-
-
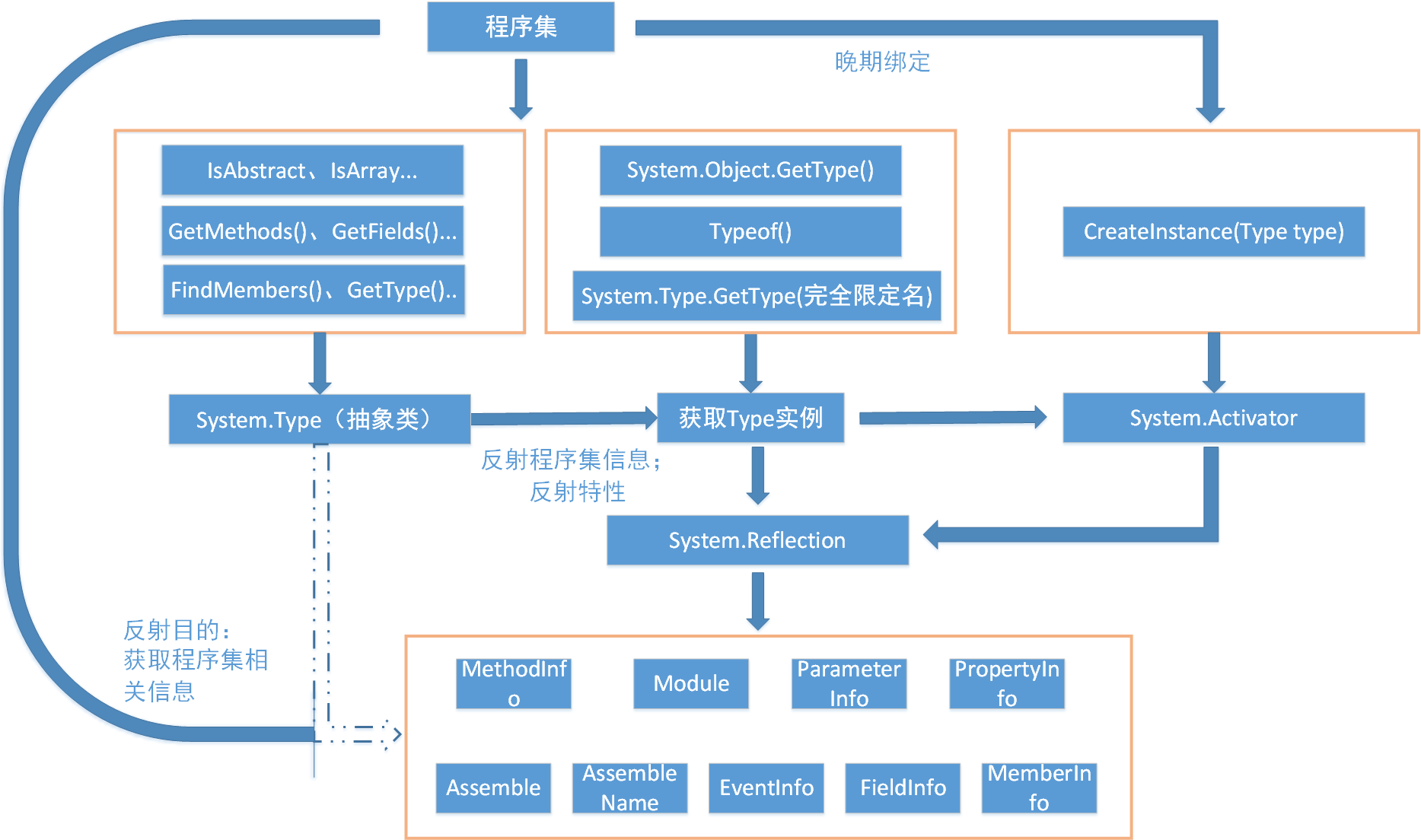
- 1.反射
- 1.1 System.Type类
- 1.2 使用System.Object.GetType()得到Type的引用
- 1.3 使用typeof()得到Type引用
- 1.4 使用System.Type.GetType()得到Type引用
- 2.构建自定义的元数据查看器
- 2.1 反射方法
- 2.2 反射字段和属性
- 2.3 反射实现的接口
- 2.4 显示其他信息
- 2.5 反射泛型信息
- 2.6 反射方法参数和返回值
- 3.动态加载程序集
- 4.反射共享程序集
- 5.晚期绑定
- 6.使用早期绑定反射特性
- 7.使用晚期绑定反射特性
- 8.反射、晚期绑定使用背景
- 9.反射的性能
- 1.反射
-
1.反射
在.Net中,反射(reflection)是一个运行库类型发现的过程。通过反射可以得到一个给定.dll或.exe程序集所包含的所有类型的列表,其中包括类型定义的方法、字段、属性和事件,也可以动态发现一组给定类型支持的接口、方法的参数或其他相关细节(基类、命名空间、清单数据等)。
System.Reflection命名空间成员示例:
| 类型 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| Assembly | 该抽象类包含了许多静态方法,通过它可以加载、了解和操纵一个程序集 |
| AssemblyName | 使用该类可以找到大量隐藏在程序集的身份中的细节(版本信息、区域信息等) |
| EventInfo | 该抽象类保存给定事件的信息 |
| FieldInfo | 该抽象类保存给定字段的信息 |
| MemberInfo | 该类是抽象类,它为EventInfo、FieldInfo、MethodInfo和PropertyInfo类型定义了公共的行为 |
| MethodInfo | 该抽象类保存给定方法的信息 |
| Module | 该抽象类可以访问多文件程序集中的给定模块 |
| ParameterInfo | 该类保存给定参数的信息 |
| PropertyInfo | 该抽象类保存给定属性的信息 |
1.1 System.Type类
System.Type的部分成员:
| 类型 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| IsAbstract、Isarray、IsClass、IsCOMObject、IEnum、 IsGenericTypeDefinition、IsGenericParameter、 IsInterface、IsPrimitive、IsNestedPrivate、 IsNestedPublic、IsSealed、IsValueType | 用于发现所引用类型的基本特性 |
| GetConstructors()、GetEvents()、GetFields()、 GetInterfaces()、GetMembers()、GetMethods()、 GetNestedType()、GetProperties() | 得到接口、方法、属性等的数组(每个方法都有单数版本,如GetMethod()) |
| FindMembers() | 该方法根据查询条件返回一个MemberInfo类型的数组 |
| GetType() | 该静态方法返回一个Type实例,给定一个字符串名称 |
| InvokeMember | 该方法允许对给定项目的晚期绑定 |
1.2 使用System.Object.GetType()得到Type的引用
使用System.Object定义的GetType()方法,返回一个表示当前对象元数据的Type类的实例。
SportsCar sc = new SportsCar();
Type t = sc.GetType(); // 需要创建实例,需知道类型的编译时信息 1.3 使用typeof()得到Type引用
另一种获取类型信息的方法是使用C# typeof操作符。
Type t = typeof(SportsCar); // 无需创建实例,需知道类型的编译时信息
1.4 使用System.Type.GetType()得到Type引用
使用System.Type.GetType()得到Type引用,不需要得到正从中提取元数据的类型的编译时信息。
// 指定两个参数,一个用来控制当前类型找不到时是否抛出异常,另一个用来指示是否区分字符串大小写
Type t = Type.GetType("Carlibrary.SportsCar", false, false) // 要得到外部程序集中类型的类型信息,字符串必须使用完全限定名,加上类型所在程序集的友好名字(逗号分隔)
Type t = Type.GetType("Carlibrary.SportsCar, Carlibrary") // 要得到当前程序集中嵌套枚举的类型信息,使用+来标记
Type t = Type.GetType("Carlibrary.JamesBondCar+SpyOption") // 获取嵌套在JamesBondCar类中的枚举类型(SpyOption) 2.构建自定义的元数据查看器
需要为反射导入命名空间:
using System.Reflection;
2.1 反射方法
Type.GetMethods()返回一个System.Reflection.MethodInfo类型的数组,并使用foreach循环枚举:
using System;
using System.Reflection;
