使用场景: app显示数据,一般步骤是:查找数据,异步加载,更新UI; 然而当数据源有更新时怎么及时更新到界面上时,可能需要在Activity或Fragment的相应生命周期中及时处理数据的变化,有时可能会造成额外的开销,有时可能是极为复杂的,耗时且容易出问题的;有时甚至仅仅是查找数据这块就需要耗费我们大部分精力,anr或其他异常问题以及采用查找的机制、性能常常困扰着我们(从网络,数据库,ContentProvider和Files加载数据,究竟选择 thread + handler,还是AsyncTask,抑或是下面这个?)
Google在android3.0之后提供了Loader机制(3.0之前有support包),极大方便我们的开发;
| Loader简介 关于Loader,查看源码及官方文档可知, A class that performs asynchronous loading of data. While Loaders are active* they should monitor the source of their data and deliver new results when the contents* change Loader 是用来实现异步加载数据的类。当Loaders处于活动状态时,将会监听数据源的变化并且当内容发生改变时传递新的结果; Loader的衍生有以下这些:
public class CursorLoader extends AsyncTaskLoader<Cursor> { public abstract class AsyncTaskLoader<D> extends Loader<D> { public class Loader<D> { Loader工作原理图如下: 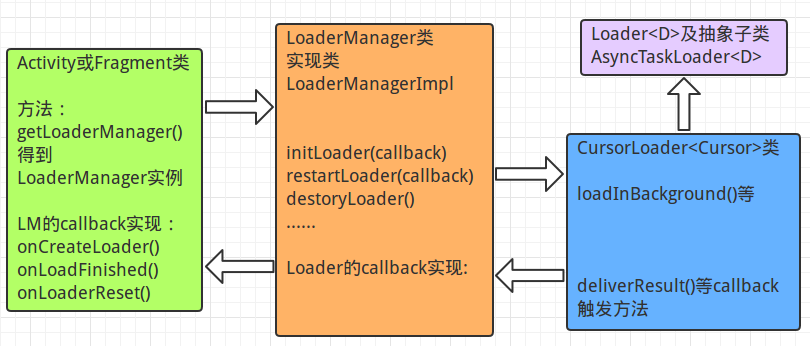
简要说明下,首先在Activity或Fragment的相应生命周期中(分别是onCreate和onActivityCreated)得到LoaderManager实例,并利用LoaderManager实例初始化Loader(装载器),通过实现LoaderManager的LoaderCallback接口,在Loader相应生命周期进行处理,而此时Loader的生命周期即与Activity或Fragment进行关联,并实时监听各个生命周期,在AsyncTaskLoader或CursorLoader中将会调用后台加载数据方法,并在加载完数据或数据发生变化,甚至是Loader被重置发生变化时及时在相应回调方法进行处理,此时一个加载数据的完整流程完成;
Loader的生命周期相关:
- onStartLoading(),
- onStopLoading(),
- onForceLoad(),
- onReset().
- 以及其他
LoaderManager.LoaderCallback回调相关:
- onCreateLoader, Instantiate and return a new Loader for the given ID. 根据initLoader()方法中制定的id重用或重建一个Loader,因此只有在Loader不存在的情况下才会调用 -onLoadFinished Called when a previously created loader has finished its load. 之前创建的Loader完成了加载操作时调用
- onLoaderReset Called when a previously created loader is being reset, and thus making its data unavailable. 之前创建的Loader被重置时调用,此时它的数据也变得不可用;
| Loader源码解读 后续添加,此篇注重Loader的理解和使用,下面是两个官方实例,有助于对Loader的理解,当然更深入的理解还是要深入源码进行研究; 如Loader基于Observer pattern的设计等,对深入的理解还是很有帮助的;
| 实例1
来自:https://developer.android.com/reference/android/app/LoaderManager.html, 功能:here is the full implementation of a Fragment that displays a ListView containing the results of a query against the contacts content provider. It uses a CursorLoader to manage the query on the provider. 一个Fragment实例,它展示了一个包含ContentProvider加载联系人数据的查询结果的ListView。它使用了一个CursorLoader来管理provider上的查询操作;
public static class CursorLoaderListFragment extends ListFragment
implements OnQueryTextListener, OnCloseListener,
LoaderManager.LoaderCallbacks<Cursor> {
// This is the Adapter being used to display the list's data.
