What Is an Exception?
The term exception is shorthand for the phrase "exceptional event."
Definition: An exception is an event, which occurs during the execution of a program, that disrupts the normal flow of the program's instructions.
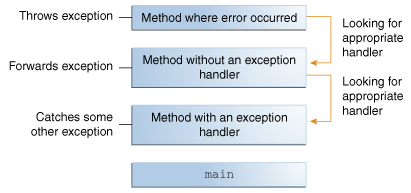
Searching the call stack for the exception handler.
The Three Kinds of Exceptions
The first kind of exception is the checked exception. These are exceptional conditions that a well-written application should anticipate and recover from.
Checked exceptions are subject to the Catch or Specify Requirement. All exceptions are checked exceptions, except for those indicated by Error, RuntimeException, and their subclasses.
The second kind of exception is the error. These are exceptional conditions that are external to the application, and that the application usually cannot anticipate or recover from.
Errors are not subject to the Catch or Specify Requirement. Errors are those exceptions indicated by Error and its subclasses.
The third kind of exception is the runtime exception. These are exceptional conditions that are internal to the application, and that the application usually cannot anticipate or recover from.
Runtime exceptions are not subject to the Catch or Specify Requirement. Runtime exceptions are those indicated by RuntimeException and its subclasses.
Errors and runtime exceptions are collectively known as unchecked exceptions.
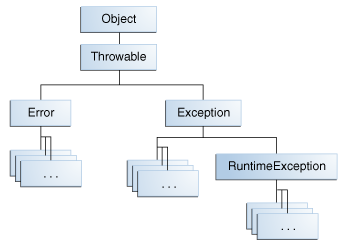
The Throwable class
The Catch or Specify Requirement
Valid Java programming language code must honor the Catch or Specify Requirement. This means that code that might throw certain exceptions must be enclosed by either of the following:
A
trystatement that catches the exception. Thetrymust provide a handler for the exception, as described in Catching and Handling Exceptions.A method that specifies that it can throw the exception. The method must provide a
throwsclause that lists the exception, as described in Specifying the Exceptions Thrown by a Method.
Code that fails to honor the Catch or Specify Requirement will not compile.
Bypassing Catch or Specify
Some programmers consider the Catch or Specify Requirement a serious flaw in the exception mechanism and bypass it by using unchecked exceptions in place of checked exceptions. In general, this is not recommended. The section Unchecked Exceptions — The Controversy talks about when it is appropriate to use unchecked exceptions.
Generally speaking, do not throw a RuntimeException or create a subclass of RuntimeException simply because you don't want to be bothered with specifying the exceptions your methods can throw.
Here's the bottom line guideline: If a client can reasonably be expected to recover from an exception, make it a checked exception. If a client cannot do anything to recover from the exception, make it an unchecked exception.
参考:Exceptions







 本文详细介绍了Java中异常的定义、分类及其处理机制,包括检查异常、错误和运行时异常的区别,如何遵循捕获或指定要求,以及在实际编程中如何正确使用异常处理。
本文详细介绍了Java中异常的定义、分类及其处理机制,包括检查异常、错误和运行时异常的区别,如何遵循捕获或指定要求,以及在实际编程中如何正确使用异常处理。

















 319
319

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