public interface IA { void M1(); }; public interface IB { void M2(); }; class SportsCar : IA { public int a = 0; public double b = 3.14; public string S { get; set; } public void A(int a) { } public void B() { } public void C() { } public void M1() { } } class Program { static void ListMethods(Type t) { Console.WriteLine("*** Methods ***"); MethodInfo[] mi = t.GetMethods(); foreach (MethodInfo m in mi) Console.WriteLine($"->{m.Name}"); } static void Main() { SportsCar sc = new SportsCar(); Type t = sc.GetType(); ListMethods(t); Console.ReadKey(); } } output
*** Methods ***
->get_S
->set_S
->A
->B ->C ->ToString ->Equals ->GetHashCode ->GetType 2.2 反射字段和属性
static void ListFields(Type t) // 字段 { Console.WriteLine("*** Fields ***"); var fieldNames = from f in t.GetFields() select f.Name; foreach (var name in fieldNames) Console.WriteLine($"->{name}"); } static void ListProps(Type t) // 属性 { Console.WriteLine("*** Methods ***"); var propsNames = from p in t.GetProperties() select p.Name; foreach (var name in propsNames) Console.WriteLine($"->{name}"); } static void Main() { SportsCar sc = new SportsCar(); Type t = sc.GetType(); ListFields(t); ListProps(t) Console.ReadKey(); } output
*** Fields ***
->a
->b
*** Propertys ***
->S 2.3 反射实现的接口
// 显示当前类实现的接口
static void ListInterfaces(Type t) { Console.WriteLine("*** Interfaces ***"); var ifacesNames = from i in t.GetInterfaces() select i.Name; foreach (var name in ifacesNames) Console.WriteLine($"->{name}"); } static void Main() { SportsCar sc = new SportsCar(); Type t = sc.GetType();; ListInterfaces(t); Console.ReadKey(); } output
*** Interfaces ***
->IA
2.4 显示其他信息
显示关于传入类型的各种统计信息(表示该类型是否是泛型,基类是什么,类型是否密封等等)
static void ListVariousStats(Type t)
{
Console.WriteLine("*** Various Statistics ***");
Console.WriteLine($"Base class is: {t.BaseType}"); Console.WriteLine($"abstract? {t.IsAbstract}"); Console.WriteLine($"sealed? {t.IsSealed}"); Console.WriteLine($"generic? {t.IsGenericTypeDefinition}"); Console.WriteLine($"class? {t.IsClass}"); } static void Main() { SportsCar sc = new SportsCar(); Type t = sc.GetType(); ListVariousStats(t); Console.ReadKey(); } output
*** Various Statistics ***
Base class is: System.Object abstract? False sealed? False generic? False class? True 2.5 反射泛型信息
如果调用Type.GetType()来获取泛型类型的元数据描述,就必须使用包含反引号(`)加上数值的语法来表示类型支持的类型参数个数
using System.Collection.Generic.List`1 // 反射List<T>元数据描述 using System.Collection.Generic.Dictionary`2 // 反射Dictionary<TKey, TValue>元数据描述 2.6 反射方法参数和返回值
使用MethodInfo类型提供的ReturnType属性和GetParameters()方法,列出方法的返回类型和输入参数类型。
static void ListMethods(Type t) { Console.WriteLine("*** Methods ***"); MethodInfo[] mi = t.GetMethods(); foreach (MethodInfo m in mi) { string retVal = m.ReflectedType.FullName; string paramInfo = "( "; foreach (ParameterInfo pi in m.GetParameters()) { paramInfo += string.Format($"{pi.ParameterType} {pi.Name}"); } paramInfo += " )"; Console.WriteLine($"->{retVal} {m.Name} {paramInfo}"); } } output