SimpleCursorAdapter mAdapter;
// The SearchView for doing filtering.
SearchView mSearchView;
// If non-null, this is the current filter the user has provided.
String mCurFilter;
@Override public void onActivityCreated(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState);
// Give some text to display if there is no data. In a real
// application this would come from a resource.
setEmptyText("No phone numbers");
// We have a menu item to show in action bar.
setHasOptionsMenu(true);
// Create an empty adapter we will use to display the loaded data.
mAdapter = new SimpleCursorAdapter(getActivity(),
android.R.layout.simple_list_item_2, null,
new String[] { Contacts.DISPLAY_NAME, Contacts.CONTACT_STATUS },
new int[] { android.R.id.text1, android.R.id.text2 }, 0);
setListAdapter(mAdapter);
// Start out with a progress indicator.
setListShown(false);
// Prepare the loader. Either re-connect with an existing one,
// or start a new one.
getLoaderManager().initLoader(0, null, this);
}
public static class MySearchView extends SearchView {
public MySearchView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
// The normal SearchView doesn't clear its search text when
// collapsed, so we will do this for it.
@Override
public void onActionViewCollapsed() {
setQuery("", false);
super.onActionViewCollapsed();
}
}
@Override public void onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu, MenuInflater inflater) {
// Place an action bar item for searching.
MenuItem item = menu.add("Search");
item.setIcon(android.R.drawable.ic_menu_search);
item.setShowAsAction(MenuItem.SHOW_AS_ACTION_IF_ROOM
| MenuItem.SHOW_AS_ACTION_COLLAPSE_ACTION_VIEW);
mSearchView = new MySearchView(getActivity());
mSearchView.setOnQueryTextListener(this);
mSearchView.setOnCloseListener(this);
mSearchView.setIconifiedByDefault(true);
item.setActionView(mSearchView);
}
public boolean onQueryTextChange(String newText) {
// Called when the action bar search text has changed. Update
// the search filter, and restart the loader to do a new query
// with this filter.
String newFilter = !TextUtils.isEmpty(newText) ? newText : null;
// Don't do anything if the filter hasn't actually changed.
// Prevents restarting the loader when restoring state.
if (mCurFilter == null && newFilter == null) {
return true;
}
if (mCurFilter != null && mCurFilter.equals(newFilter)) {
return true;
}
mCurFilter = newFilter;
getLoaderManager().restartLoader(0, null, this);
return true;
}
@Override public boolean onQueryTextSubmit(String query) {
// Don't care about this.
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean onClose() {
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(mSearchView.getQuery())) {
mSearchView.setQuery(null, true);
}
return true;
}
@Override public void onListItemClick(ListView l, View v, int position, long id) {
// Insert desired behavior here.
Log.i("FragmentComplexList", "Item clicked: " + id);
}
// These are the Contacts rows that we will retrieve.
static final String[] CONTACTS_SUMMARY_PROJECTION = new String[] {
Contacts._ID,
Contacts.DISPLAY_NAME,
Contacts.CONTACT_STATUS,
Contacts.CONTACT_PRESENCE,
Contacts.PHOTO_ID,
Contacts.LOOKUP_KEY,
};
public Loader<Cursor> onCreateLoader(int id, Bundle args) {
// This is called when a new Loader needs to be created. This
// sample only has one Loader, so we don't care about the ID.
// First, pick the base URI to use depending on whether we are
// currently filtering.
