Summary: in this tutorial, we will show you how to use the MySQL subquery to write complex queries and explain the correlated subquery concept.
A MySQL subquery is a query that is nested inside another query such as SELECT, INSERT, UPDATEor DELETE. In addition, a MySQL subquery can be nested inside another subquery.
A MySQL subquery is also called an inner query while the query that contains the subquery is called an outer query.
Let’s take a look at the following subquery that returns employees who locate in the offices in the USA.
- The subquery returns all offices codes of the offices that locate in the USA.
- The outer query selects the last name and first name of employees whose office code is in the result set returned by the subquery.
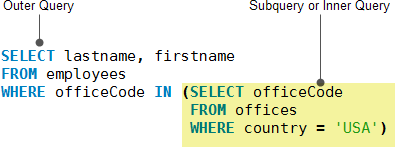
You can use a subquery anywhere that you use an expression. In addition, you must enclose a subquery in parentheses.
MySQL subquery within a WHERE clause
We will use the payments table for the demonstration.
MySQL subquery with comparison operators
You can use comparison operators e.g., =, >, <, etc., to compare a single value returned by the subquery with the expression in the WHERE clause.
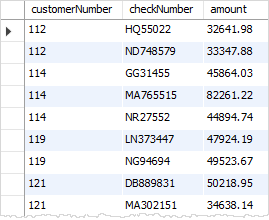
For example, the following query returns the customer who has the maximum payment.
SELECT customerNumber, checkNumber, amount FROM payments WHERE amount = ( SELECT MAX(amount) FROM payments );
![]()
In addition to the equality operator, you can use other comparison operators such as greater than (>), less than(<), etc.
For example, you can find customers whose payments are greater than the average payment using a subquery.
First, you use a subquery to calculate the average payment using the AVG aggregate function. Then, in the outer query, you query payments that are greater than the average payment returned by the subquery.
SELECT customerNumber, checkNumber, amount FROM payments WHERE amount > ( SELECT AVG(amount) FROM payments );
MySQL subquery with IN and NOT IN operators
If a subquery returns more than one value, you can use other operators such as IN or NOT INoperator in the WHERE clause.
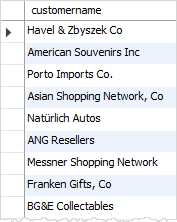
See the following customers and orders tables.
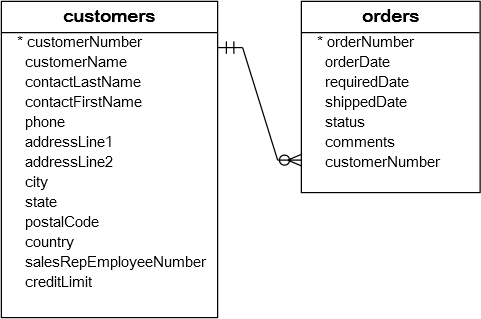
For example, you can use a subquery with NOT IN operator to find customer who has not ordered any products as follows:
SELECT customername FROM customers WHERE customerNumber NOT IN( SELECT DISTINCT customernumber FROM orders );
MySQL subquery with EXISTS and NOT EXISTS
When a subquery is used with EXISTS or NOT EXISTS operator, a subquery returns a Boolean value of TRUE or FALSE. The subquery acts as an existence check.
In the following example, we select a list of customers who have at least one order with total sales greater than 10K.
First, we build a query that checks if there is, at least, one order with total sales greater than 10K:
SELECT priceEach * quantityOrdered FROM orderdetails WHERE priceEach * quantityOrdered > 10000 GROUP BY orderNumber;

The query returns 6 rows so that when we use it as a subquery, it will return TRUE; therefore the whole query will return all customers:
SELECT customerName FROM customers WHERE EXISTS ( SELECT priceEach * quantityOrdered FROM orderdetails WHERE priceEach * quantityOrdered > 10000 GROUP BY orderNumber )

If you replace the EXISTS with NOT EXIST, the query will not return any records at all.
MySQL subquery in FROM clause
When you use a subquery in the FROM clause, the result set returned from a subquery is used as a table. This table is referred to as a derived table or materialized subquery.
The following subquery finds the maximum, minimum and average number of items in sale orders:
SELECT MAX(items), MIN(items), FLOOR(AVG(items)) FROM ( SELECT orderNumber, COUNT(orderNumber) AS items FROM orderdetails GROUP BY orderNumber ) AS lineitems;
![]()
Notice that the subquery returns the following result set that is used as a derived table for the outer query.
MySQL correlated subquery
In the previous examples, you notice that the subquery is independent. It means you can execute the subquery as a single query. However, a correlated subquery is a subquery that uses the information from the outer query. In other words, a correlated subquery depends on the outer query. A correlated subquery is evaluated once for each row in the outer query.
In the following correlated subquery, we select products whose buy prices are greater than the average buy price of all products for a specific product line.
SELECT productname, buyprice FROM products AS p1 WHERE buyprice > ( SELECT AVG(buyprice) FROM products WHERE productline = p1.productline )
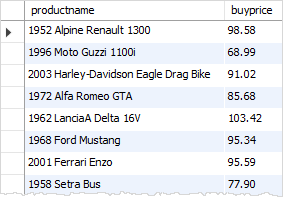
The inner query executes for every product line because the product line is changed for every row. Hence, the average buy price will also change.
In this tutorial, we have shown you how to use MySQL subquery and correlated subquery to write more complex queries.




 本文介绍如何使用MySQL子查询来编写复杂查询,并解释相关子查询的概念。包括子查询的基础用法、不同运算符的应用、IN和NOT IN操作符、EXISTS和NOT EXISTS操作符的使用,以及子查询在FROM子句中的应用。
本文介绍如何使用MySQL子查询来编写复杂查询,并解释相关子查询的概念。包括子查询的基础用法、不同运算符的应用、IN和NOT IN操作符、EXISTS和NOT EXISTS操作符的使用,以及子查询在FROM子句中的应用。

















 3783
3783

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