*** Methods ***
->SportsCar get_S ( )
->SportsCar set_S ( System.String value ) ->SportsCar A ( System.Int32 a ) ->SportsCar B ( ) ->SportsCar C ( ) ->SportsCar M1 ( ) ->SportsCar ToString ( ) ->SportsCar Equals ( System.Object obj ) ->SportsCar GetHashCode ( ) ->SportsCar GetType ( ) 或者使用以下语法(每一个XXXInfo类型都重写了ToString()方法)
static void ListMethods(Type t) { Console.WriteLine("*** Methods ***"); var fieldNames = from f in t.GetMethods() select f; foreach (var name in fieldNames) Console.WriteLine($"->{name}"); } output
*** Methods ***
->System.String get_S()
->Void set_S(System.String) ->Void A(Int32) ->Void B() ->Void C() ->Void M1() ->System.String ToString() ->Boolean Equals(System.Object) ->Int32 GetHashCode() ->System.Type GetType() 3.动态加载程序集
使用System.Reflection下的Assembly类,动态加载程序集,并找出关于程序集自身的属性。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Reflection; using System.IO; // For FileNotFoundException definition. namespace ExternalAssemblyReflector { class Program { #region Helper function static void DisplayTypesInAsm(Assembly asm) { Console.WriteLine("\n***** Types in Assembly *****"); Console.WriteLine("->{0}", asm.FullName); Type[] types = asm.GetTypes(); foreach (Type t in types) Console.WriteLine("Type: {0}", t); Console.WriteLine(""); } #endregion static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("***** External Assembly Viewer *****"); string asmName = ""; Assembly asm = null; do { Console.WriteLine("\nEnter an assembly to evaluate"); Console.Write("or enter Q to quit: "); // Get name of assembly. asmName = Console.ReadLine(); // Does user want to quit? if (asmName.ToUpper() == "Q") { break; } // Try to load assembly. try { asm = Assembly.LoadFrom(asmName); DisplayTypesInAsm(asm); } catch { Console.WriteLine("Sorry, can't find assembly."); } } while (true); } } } 加载程序集方法Load()与LoadFrom()的区别:
| Assembly.Load() | Assembly.LoadFrom() |
|---|---|
| 使用程序集友好名称(其dll文件应置于\bin\Debug目录下) | 使用绝对路径 |
| Assembly.Load("CarLibrary") | Assembly.LoadFrom("C:\MyApp\MyAsm.dll") |
4.反射共享程序集
Assembly.Load()的一种重载允许指定一个区域设置(为本地化程序集)、一个版本号和公钥标记值(为共享程序集)。整体来说,识别一个程序集的一组术语称为显示名称(display name),显示名称以程序集友好名称开头。
Name(,Version = major.minor.build.revision)(,culture = culture token)(,PublicKeyToken = public key token) 如:
Assembly a = Assembly.Load(@"CarLibrary, Version = 1.0.0.0, PublicKeyToken = null, Culture = """);
可以使用System.Reflection命名空间提供的AssemblyName类型创建显示名称。
AssemblyName asmName;
asmName = new AssemblyName();