Uri baseUri;
if (mCurFilter != null) {
baseUri = Uri.withAppendedPath(Contacts.CONTENT_FILTER_URI,
Uri.encode(mCurFilter));
} else {
baseUri = Contacts.CONTENT_URI;
}
// Now create and return a CursorLoader that will take care of
// creating a Cursor for the data being displayed.
String select = "((" + Contacts.DISPLAY_NAME + " NOTNULL) AND ("
+ Contacts.HAS_PHONE_NUMBER + "=1) AND ("
+ Contacts.DISPLAY_NAME + " != '' ))";
return new CursorLoader(getActivity(), baseUri,
CONTACTS_SUMMARY_PROJECTION, select, null,
Contacts.DISPLAY_NAME + " COLLATE LOCALIZED ASC");
}
public void onLoadFinished(Loader<Cursor> loader, Cursor data) {
// Swap the new cursor in. (The framework will take care of closing the
// old cursor once we return.)
mAdapter.swapCursor(data);
// The list should now be shown.
if (isResumed()) {
setListShown(true);
} else {
setListShownNoAnimation(true);
}
}
public void onLoaderReset(Loader<Cursor> loader) {
// This is called when the last Cursor provided to onLoadFinished()
// above is about to be closed. We need to make sure we are no
// longer using it.
mAdapter.swapCursor(null);
}
}
该实例,使用了CursorLoader从ContentProvider中查找联系人数据并实时更新; 需要注意的是,SearchView 的OnQueryTextChange方法调用了loaderManager,并执行了loaderManager的restartLoader方法,它对Loader的生命周期的影响在于,已存在的Loader需要重启并使用新的过滤条件重新查询数据;
| 实例2 来自:https://developer.android.com/reference/android/content/AsyncTaskLoader.html 功能:Here is an example implementation of an AsyncTaskLoader subclass that loads the currently installed applications from the package manager. This implementation takes care of retrieving the application labels and sorting its result set from them, monitoring for changes to the installed applications, and rebuilding the list when a change in configuration requires this (such as a locale change). 下面这个例子使用了一个AsyncTaskLoader来从packageManager中加载当前手机上安装的应用。能够获取应用名称,排序,监听安装应用的变化以及党配置变化需要时修改应用列表等;
/**
* This class holds the per-item data in our Loader.
*/
public static class AppEntry {
public AppEntry(AppListLoader loader, ApplicationInfo info) {
mLoader = loader;
mInfo = info;
mApkFile = new File(info.sourceDir);
}
public ApplicationInfo getApplicationInfo() {
return mInfo;
}
public String getLabel() {
return mLabel;
}
public Drawable getIcon() {
if (mIcon == null) {
if (mApkFile.exists()) {
mIcon = mInfo.loadIcon(mLoader.mPm);
return mIcon;
} else {
mMounted = false;
}
} else if (!mMounted) {
// If the app wasn't mounted but is now mounted, reload
// its icon.
if (mApkFile.exists()) {
mMounted = true;
mIcon = mInfo.loadIcon(mLoader.mPm);
return mIcon;
}
} else {
return mIcon;
}
return mLoader.getContext().getResources().getDrawable(
android.R.drawable.sym_def_app_icon);
}
@Override public String toString() {
return mLabel;
}
void loadLabel(Context context) {
if (mLabel == null || !mMounted) {
if (!mApkFile.exists()) {
mMounted = false;
mLabel = mInfo.packageName;
} else {
mMounted = true;
CharSequence label = mInfo.loadLabel(context.getPackageManager());
mLabel = label != null ? label.toString() : mInfo.packageName;
}
}
}
private final AppListLoader mLoader;
private final ApplicationInfo mInfo;
private final File mApkFile;
private String mLabel;
private Drawable mIcon;
private boolean mMounted;
}
/**
* Perform alphabetical comparison of application entry objects.
