什么是软链接?
linux下的软链接(In computing, a symbolic link (also symlink or soft link) is a special type of file that contains a reference to another file or directory in the form of an absolute or relative path and that affects pathname resolution.)软链接又叫符号链接,这个文件包含了另一个文件的路径名。可以是任意文件或目录,可以链接不同文件系统的文件。它类似于windows下的创建快捷方式,但是又有本质的不同。
dongchao@linux104:~/rwcap/src$ ln --help
Usage: ln [OPTION]... [-T] TARGET LINK_NAME (1st form)
or: ln [OPTION]... TARGET (2nd form)
or: ln [OPTION]... TARGET... DIRECTORY (3rd form)
or: ln [OPTION]... -t DIRECTORY TARGET... (4th form)
In the 1st form, create a link to TARGET with the name LINK_NAME.
In the 2nd form, create a link to TARGET in the current directory.
In the 3rd and 4th forms, create links to each TARGET in DIRECTORY.
Create hard links by default, symbolic links with --symbolic.
By default, each destination (name of new link) should not already exist.
When creating hard links, each TARGET must exist. Symbolic links
can hold arbitrary text; if later resolved, a relative link is
interpreted in relation to its parent directory.
Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too.
--backup[=CONTROL] make a backup of each existing destination file
-b like --backup but does not accept an argument
-d, -F, --directory allow the superuser to attempt to hard link
directories (note: will probably fail due to
system restrictions, even for the superuser)
-f, --force remove existing destination files
-i, --interactive prompt whether to remove destinations
-L, --logical dereference TARGETs that are symbolic links
-n, --no-dereference treat LINK_NAME as a normal file if
it is a symbolic link to a directory
-P, --physical make hard links directly to symbolic links
-r, --relative create symbolic links relative to link location
-s, --symbolic make symbolic links instead of hard links
-S, --suffix=SUFFIX override the usual backup suffix
-t, --target-directory=DIRECTORY specify the DIRECTORY in which to create
the links
-T, --no-target-directory treat LINK_NAME as a normal file always
-v, --verbose print name of each linked file
--help display this help and exit
--version output version information and exit
The backup suffix is '~', unless set with --suffix or SIMPLE_BACKUP_SUFFIX.
The version control method may be selected via the --backup option or through
the VERSION_CONTROL environment variable. Here are the values:
none, off never make backups (even if --backup is given)
numbered, t make numbered backups
existing, nil numbered if numbered backups exist, simple otherwise
simple, never always make simple backups
Using -s ignores -L and -P. Otherwise, the last option specified controls
behavior when a TARGET is a symbolic link, defaulting to -P.
Report ln bugs to bug-coreutils@gnu.org
GNU coreutils home page: <http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/>
General help using GNU software: <http://www.gnu.org/gethelp/>
For complete documentation, run: info coreutils 'ln invocation'创建软链接
ln – The command line tool to create links. By default, it creates a hard link. In order to create a symbolic link, we must add the -s ( --symbolic ) option. target – The existing file/directory you would like to link to point to.
命令行模式如下:
ln -s target linkname具体的:
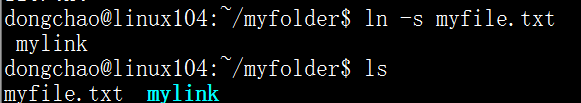
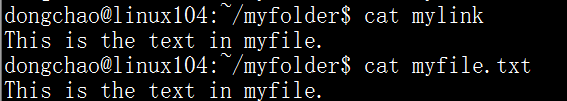
mylink就是软链接。也可以在myfile.txt前加上绝对路径,这样即使把mylink移动到别的路径下也不会出错了,软链接会依然有效。对于软链接的操作等同于对目标文件的操作:
当新建另外一个目录时,也可以新建一个软链接。(软链接可以链接到目标目录或者目标文件)

删除软链接
如果要删除软链接,可以这样:
rm -r /newlink复制软链接
复制链接文件的时候,需要注意添加-d参数,否则,复制的将会是链接文件指代的源文件。
[root@localhost tmp]# cp bashrc_slink bashrc_slink_1
[root@localhost tmp]# cp -d bashrc_slink bashrc_slink_2
[root@localhost tmp]# ls -l bashrc bashrc_slink*
-rw-r--r--. 2 root root 176 Dec 1 05:33 bashrc
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 6 Dec 1 05:48 bashrc_slink -> bashrc
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 176 Dec 1 05:51 bashrc_slink_1
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 6 Dec 1 05:51 bashrc_slink_2 -> bashrc以上的实例说明,当使用cp -d时,才保持了链接原本的属性,使得复制之后的文件(bashrc_slink2)依然是链接。





















 6328
6328

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








