一.基本概念及特点
1.概念-常用流

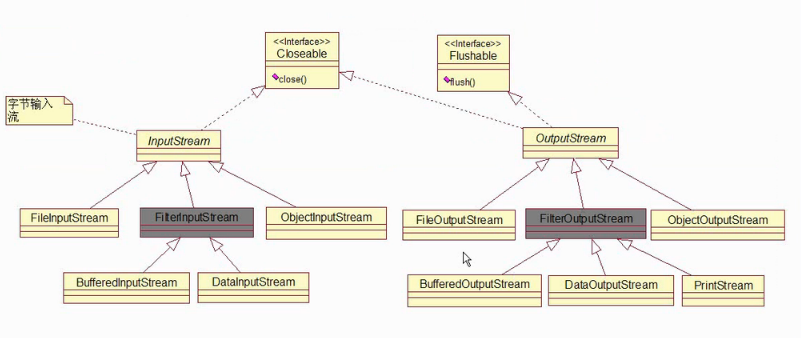
2.Input_OutputStream继承结构图
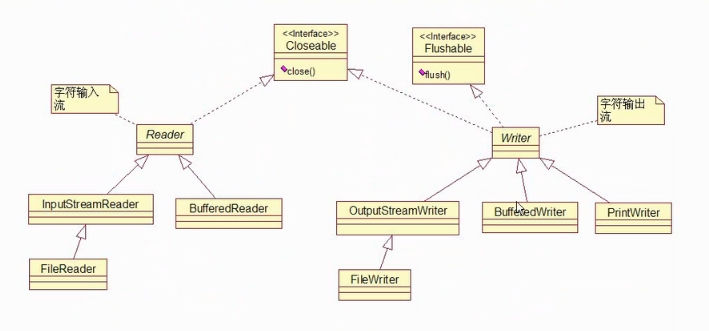
3.Reader_Writer继承结构图
二.基本操作
1.基本读操作- read()方法
例1.1:


1 /* 2 java.io.InputStream 3 java.io.FileInputStream 4 按照字节方式读取 5 */ 6 import java.io.*; 7 class FileInputStreamtest 8 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) 10 { 11 FileInputStream fis = null; 12 try{ 13 //文件路径 14 //String filePath="text1.txt";//相对路径,在当前路径下 15 // String filePath="D:\\Sourcecode\\Editplus\\java\\file\\text1.txt"; 16 String filePath="D:/Sourcecode/Editplus/java/file/text1.txt"; 17 fis = new FileInputStream(filePath); 18 //读 19 int i1 = fis.read();//以字节方式读,只能读取一个字母 20 System.out.println(i1);//输出字母对应的ASSICK值 21 22 }catch(FileNotFoundException e){ 23 e.printStackTrace(); 24 }catch(IOException e){ 25 e.printStackTrace(); 26 }finally{ 27 //保证流一定释放,使用try..catch语句 28 if(fis!=null){ 29 try{ 30 fis.close(); 31 }catch(IOException e){ 32 e.printStackTrace(); 33 } 34 } 35 36 } 37 } 38 }
例1.2:


1 import java.io.*; 2 class FileInputStreamtest02 3 { 4 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception 5 { 6 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("text1.txt"); 7 int temp =0; 8 while((temp=fis.read())!=-1){ 9 System.out.println(temp); 10 } 11 fis.close(); 12 } 13 }
例2.1:


1 /* 2 int read(byte[] bytes) 3 读取之前在内存中准备一个byte数组,每次读取多个字节存储到byte数组中,一次读取多个字节。 4 效率高 5 text1.txt文件中的内容为abcdefg 6 */ 7 import java.io.*; 8 class FileInputStreamtest03 9 { 10 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception 11 { 12 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("text1.txt"); 13 byte[] bytes = new byte[3];//每次读3个字节 14 15 int i1 = fis.read(bytes); 16 System.out.println(new String(bytes));//abc 17 int i2 = fis.read(bytes); 18 System.out.println(new String(bytes));//def 19 int i3 = fis.read(bytes); 20 System.out.println(new String(bytes));//gef 21 System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,i3));//g 22 int i4 = fis.read(bytes); 23 24 //int类型的i表示每次读取的字节数 25 System.out.println(i1);//3 26 System.out.println(i2);//3 27 System.out.println(i3);//1 28 System.out.println(i4);//-1 29 30 31 32 } 33 }
例2.2:


1 /* 2 循环读取 3 text1.txt文件中的内容为abcdefg 4 */ 5 import java.io.*; 6 class FileInputStreamtest04 7 { 8 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception 9 { 10 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("text1.txt"); 11 byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];//每次读3个字节 12 int temp =0; 13 while((temp=fis.read(bytes))!=-1){ 14 System.out.print(new String(bytes,0,temp)); 15 } 16 fis.close(); 17 } 18 }
2.available()方法和skip()方法
例:


1 import java.io.*; 2 /* 3 available()方法:返回流中剩余的字节数 4 skip(n)方法:跳过n个字节不读取 5 text1.txt文件中的内容为abcdefg 6 */ 7 class FileInputStreamtest05 8 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception 10 { 11 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("text1.txt"); 12 System.out.println(fis.available());//7 13 System.out.println(fis.read());//97 14 System.out.println(fis.available());//6 15 fis.skip(2);//跳过两个字节不读取 16 System.out.println(fis.read());//100 17 fis.close(); 18 19 } 20 }
3.写入数据的方法
例:FileOutputStream


1 /* 2 java.io.OutputStream 3 java.io.FileOutputStream;文件字节输出流 4 将计算机内存中的数据写入硬盘文件中 5 */ 6 import java.io.*; 7 class FileOutputStreamtest01 8 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) 10 { 11 FileOutputStream fos=null; 12 try{ 13 //fos= new FileOutputStream("text2.txt");//多次运行,会覆盖源文件内容 14 fos= new FileOutputStream("text2.txt",true);//追加写入 15 //写入 16 String msg = "Hello World"; 17 //将String转换成byte数组 18 byte[] bytes = msg.getBytes(); 19 fos.flush();//强制写入,保证数据完全写入硬盘,与、需要刷新 20 //fos.write(bytes);//强制写入,写入全部 21 fos.write(bytes,0,3);//写入3个,将byte数组部分写入 22 23 }catch(Exception e){ 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 }finally{ 26 if(fos!=null){ 27 try{ 28 fos.close(); 29 }catch(Exception e){ 30 e.printStackTrace(); 31 } 32 } 33 34 } 35 } 36 }
4.文件的复制粘贴
例4.1:FileInputStream FileOutputStream


1 /* 2 文件的复制粘贴 3 */ 4 import java.io.*; 5 class Copy01 6 { 7 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception 8 { 9 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("text1.txt"); 10 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("text2.txt"); 11 //读,写 12 byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; 13 int temp = 0; 14 while((temp=fis.read(bytes))!=-1){ 15 fos.write(bytes,0,temp); 16 } 17 fis.close(); 18 fos.close(); 19 20 } 21 }
例4.2-fileReader,FileWriter


1 /* 2 文件复制,只能复制纯文本文件 3 */ 4 import java.io.*; 5 class Copy02 6 { 7 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception 8 { 9 FileReader fr = new FileReader("text1.txt");//一个已经存在的文件 10 FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("text4.txt");//运行后复制出一个文件 11 char [] chars = new char[1024]; 12 int temp =0; 13 while((temp=fr.read(chars)) != -1){ 14 fw.write(chars,0,temp); 15 } 16 fw.flush(); 17 fr.close(); 18 fw.close(); 19 } 20 }
5.FileWriter()方法写入文件
例:


1 /* 2 java.io.Writer; 3 java.io.OutputStream;转换流 4 java.io.FileWriter文件字符输出流 5 */ 6 import java.io.*; 7 class FileWritertest01 8 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception 10 { 11 FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("text3.txt",true); 12 fw.write("写入文件");//直接写入字符串 13 char [] chars = {'写','入','文','件','{','。','、',}; 14 fw.write(chars,0,6); 15 fw.flush(); 16 fw.close(); 17 } 18 } 19 /* 20 运行结果: 21 写入文件写入文件{。 22 */
6.BufferedReader带有缓冲区的字符输入流
例6.1


1 /* 2 readLine() 方法一次读取一行文本 3 */ 4 import java.io.*; 5 class BufferedReadertest01 6 { 7 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception 8 { 9 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("BufferedReadertest01.java")); 10 String temp = null; 11 while((temp=br.readLine())!=null){ 12 System.out.println(temp); 13 } 14 br.close(); 15 } 16 }
例6.2


