Abstract
本文介紹如何使用ANSI C同時讀寫24/32位元的BMP圖檔做簡單的影像處理,並解析BMP格式。
Introduction
在(原創) 如何使用ANSI C讀寫24位元的BMP圖檔? (C/C++) (C) (Image Processing)與(原創) 如何使用ANSI C讀寫32位元的BMP圖檔? (C/C++) (C) (Image Processing)中,我們發現24位元與32位元BMP格式大致上相同,僅有些許的差異,是否能打造一個能同時讀寫24/32位元BMP圖檔的ANSI C程式?
24位元BMP與32位元BMP的差異
在(原創) 如何使用ANSI C讀寫32位元的BMP圖檔? (C/C++) (C) (Image Processing)有詳述兩種BMP的差異,更簡單的說,若我們能從BMP header中得知目前是24位元還是32位元BMP,然後動態的處理1個pixel該用3 byte還是4 byte處理,就能同時讀寫24/32位元BMP。
C語言 / Bmp24_32ReadWrite.c
2 (C) OOMusou 2007 http://oomusou.cnblogs.com
3
4 Filename : Bmp24_32ReadWrite.c
5 Compiler : Visual C++ 8.0 / ANSI C
6 Description : Demo the how to read and write bmp by standard library
7 Release : 05/18/2008 1.0
8 */
9 #include < stdio.h >
10 #include < stdlib.h >
11
12 int upside_down( const char * fname_s, const char * fname_t) {
13 FILE * fp_s = NULL; // source file handler
14 FILE * fp_t = NULL; // target file handler
15 unsigned int x,y; // for loop counter
16 unsigned int width, height; // image width, image height
17 unsigned char * image_s = NULL; // source image array
18 unsigned char * image_t = NULL; // target image array
19 unsigned char R, G, B; // color of R, G, B
20 unsigned int y_avg; // average of y axle
21 unsigned int y_t; // target of y axle
22
23 unsigned char header[ 54 ] = {
24 0x42 , // identity : B
25 0x4d , // identity : M
26 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , // file size
27 0 , 0 , // reserved1
28 0 , 0 , // reserved2
29 54 , 0 , 0 , 0 , // RGB data offset
30 40 , 0 , 0 , 0 , // struct BITMAPINFOHEADER size
31 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , // bmp width
32 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , // bmp height
33 1 , 0 , // planes
34 24 , 0 , // bit per pixel
35 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , // compression
36 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , // data size
37 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , // h resolution
38 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , // v resolution
39 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , // used colors
40 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 // important colors
41 };
42
43 unsigned int file_size; // file size
44 unsigned int rgb_raw_data_offset; // RGB raw data offset
