heap definition
- completely balanced binary tree.
- the value of each node >= each of the node's children.
heap data structure
completely balanced binary tree implemented by an array
- the root is stored in A[1]
- the parent of A[i] is A[floor(i/2)]
- the left child of A[i] is A[2*i]
- the right child of A[i] is A[2*i +1]
- the node in the far right of the bottom level is stored in A[n]
- if 2*i +1 >n, then the node does not have a right child
heapify
def heapify(r): """pre-cond: the balanced binary tree rooted at A[r] is such that its left and right subtrees are heaps.""" """post-cond:its values are rearranged in place to make it complete heap. """running time: the height of the tree""" i=r; while(true): """loop-invariant: the entire tree rooted at A[r] is a heap except that node i might not greater or equal to both of its children. As well, the value of i's parent is at least the value of i and i's children.""" if(i is leaf): EXIT; elseif(left(i) ==max(A[i],A[leftchild[i]],A[rightchild[i]]): swap(A[i],A[leftchild[i]]); i=leftchild[i]; elseif(right(i) ==max(A[i],A[leftchild[i]],A[rightchild[i]]): swap(A[i],A[rightchild[i]]); i=rightchild[i]; else(A[i] ==max(A[i],A[leftchild[i]],A[rightchild[i]]): EXIT;
OR
pre-cond: left and right child are heapified
post-cond: the whole tree is heapified
algorithm:
heapify(r){
if(r is leaf): exit;
//
if(max(r,left,right)==r): exit;
else if(max(r,left,right)==left): swap(r,left); heapify(left);
else:swap(r,right):heapify(right);
}
T(n)=T(n/2)+O(1)=T(n/4)+2O(1)=T(n/8)+3O(1)=T(1)+lognO(1)=O(logn)
make heap
- recursive way
get help from friends:
T(n)=2T(n/2)+logn=4(2T(n/4)+log(n/2))+logn=O(n)
- loop
from k=n/2,n/2-1,n/2-2,...2,1
heapify(k)
Time: induction as
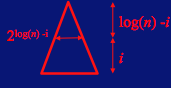
the number of subtrees of height i is 2logn-i
because each such tree has its root as level(logn-i) in the tree.
each take O(i) to heapify.
T(n) = Σlogni=1 (2logn-i)i
The sum is geometric.
T(n)=O(n)
selection sort==> heap sort
largest i values are sorted on side.
remaining values are off to side.
max is easier to find if a heap.
largest i values are sorted on side and remaining values are in a heap.
heap-sort loop invariant:
the n-i largest elements have been removed and are sorted in A[i+1,n] and the remaining i elements form a heap in A[1,i].
running time:
make heap takes O(n) time.
heapifing a tree of size i takes log(i);
T(n) = O(n) + Σ1i=n logi
the sum is arithmetic.
T(n) = n * maximum value = O(nlogn).




 本文深入探讨了堆数据结构及其在完全二叉树中的实现,包括堆排序算法的具体步骤与时间复杂度分析。通过递归与循环方式实现堆排序,并解析堆的构建与调整过程。
本文深入探讨了堆数据结构及其在完全二叉树中的实现,包括堆排序算法的具体步骤与时间复杂度分析。通过递归与循环方式实现堆排序,并解析堆的构建与调整过程。
















 1559
1559

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