1 /* 2 readLine() 方法一次读取一行文本 3 */ 4 import java.io.*; 5 class BufferedReadertest02 6 { 7 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception 8 { 9 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("BufferedReadertest01.java");//文件字节输入流 10 InputStreamReader brs = new InputStreamReader(fis); //将字节流转换成字符流 11 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(brs);//brs是字符流 12 //将上面的语句合并 13 // BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("BufferedReadertest01.java"))); 14 String temp = null; 15 while((temp=br.readLine())!=null){ 16 System.out.println(temp); 17 } 18 br.close(); 19 } 20 }
三.序列化和反序列化-对象流
1.序列化-ObjectOutputStream
序列化就是将堆中的Java对象存入到硬盘中。
例3.1.1:


1 import java.io.Serializable;//可序列化的,没有任何方法的标识接口 2 class User implements Serializable 3 { 4 String name; 5 User(String name){ 6 this.name = name; 7 } 8 public String toString(){ 9 return "User[name="+name+"]"; 10 } 11 }
注: User 实现了 Serializable 接口, JVM会给该类添加自动一个属性:序列化版本号。(可以自定义一个序列化版本号,则系统不会再成序列化版本号,
也不会出现版本号不相同的情况)
例:自定义序列化版本号
static final long seriaVersionUID="xxxxxxxxx";
如果不让某个属性参与序列化,可以使用transient关键字修饰;
如:
transient String name;
例3.1.2:


1 /* 2 java.io.ObjectOutputStream;序列化Java对象到硬盘 3 java.io.ObjectInputStream;将硬盘中的数据反序列化到jvm内存 4 */ 5 import java.io.*; 6 class ObjectOutputStreamtest01 7 { 8 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception 9 { 10 //创建Java对象 11 User u1 = new User("Java对象"); 12 //创建输出流(序列化流)jvm中的java对象状态保存到硬盘中 13 ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("text6.txt")); 14 //写 15 oos.writeObject(u1); 16 oos.flush(); 17 oos.close(); 18 } 19 }
2.反序列化-ObjectInputStream
反序列化就是将硬盘中的对象恢复到内存中。
例:


1 /* 2 反序列化 3 */ 4 import java.io.*; 5 class ObjectInputStreamtest01 6 { 7 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception 8 { 9 //创建反序列化流 10 ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("text6.txt")); 11 //反序列化 12 Object o = ois.readObject(); 13 System.out.println(o); 14 ois.close(); 15 } 16 } 17 /* 18 User[name=Java对象] 19 请按任意键继续. . . 20 */
四.File
1.特点:
Java.io.File;File类和流无关,不能通过该类完成文件的读和写,File是文件和目录路径名的抽象表示形式,File代表的是硬盘上的文件夹和文件名。
2.常用方法:
例4.2.1:


1 import java.io.*; 2 /* 3 判断指定路径或文件是否存在,不存在则创建 4 */ 5 class Filetest01 6 { 7 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception 8 { 9 //相对路径 10 File f1 = new File("text1.txt"); 11 //绝对路径 12 File f2 = new File("D:\\Sourcecode\\Editplus\\java"); 13 14 System.out.println(f1.exists());//true 15 System.out.println(f2.exists());//true 16 17 File f3 = new File("D:\\Sourcecode\\Editplus\\java\\AA"); 18 System.out.println(f3.exists());//false 19 //如果不存在则创建 20 if(!f3.exists()){ 21 //创建目录 22 //f3.mkdir(); 23 //创建文件 24 f3.createNewFile(); 25 } 26 File f4 = new File("D:/a/b/c"); 27 if(!f4.exists()){ 28 //创建多重目录 29 f4.mkdirs(); 30 } 31 } 32 }
.




 本文详细介绍了Java中的IO流概念、基本操作,包括FileInputStream、FileOutputStream等类的使用方法,并探讨了序列化与反序列化的实现过程。
本文详细介绍了Java中的IO流概念、基本操作,包括FileInputStream、FileOutputStream等类的使用方法,并探讨了序列化与反序列化的实现过程。
















 10万+
10万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