45 unsigned short bit_per_pixel; // bit per pixel
46 unsigned short byte_per_pixel; // byte per pixel
47
48 fp_s = fopen(fname_s, " rb " );
49 if (fp_s == NULL) {
50 printf( " fopen fp_s error\n " );
51 return - 1 ;
52 }
53
54 // move offset to 10 to find rgb raw data offset
55 fseek(fp_s, 10 , SEEK_SET);
56 fread( & rgb_raw_data_offset, sizeof (unsigned int ), 1 , fp_s);
57 // move offset to 18 to get width & height;
58 fseek(fp_s, 18 , SEEK_SET);
59 fread( & width, sizeof (unsigned int ), 1 , fp_s);
60 fread( & height, sizeof (unsigned int ), 1 , fp_s);
61 // get bit per pixel
62 fseek(fp_s, 28 , SEEK_SET);
63 fread( & bit_per_pixel, sizeof (unsigned short ), 1 , fp_s);
64 byte_per_pixel = bit_per_pixel / 8 ;
65 // move offset to rgb_raw_data_offset to get RGB raw data
66 fseek(fp_s, rgb_raw_data_offset, SEEK_SET);
67
68 image_s = (unsigned char * )malloc((size_t)width * height * byte_per_pixel);
69 if (image_s == NULL) {
70 printf( " malloc images_s error\n " );
71 return - 1 ;
72 }
73
74 image_t = (unsigned char * )malloc((size_t)width * height * byte_per_pixel);
75 if (image_t == NULL) {
76 printf( " malloc image_t error\n " );
77 return - 1 ;
78 }
79
80 fread(image_s, sizeof (unsigned char ), (size_t)( long )width * height * byte_per_pixel, fp_s);
81
82 // vertical inverse algorithm
83 y_avg = 0 + (height - 1 );
84
85 for (y = 0 ; y != height; ++ y) {
86 for (x = 0 ; x != width; ++ x) {
87 R = * (image_s + byte_per_pixel * (width * y + x) + 2 );
88 G = * (image_s + byte_per_pixel * (width * y + x) + 1 );
89 B = * (image_s + byte_per_pixel * (width * y + x) + 0 );
90
91 y_t = y_avg - y;
92
93 * (image_t + byte_per_pixel * (width * y_t + x) + 2 ) = R;
94 * (image_t + byte_per_pixel * (width * y_t + x) + 1 ) = G;
95 * (image_t + byte_per_pixel * (width * y_t + x) + 0 ) = B;
96 }
97 }
98
99 // write to new bmp
100 fp_t = fopen(fname_t, " wb " );
101 if (fp_t == NULL) {
102 printf( " fopen fname_t error\n " );
103 return - 1 ;
104 }
105
106 // file size
107 file_size = width * height * byte_per_pixel + rgb_raw_data_offset;
108 header[ 2 ] = (unsigned char )(file_size & 0x000000ff );
109 header[ 3 ] = (file_size >> 8 ) & 0x000000ff ;
110 header[ 4 ] = (file_size >> 16 ) & 0x000000ff ;
111 header[ 5 ] = (file_size >> 24 ) & 0x000000ff ;
112
113 // width
114 header[ 18 ] = width & 0x000000ff ;