*/
public static final Comparator<AppEntry> ALPHA_COMPARATOR = new Comparator<AppEntry>() {
private final Collator sCollator = Collator.getInstance();
@Override
public int compare(AppEntry object1, AppEntry object2) {
return sCollator.compare(object1.getLabel(), object2.getLabel());
}
};
/**
* Helper for determining if the configuration has changed in an interesting
* way so we need to rebuild the app list.
*/
public static class InterestingConfigChanges {
final Configuration mLastConfiguration = new Configuration();
int mLastDensity;
boolean applyNewConfig(Resources res) {
int configChanges = mLastConfiguration.updateFrom(res.getConfiguration());
boolean densityChanged = mLastDensity != res.getDisplayMetrics().densityDpi;
if (densityChanged || (configChanges&(ActivityInfo.CONFIG_LOCALE
|ActivityInfo.CONFIG_UI_MODE|ActivityInfo.CONFIG_SCREEN_LAYOUT)) != 0) {
mLastDensity = res.getDisplayMetrics().densityDpi;
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
/**
* Helper class to look for interesting changes to the installed apps
* so that the loader can be updated.
*/
public static class PackageIntentReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
final AppListLoader mLoader;
public PackageIntentReceiver(AppListLoader loader) {
mLoader = loader;
IntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter(Intent.ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED);
filter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_PACKAGE_REMOVED);
filter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_PACKAGE_CHANGED);
filter.addDataScheme("package");
mLoader.getContext().registerReceiver(this, filter);
// Register for events related to sdcard installation.
IntentFilter sdFilter = new IntentFilter();
sdFilter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_EXTERNAL_APPLICATIONS_AVAILABLE);
sdFilter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_EXTERNAL_APPLICATIONS_UNAVAILABLE);
mLoader.getContext().registerReceiver(this, sdFilter);
}
@Override public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
// Tell the loader about the change.
mLoader.onContentChanged();
}
}
/**
* A custom Loader that loads all of the installed applications.
*/
public static class AppListLoader extends AsyncTaskLoader<List<AppEntry>> {
final InterestingConfigChanges mLastConfig = new InterestingConfigChanges();
final PackageManager mPm;
List<AppEntry> mApps;
PackageIntentReceiver mPackageObserver;
public AppListLoader(Context context) {
super(context);
// Retrieve the package manager for later use; note we don't
// use 'context' directly but instead the save global application
// context returned by getContext().
mPm = getContext().getPackageManager();
}
/**
* This is where the bulk of our work is done. This function is
* called in a background thread and should generate a new set of
* data to be published by the loader.
*/
@Override public List<AppEntry> loadInBackground() {
// Retrieve all known applications.
List<ApplicationInfo> apps = mPm.getInstalledApplications(
PackageManager.GET_UNINSTALLED_PACKAGES |
PackageManager.GET_DISABLED_COMPONENTS);
if (apps == null) {
apps = new ArrayList<ApplicationInfo>();
}
final Context context = getContext();
// Create corresponding array of entries and load their labels.
List<AppEntry> entries = new ArrayList<AppEntry>(apps.size());
for (int i=0; i<apps.size(); i++) {
AppEntry entry = new AppEntry(this, apps.get(i));
entry.loadLabel(context);
entries.add(entry);
}
// Sort the list.
Collections.sort(entries, ALPHA_COMPARATOR);
// Done!
return entries;
}
/**
* Called when there is new data to deliver to the client. The
* super class will take care of delivering it; the implementation
* here just adds a little more logic.
*/
@Override public void deliverResult(List<AppEntry> apps) {
if (isReset()) {
// An async query came in while the loader is stopped. We
// don't need the result.
if (apps != null) {
onReleaseResources(apps);
}
}
List<AppEntry> oldApps = mApps;
mApps = apps;
if (isStarted()) {
// If the Loader is currently started, we can immediately
// deliver its results.
super.deliverResult(apps);
}
// At this point we can release the resources associated with
// 'oldApps' if needed; now that the new result is delivered we
// know that it is no longer in use.
if (oldApps != null) {
onReleaseResources(oldApps);
}
}
/**
* Handles a request to start the Loader.