asmName.Name = "CarLibrary"; Version v = new Version("1.0.0.0"); asmName.Version = v; Assembly a = Assembly.Load(asmName); namespace SharedAsmReflector
{
public class SharedAsmReflector { #region DisplayInfo helper method private static void DisplayInfo(Assembly a) { Console.WriteLine("***** Info about Assembly *****"); Console.WriteLine("Loaded from GAC? {0}", a.GlobalAssemblyCache); Console.WriteLine("Asm Name: {0}", a.GetName().Name); Console.WriteLine("Asm Version: {0}", a.GetName().Version); Console.WriteLine("Asm Culture: {0}", a.GetName().CultureInfo.DisplayName); Console.WriteLine("\nHere are the public enums:"); // Use a LINQ query to find the public enums. Type[] types = a.GetTypes(); var publicEnums = from pe in types where pe.IsEnum && pe.IsPublic select pe; foreach (var pe in types) { Console.WriteLine(pe); } } #endregion static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("***** The Shared Asm Reflector App *****\n"); // Load System.Windows.Forms.dll from GAC. GAC:全局程序集缓存 string displayName = null; displayName = "System.Windows.Forms," + "Version=4.0.0.0," + "PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089," + @"Culture="""; Assembly asm = Assembly.Load(displayName); DisplayInfo(asm); Console.WriteLine("Done!"); Console.ReadLine(); } } } 5.晚期绑定
晚期绑定(late binding)是一种创建一个给定类型的实例并在运行时调用其成员,而不需要在编译时知道它存在的一种技术。即通过编程的方式在内存中加载.NET程序集。
使用Activator.CreateInstance()方法建立一个晚期绑定类型的实例。
namespace LateBindingApp
{
// 这个程序将加载一个外部库并使用晚期绑定创建一个对象
public class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("***** Fun with Late Binding *****"); // 尝试加载一个本地CarLibrary副本 Assembly a = null; try { a = Assembly.Load("CarLibrary"); } catch (FileNotFoundException ex) { Console.WriteLine(ex.Message); return; } if (a != null) { // CreateUsingLateBinding(a); InvokeMethodWithArgsUsingLateBinding(a); } Console.ReadLine(); } #region Invoke method with no args static void CreateUsingLateBinding(Assembly asm) { try { // 获取Minivan类型的元数据 Type miniVan = asm.GetType("CarLibrary.MiniVan"); // 在运行时创建Minivan // 返回System.Object类型,由于未引用CarLibrary.dll,故无法强制转换 object obj = Activator.CreateInstance(miniVan); Console.WriteLine("Created a {0} using late binding!", obj); // 利用反射获得CarLibrary中TurboBoost()方法的信息. MethodInfo mi = miniVan.GetMethod("TurboBoost"); // 调用方法(“null”表示没有参数) mi.Invoke(obj, null); } catch (Exception ex) { Console.WriteLine(ex.Message); } } #endregion #region Invoke method with args static void InvokeMethodWithArgsUsingLateBinding(Assembly asm) { try { // 首先,获得元数据描述 Type sport = asm.GetType("CarLibrary.SportsCar"); // 创建对象 object obj = Activator.CreateInstance(sport); // 调用包含参数的TurnOnRadio()方法 MethodInfo mi = sport.GetMethod("TurnOnRadio"); mi.Invoke(obj, new object[] { true, 2 }); // 使用object数组存放参数 } catch (Exception ex) { Console.WriteLine(ex.Message); } } #endregion } } 6.使用早期绑定反射特性