115 header[ 19 ] = (width >> 8 ) & 0x000000ff ;
116 header[ 20 ] = (width >> 16 ) & 0x000000ff ;
117 header[ 21 ] = (width >> 24 ) & 0x000000ff ;
118
119 // height
120 header[ 22 ] = height & 0x000000ff ;
121 header[ 23 ] = (height >> 8 ) & 0x000000ff ;
122 header[ 24 ] = (height >> 16 ) & 0x000000ff ;
123 header[ 25 ] = (height >> 24 ) & 0x000000ff ;
124
125 // bit per pixel
126 header[ 28 ] = bit_per_pixel;
127
128 // write header
129 fwrite(header, sizeof (unsigned char ), rgb_raw_data_offset, fp_t);
130 // write image
131 fwrite(image_t, sizeof (unsigned char ), (size_t)( long )width * height * byte_per_pixel, fp_t);
132
133 fclose(fp_s);
134 fclose(fp_t);
135
136 return 0 ;
137 }
138
139 int main() {
140 upside_down( " capture32.bmp " , " capture32_v.bmp " );
141 }
原圖(24位元)
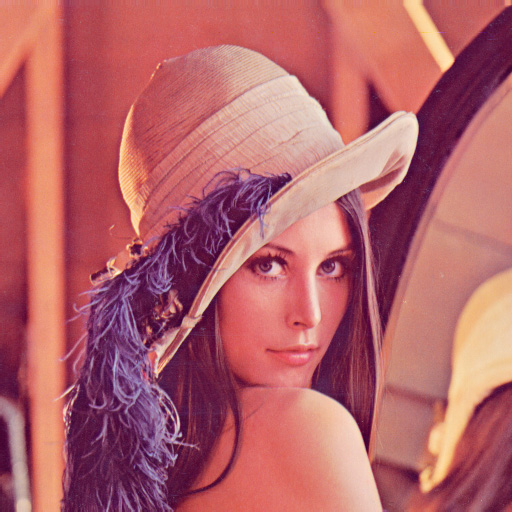

執行結果(24位元)
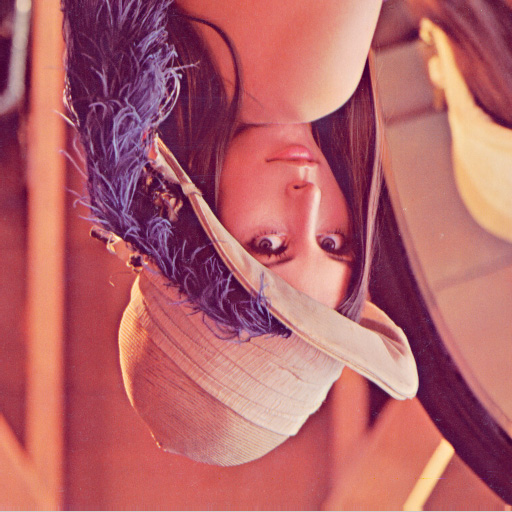

原圖(32位元)
執行結果(32位元)
34行
暫時將header設定為24位元,後面會依照實際狀況去修改。
45、46行
unsigned short byte_per_pixel; // byte per pixel

新增兩個變數,判斷bit per pixel與byte per pixel。
61行
fseek(fp_s, 28 , SEEK_SET);
fread( & bit_per_pixel, sizeof (unsigned short ), 1 , fp_s);
byte_per_pixel = bit_per_pixel / 8 ;
從BMP header讀出目前的圖片是24位元還是32位元,並計算出一個pixel是3 byte還是4 byte,之後就依照byte_per_pixel變數去做運算。
之後的程式,凡事遇到處理byte處,就不用寫死3 byte或4 byte了,完全依照byte_per_pixel決定,道理相同,我們就不在多做解釋。
125行
header[ 28 ] = bit_per_pixel;
從新依照實際的bit_per_pixel變數寫入文字檔,不再受限於24 bit。
Conclusion
之所以還分(原創) 如何使用ANSI C讀寫32位元的BMP圖檔? (C/C++) (C) (Image Processing)討論32位元BMP,實為了解說方便,在實務上,建議用此程式,可一次讀寫24/32位元BMP。
See Also
(原創) 如何使用ANSI C讀寫24位元的BMP圖檔? (C/C++) (C) (Image Processing)
(原創) 如何使用ANSI C讀寫32位元的BMP圖檔? (C/C++) (C) (Image Processing)
(原創) 如何將CMOS所擷取的影像傳到PC端? (IC Design) (DE2)
(原創) 如何使用ISO C++讀寫bmp圖檔? (C/C++) (Image Processing)
(原創) 如何使用C++/CLI读/写jpg檔? (C++/CLI)
(原創) 如何用程序的方式载入jpg图形文件? (C#/ASP.NET)
Reference
[1] swwuyam的BMP檔案格式
[2] Charles Petzold 1998, Programming Windows, Microsoft Press
瘋小貓的華麗冒險的點陣圖(Bitmap)檔案格式
BMP文件格式分析
賴岱佑、劉敏 2007,數位影像處理 技術手冊,文魁資訊
井上誠喜、八木申行、林 正樹、中須英輔、三古公二、奧井誠人 著 2006,吳上立,林宏燉 編譯,C語言數位影像處理,全華出版社




 本文介绍了一种使用ANSIC同时读写24位和32位BMP图像的方法,通过动态判断像素大小实现通用处理。文章详细展示了代码示例,包括读取BMP头信息、处理像素数据以及重新写入新图像。
本文介绍了一种使用ANSIC同时读写24位和32位BMP图像的方法,通过动态判断像素大小实现通用处理。文章详细展示了代码示例,包括读取BMP头信息、处理像素数据以及重新写入新图像。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








