:“超声波***”");
}
}
class BatMan extends Hero{
BatMan(int age,int hp,int protect,int power){
super(19,80,95,100);
}
void fly(){
System.out.println("触发技能:i can fly^-^");
}
}
class SuperBatMan extends BatMan{
SuperBatMan(int age,int hp,int protect,int power){
super(19,80,95,100);
}
void fly(){
System.out.println("触发技能:i can fly^-^^-^");
}
}3. 实现一个猜数的小游戏.
随机产生一个数(a)。
Scanner 的方式来输入一个数字,并提供反馈,告诉用户该输入的值比a大还是比a小,直到最终用户猜中,显示结果.
import java.util.*;
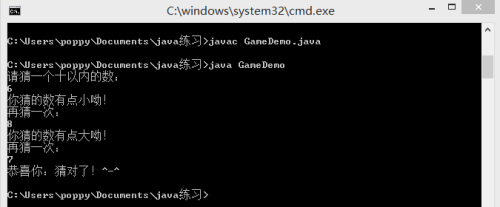
public class GameDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
int num = (int)(Math.random()*10)+1;
System.out.println("请猜一个十以内的数:");
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int num1=sc.nextInt();
while(num!=num1){
if(num1>num){
System.out.println("你猜的数有点大呦!");
}else
System.out.println("你猜的数有点小呦!");
System.out.println("再猜一次:");
Scanner sc1=new Scanner(System.in);
num1=sc1.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("恭喜你:猜对了!^-^");
}
}转载于:https://blog.51cto.com/13355940/1974483







 本文通过三个实战案例介绍Java编程技巧:1. 设计工具类处理数组操作;2. 实现英雄类及其子类的方法覆盖;3. 开发一个猜数字小游戏。文章详细展示了类的设计、方法的实现及游戏逻辑。
本文通过三个实战案例介绍Java编程技巧:1. 设计工具类处理数组操作;2. 实现英雄类及其子类的方法覆盖;3. 开发一个猜数字小游戏。文章详细展示了类的设计、方法的实现及游戏逻辑。
![LJNON]Y0XP)8)6K}ZTVZX04.png 7ba97ebdb240aea0e8ecb1dade274458.png-wh_](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/blog_migrate/a8ad8cf002a71fabb69656ee283ff5b3.png)
















 1939
1939

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