using AttributedCarLibrary; //引入AttributedCarLibrary
namespace VehicleDescriptionAttributeReader { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("***** Value of VehicleDescriptionAttribute *****\n"); ReflectOnAttributesWithEarlyBinding(); Console.ReadLine(); } private static void ReflectOnAttributesWithEarlyBinding() { // 获取Winnebago元数据描述 Type t = typeof(Winnebago); // 使用GetCustomAttributes(bool)获取所有特性,返回一个对象数组,其中bool值控制是否扩展到继承链 object[] customAtts = t.GetCustomAttributes(false); // 输出描述 foreach (VehicleDescriptionAttribute v in customAtts) Console.WriteLine("-> {0}\n", v.Description); } } } 7.使用晚期绑定反射特性
using System.Reflection;
namespace VehicleDescriptionAttributeReaderLateBinding
{
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("***** Value of VehicleDescriptionAttribute *****\n"); ReflectAttributesUsingLateBinding(); Console.ReadLine(); } #region Helper method private static void ReflectAttributesUsingLateBinding() { try { // 加载本地AttributedCarLibrary副本 Assembly asm = Assembly.Load("AttributedCarLibrary"); // 得到VehicleDescriptionAttribute的类型信息 Type vehicleDesc = asm.GetType("AttributedCarLibrary.VehicleDescriptionAttribute"); // 得到Description属性的类型信息 PropertyInfo propDesc = vehicleDesc.GetProperty("Description"); // 得到程序集中所有类型 Type[] types = asm.GetTypes(); // 遍历每个类型,得到所有VehicleDescriptionAttributes. foreach (Type t in types) { object[] objs = t.GetCustomAttributes(vehicleDesc, false); // 遍历每个VehicleDescriptionAttribute并使用晚期绑定输出描述 foreach (object o in objs) { Console.WriteLine("-> {0}: {1}\n", t.Name, propDesc.GetValue(o, null)); } } } catch (Exception ex) { Console.WriteLine(ex.Message); } } #endregion } } 8.反射、晚期绑定使用背景
- 首先,可扩展的应用程序必须提供一些输入手段,允许用户指定被插入的模块,这需要动态加载
- 其次,可扩展的应用程序必须要确定模块是否支持正确的功能,这需要反射
- 最后,可扩展的应用程序必须获取一个需要的基础架构的引用并调用成员触发底层功能,这需要晚期绑定
9.反射的性能
反射时相当强大的机制,允许在运行时发现并使用编译时还不了解的类型及其成员,但是,反射也存在以下两个缺点:
- 反射造成编译时无法保证类型安全性。 由于反射严重依赖于字符串,所以会丧失编译时的类型安全性。例如,执行type.GetType("int");要求通过反射在程序集中查找名为“int”的类型,代码会通过编译,但运行时会返回null,因为CLR只知“System.Int32”,不知“int”。
- 反射速度慢。
- 使用反射时,类型及其成员的名称在编译时是未知的;要用字符串名称标识每个类及其成员,然后在运行时发现它们,即使用System.Reflection命名空间中的类型扫描程序集的元数据时,反射机制会不停的执行字符串搜索,且通常执行的是不区分大小的比较,这会进一步影响速度。
- 使用反射调用一个成员时。比如调用方法,首先必须将实参打包(pack)成一个数组;在内部,反射必须将这些实参解包(unpack)到线程栈上。此外,在调用方法前,CLR必须检查实参具有正确的数据类型。最后,CLR必须确保调用者有正确的安全权限来访问被调用的成员。
改善方法:




















 8661
8661

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








