Naive Bayes method is based on applying Bayes’s theorm with the “naive” assumption of independence between features![]()
Gaussian Naive Bayes assumes the likelihood is gaussian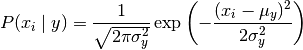
from __future__ import division
import numpy as np
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
from scipy.stats import norm
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from pylab import scatter, show, legend, xlabel, ylabel
data = load_iris()
X = data.data
y = data.target
def visualize(X, y):
ys = np.unique(y)
for v in ys:
pos = np.where(y == v)
scatter(X[pos, 0], X[pos, 1])
show()
visualize(X, y)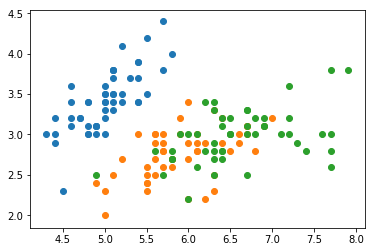
class myGaussianNB:
def fit(self, X, y):
self.pys = {}
for v in np.unique(y):
self.pys[v] = y[y==v].shape[0] / y.shape[0]
self.pxys = {}
for v in np.unique(y):
for i in range(X.shape[1]):
xs = X[y==v]
x_mean = np.mean(xs[:,i])
x_std = np.std(xs[:,i])
self.pxys[(v,i)] = (x_mean, x_std)
def predict_single(self, x):
ps = [ self.pys[v] * np.sum([ norm.pdf(x[i], self.pxys[(v,i)][0], self.pxys[(v,i)][1]) for i in range(X.shape[1])]) for v in np.unique(y)]
return np.unique(y)[np.argmax(ps)]
def predict(self, X):
return np.array(map(self.predict_single, X))
def score(self, X, y):
res = self.predict(X)
return np.count_nonzero((res == y) == True) / y.shape[0]
nb = myGaussianNB()
nb.fit(X, y)
print 'score:',nb.score(X, y)
#score: 0.953333333333
 朴素贝叶斯分类器
朴素贝叶斯分类器







 本文介绍了一种基于高斯分布的朴素贝叶斯分类器实现,并使用鸢尾花数据集进行演示。该分类器假设特征间相互独立,并采用高斯分布估计特征的似然概率。
本文介绍了一种基于高斯分布的朴素贝叶斯分类器实现,并使用鸢尾花数据集进行演示。该分类器假设特征间相互独立,并采用高斯分布估计特征的似然概率。

















 628
628

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