*/
@Override protected void onStartLoading() {
if (mApps != null) {
// If we currently have a result available, deliver it
// immediately.
deliverResult(mApps);
}
// Start watching for changes in the app data.
if (mPackageObserver == null) {
mPackageObserver = new PackageIntentReceiver(this);
}
// Has something interesting in the configuration changed since we
// last built the app list?
boolean configChange = mLastConfig.applyNewConfig(getContext().getResources());
if (takeContentChanged() || mApps == null || configChange) {
// If the data has changed since the last time it was loaded
// or is not currently available, start a load.
forceLoad();
}
}
/**
* Handles a request to stop the Loader.
*/
@Override protected void onStopLoading() {
// Attempt to cancel the current load task if possible.
cancelLoad();
}
/**
* Handles a request to cancel a load.
*/
@Override public void onCanceled(List<AppEntry> apps) {
super.onCanceled(apps);
// At this point we can release the resources associated with 'apps'
// if needed.
onReleaseResources(apps);
}
/**
* Handles a request to completely reset the Loader.
*/
@Override protected void onReset() {
super.onReset();
// Ensure the loader is stopped
onStopLoading();
// At this point we can release the resources associated with 'apps'
// if needed.
if (mApps != null) {
onReleaseResources(mApps);
mApps = null;
}
// Stop monitoring for changes.
if (mPackageObserver != null) {
getContext().unregisterReceiver(mPackageObserver);
mPackageObserver = null;
}
}
/**
* Helper function to take care of releasing resources associated
* with an actively loaded data set.
*/
protected void onReleaseResources(List<AppEntry> apps) {
// For a simple List<> there is nothing to do. For something
// like a Cursor, we would close it here.
}
}
An example implementation of a fragment that uses the above loader to show the currently installed applications in a list is below.
public static class AppListAdapter extends ArrayAdapter<AppEntry> {
private final LayoutInflater mInflater;
public AppListAdapter(Context context) {
super(context, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_2);
mInflater = (LayoutInflater)context.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
}
public void setData(List<AppEntry> data) {
clear();
if (data != null) {
addAll(data);
}
}
/**
* Populate new items in the list.
*/
@Override public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
View view;
if (convertView == null) {
view = mInflater.inflate(R.layout.list_item_icon_text, parent, false);
} else {
view = convertView;
}
AppEntry item = getItem(position);
((ImageView)view.findViewById(R.id.icon)).setImageDrawable(item.getIcon());
((TextView)view.findViewById(R.id.text)).setText(item.getLabel());
return view;
}
}
public static class AppListFragment extends ListFragment
implements OnQueryTextListener, OnCloseListener,
LoaderManager.LoaderCallbacks<List<AppEntry>> {
// This is the Adapter being used to display the list's data.
AppListAdapter mAdapter;
// The SearchView for doing filtering.
SearchView mSearchView;
// If non-null, this is the current filter the user has provided.
String mCurFilter;
@Override public void onActivityCreated(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState);
// Give some text to display if there is no data. In a real
// application this would come from a resource.
setEmptyText("No applications");
// We have a menu item to show in action bar.
setHasOptionsMenu(true);
// Create an empty adapter we will use to display the loaded data.
mAdapter = new AppListAdapter(getActivity());
setListAdapter(mAdapter);
// Start out with a progress indicator.
setListShown(false);
// Prepare the loader. Either re-connect with an existing one,
// or start a new one.
getLoaderManager().initLoader(0, null, this);
}
public static class MySearchView extends SearchView {
public MySearchView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
// The normal SearchView doesn't clear its search text when
// collapsed, so we will do this for it.
@Override
public void onActionViewCollapsed() {
setQuery("", false);
super.onActionViewCollapsed();
}
}
@Override public void onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu, MenuInflater inflater) {
// Place an action bar item for searching.
