Class 的 getResource 方法,通过ClassLoader实现:
注意参数格式,可以是绝对路径(在 类路径 变量指定的目录下或jar中 查找) 也可以是相对路径(相对当前类的类文件包名)
resolveName(..)方法将输入的资源名转化为 类路径 下的文件名。
通过该方法可知,除了使用Class加载资源文件外,也可以直接通过ClassLoader加载资源文件,把资源文件当成 一个普通的 类文件 就可以了,只是这时候的 package name 需要把 '.' 变成 '/'
/**
* Finds a resource with a given name. The rules for searching resources
* associated with a given class are implemented by the defining
* {@linkplain ClassLoader class loader} of the class. This method
* delegates to this object's class loader. If this object was loaded by
* the bootstrap class loader, the method delegates to {@link
* ClassLoader#getSystemResource}.
*
* <p> Before delegation, an absolute resource name is constructed from the
* given resource name using this algorithm:
*
* <ul>
*
* <li> If the {@code name} begins with a {@code '/'}
* (<tt>'\u002f'</tt>), then the absolute name of the resource is the
* portion of the {@code name} following the {@code '/'}.
*
* <li> Otherwise, the absolute name is of the following form:
*
* <blockquote>
* {@code modified_package_name/name}
* </blockquote>
*
* <p> Where the {@code modified_package_name} is the package name of this
* object with {@code '/'} substituted for {@code '.'}
* (<tt>'\u002e'</tt>).
*
* </ul>
*
* @param name name of the desired resource
* @return A {@link java.net.URL} object or {@code null} if no
* resource with this name is found
* @since JDK1.1
*/
public java.net.URL getResource(String name) {
name = resolveName(name);
ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader0();
if (cl==null) {
// A system class.
return ClassLoader.getSystemResource(name);
}
return cl.getResource(name);
}ClassLoader 的getResource方法:
实现的自己的ClassLoader时,可以复写findResource方法在特定的位置查找资源,默认在在 类路径 下查找,就像查找 类文件一样
/**
* Finds the resource with the given name. A resource is some data
* (images, audio, text, etc) that can be accessed by class code in a way
* that is independent of the location of the code.
*
* <p> The name of a resource is a '<tt>/</tt>'-separated path name that
* identifies the resource.
*
* <p> This method will first search the parent class loader for the
* resource; if the parent is <tt>null</tt> the path of the class loader
* built-in to the virtual machine is searched. That failing, this method
* will invoke {@link #findResource(String)} to find the resource. </p>
*
* @param name
* The resource name
*
* @return A <tt>URL</tt> object for reading the resource, or
* <tt>null</tt> if the resource could not be found or the invoker
* doesn't have adequate privileges to get the resource.
*
* @since 1.1
*/
public URL getResource(String name) {
URL url;
if (parent != null) {
url = parent.getResource(name);
} else {
url = getBootstrapResource(name);
}
if (url == null) {
url = findResource(name);
}
return url;
}
/**
* Find a resource of the specified name from the search path used to load
* classes. This method locates the resource through the system class
* loader (see {@link #getSystemClassLoader()}). </p>
*
* @param name
* The resource name
*
* @return A {@link java.net.URL <tt>URL</tt>} object for reading the
* resource, or <tt>null</tt> if the resource could not be found
*
* @since 1.1
*/
public static URL getSystemResource(String name) {
ClassLoader system = getSystemClassLoader();
if (system == null) {
return getBootstrapResource(name);
}
return system.getResource(name);
}
/**
* Returns an enumeration of {@link java.net.URL <tt>URL</tt>} objects
* representing all the resources with the given name. Class loader
* implementations should override this method to specify where to load
* resources from. </p>
*
* @param name
* The resource name
*
* @return An enumeration of {@link java.net.URL <tt>URL</tt>} objects for
* the resources
*
* @throws IOException
* If I/O errors occur
*
* @since 1.2
*/
protected Enumeration<URL> findResources(String name) throws IOException {
return java.util.Collections.emptyEnumeration();
}ClassLoader:
loadClass 、loadLibrary:

findClass、findLibray、findResource:
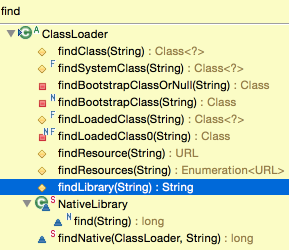

下面是一个例子:

package test;
import java.net.URL;
public class LoadResourceByClassLoader {
public static void main(String[] args){
LoadResource lr = new LoadResource();
lr.load();
}
}
class LoadResource{
public void load(){
ClassLoader cl = this.getClass().getClassLoader();
String name = resolveName("/abs.txt");
URL aurl = cl.getResource(name);
System.out.println(aurl != null? "resource url:" + aurl.toString(): "/abs.txt is null");
name = resolveName("abs.txt");
aurl = cl.getResource(name);
System.out.println(aurl != null? "resource url:" + aurl.toString(): "abs.txt is null");
name = resolveName("relative.txt");
URL rurl = cl.getResource(name);
System.out.println(rurl != null? "resource url:" + rurl.toString(): "relative.txt is null");
name = resolveName("d/relative.txt");
rurl = cl.getResource(name);
System.out.println(rurl != null? "resource url:" + rurl.toString(): "relative.txt is null");
}
/**
* Copied from Class.java
*
* Add a package name prefix if the name is not absolute Remove leading "/"
* if name is absolute
*/
private String resolveName(String name) {
System.out.println( "befor resolving: " + name );
if (name == null) {
return name;
}
if (!name.startsWith("/")) {
Class<?> c = this.getClass();
while (c.isArray()) {
c = c.getComponentType();
}
String baseName = c.getName();
int index = baseName.lastIndexOf('.');
if (index != -1) {
name = baseName.substring(0, index).replace('.', '/')
+"/"+name;
}
} else {
name = name.substring(1);
}
System.out.println(" after resolving: " +name );
return name;
}
}输出:
befor resolving: /abs.txt
after resolving: abs.txt
resource url:file:/Users/may/Documents/workspace/TESTcore/bin/abs.txt
befor resolving: abs.txt
after resolving: test/abs.txt
abs.txt is null
befor resolving: relative.txt
after resolving: test/relative.txt
resource url:file:/Users/may/Documents/workspace/TESTcore/bin/test/relative.txt
befor resolving: d/relative.txt
after resolving: test/d/relative.txt
resource url:file:/Users/may/Documents/workspace/TESTcore/bin/test/d/relative.txt





















 1042
1042

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








