- 定义:用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并且通过拷贝这些原型创建新的对象。
- 通用类图
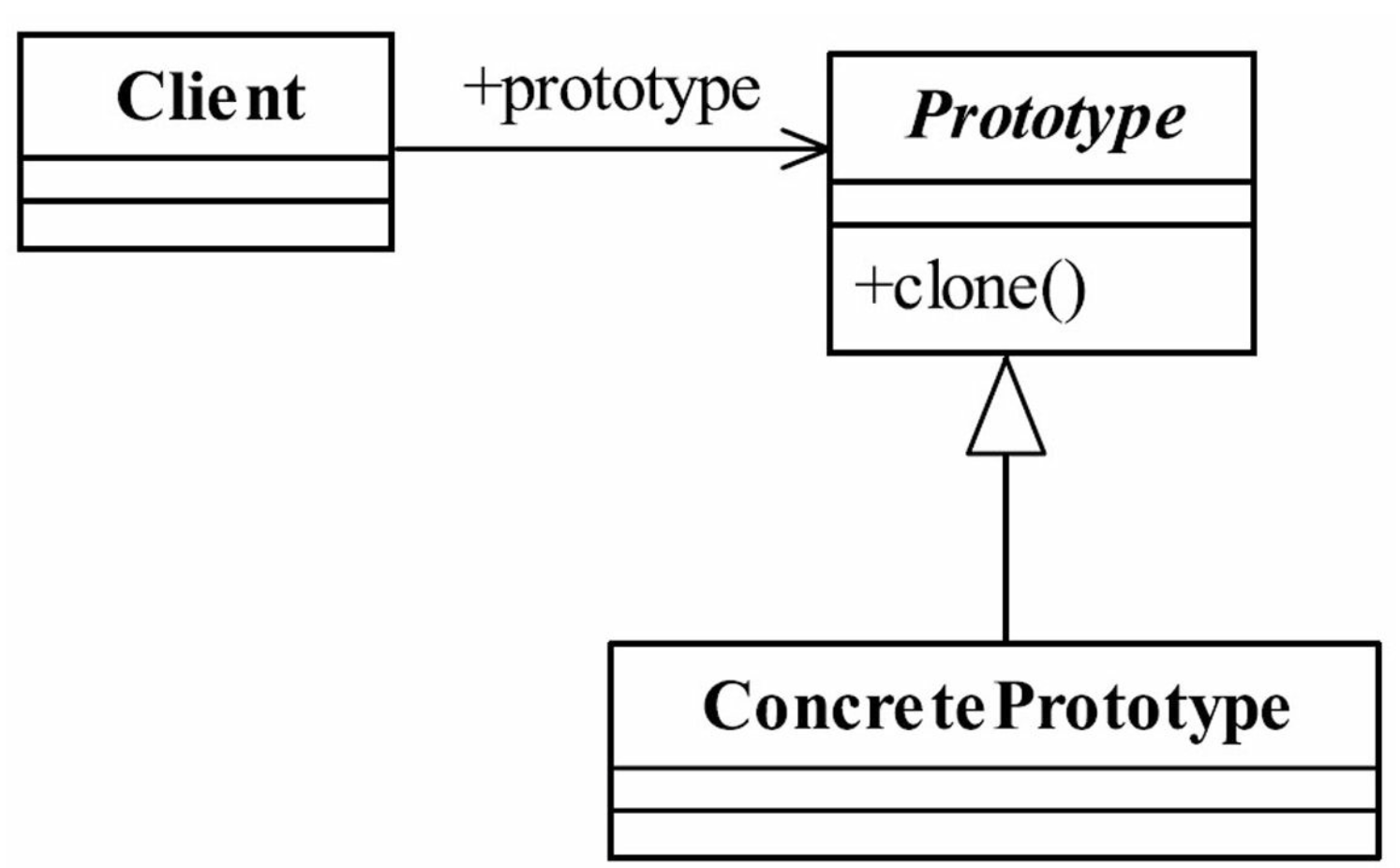
3,实例代码
/**
* 只是一个类,作为clone对象全局变量,clone对象被clone的时候,它会不会被clone
*/
public class TestObject {
private String testName;
public String getTestName() {
return testName;
}
public void setTestName(String testName) {
this.testName = testName;
}
}
/**
* 原型对象,用于clone测试
*/
public class ConcretePrototype implements Cloneable{
private String attr1;
private Integer attr2;
private TestObject testObject;
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
ConcretePrototype concretePrototype = null;
try {
concretePrototype = (ConcretePrototype)super.clone();
}catch (CloneNotSupportedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return concretePrototype;
}
public String getAttr1() {
return attr1;
}
public void setAttr1(String attr1) {
this.attr1 = attr1;
}
public Integer getAttr2() {
return attr2;
}
public void setAttr2(Integer attr2) {
this.attr2 = attr2;
}
public TestObject getTestObject() {
return testObject;
}
public void setTestObject(TestObject testObject) {
this.testObject = testObject;
}
}
/**
* 显示clone 结果
*/
public class MineClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestObject testObject = new TestObject();
testObject.setTestName("testName");
ConcretePrototype concretePrototype = new ConcretePrototype();
concretePrototype.setAttr1("ceshi");
concretePrototype.setAttr2(1);
concretePrototype.setTestObject(testObject);
try {
ConcretePrototype cp = (ConcretePrototype)concretePrototype.clone();
System.out.println(cp.getAttr1());
System.out.println(cp.getAttr2());
System.out.println(cp.getTestObject().getTestName());
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
4,注意事项:
- 利用clone 创造对象的时候,不会执行对象的构造方法
- 要注意深拷贝和浅拷贝(在对象拷贝的时候,对象关联的数组和引用对象是不会被拷贝的,其他基本类型包括string可以被拷贝)




 本文详细介绍了Java中克隆模式的实现方式,包括如何通过实现Cloneable接口并重写clone方法来复制对象,同时探讨了深拷贝和浅拷贝的区别。
本文详细介绍了Java中克隆模式的实现方式,包括如何通过实现Cloneable接口并重写clone方法来复制对象,同时探讨了深拷贝和浅拷贝的区别。

















 889
889

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