MenuItem item = menu.add("Search");
item.setIcon(android.R.drawable.ic_menu_search);
item.setShowAsAction(MenuItem.SHOW_AS_ACTION_IF_ROOM
| MenuItem.SHOW_AS_ACTION_COLLAPSE_ACTION_VIEW);
mSearchView = new MySearchView(getActivity());
mSearchView.setOnQueryTextListener(this);
mSearchView.setOnCloseListener(this);
mSearchView.setIconifiedByDefault(true);
item.setActionView(mSearchView);
}
@Override public boolean onQueryTextChange(String newText) {
// Called when the action bar search text has changed. Since this
// is a simple array adapter, we can just have it do the filtering.
mCurFilter = !TextUtils.isEmpty(newText) ? newText : null;
mAdapter.getFilter().filter(mCurFilter);
return true;
}
@Override public boolean onQueryTextSubmit(String query) {
// Don't care about this.
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean onClose() {
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(mSearchView.getQuery())) {
mSearchView.setQuery(null, true);
}
return true;
}
@Override public void onListItemClick(ListView l, View v, int position, long id) {
// Insert desired behavior here.
Log.i("LoaderCustom", "Item clicked: " + id);
}
@Override public Loader<List<AppEntry>> onCreateLoader(int id, Bundle args) {
// This is called when a new Loader needs to be created. This
// sample only has one Loader with no arguments, so it is simple.
return new AppListLoader(getActivity());
}
@Override public void onLoadFinished(Loader<List<AppEntry>> loader, List<AppEntry> data) {
// Set the new data in the adapter.
mAdapter.setData(data);
// The list should now be shown.
if (isResumed()) {
setListShown(true);
} else {
setListShownNoAnimation(true);
}
}
@Override public void onLoaderReset(Loader<List<AppEntry>> loader) {
// Clear the data in the adapter.
mAdapter.setData(null);
}
}
上述实例,自定义了一个继承AsyncTaskLoader的装载器,用来加载手机上的应用列表,通过监听广播 PackageIntentReceiver的变化捕获系统app的数据,并自定义一个 InterestingConfigChanges来监听用户自定义配置的变化。 需要注意的是 自定义的Loader,onReleaseResources方法,需要及时释放资源,比如: // For a simple List<> there is nothing to do. For something // like a Cursor, we would close it here. 如果数据源是这样的 :List<>,不用做任何操作;如果是Cursor,需要在这里close掉;比如实例1中的simpleCursorAdapter的swapCursor方法,传入了一个null, // This is called when the last Cursor provided to onLoadFinished() // above is about to be closed. We need to make sure we are no // longer using it. mAdapter.swapCursor(null); | 优化 可参考例子:LoaderThrottle, https://github.com/appium/android-apidemos/blob/master/src/io/appium/android/apis/app/LoaderThrottle.java
| 参考
官方文档(请自备梯子):
http://developer.android.com/intl/zh-cn/reference/android/app/LoaderManager.html
http://developer.android.com/intl/zh-cn/reference/android/content/AsyncTaskLoader.html
http://developer.android.com/intl/zh-cn/guide/components/loaders.html
坚持原创技术分享,您的支持将鼓励我继续创作!







 本文深入解析Android中的Loader机制,包括其工作原理、生命周期及其三种主要类型:Loader、AsyncTaskLoader和CursorLoader。并通过两个官方实例展示了如何使用Loader来实现异步数据加载,以及如何处理数据变化,特别关注自定义Loader的实现。
本文深入解析Android中的Loader机制,包括其工作原理、生命周期及其三种主要类型:Loader、AsyncTaskLoader和CursorLoader。并通过两个官方实例展示了如何使用Loader来实现异步数据加载,以及如何处理数据变化,特别关注自定义Loader的实现。

















 558
558

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








