一、idr构建的结构可以看成是32叉树, 它需要用到2个结构体:
struct idr { struct idr_layer __rcu *top; /*根节点*/ struct idr_layer *id_free; /*空闲节点*/ int layers; /*树的高度*/ int id_free_cnt; /*空闲节点数*/ spinlock_t lock; }; struct idr_layer { unsigned long bitmap; /*位图*/ struct idr_layer __rcu *ary[1<<IDR_BITS]; /*孩子节点或者地址数据*/ int count; /*ary已存放数*/ int layer; /* 相对叶子节点的高度 */ struct rcu_head rcu_head; };
二、idr初始化:


1 #define IDR_INIT(name) \ 2 { \ 3 .top = NULL, \ 4 .id_free = NULL, \ 5 .layers = 0, \ 6 .id_free_cnt = 0, \ 7 .lock = __SPIN_LOCK_UNLOCKED(name.lock), \ 8 } 9 #define DEFINE_IDR(name) struct idr name = IDR_INIT(name)

三、分配空闲节点


1 /*创建多个idr_layer结构,组成一条链,存入idr->id_free区域, 区域含有 2 *IDR_FREE_MAX个这样的结构, id_free_cnt = IDR_FREE_MAX 3 */ 4 5 int idr_pre_get(struct idr *idp, gfp_t gfp_mask) 6 { 7 while (idp->id_free_cnt < IDR_FREE_MAX) { 8 struct idr_layer *new; 9 new = kmem_cache_zalloc(idr_layer_cache, gfp_mask); 10 if (new == NULL) 11 return (0); 12 move_to_free_list(idp, new); 13 } 14 return 1; 15 } 16 17 static void move_to_free_list(struct idr *idp, struct idr_layer *p) 18 { 19 unsigned long flags; 20 21 /* 22 * Depends on the return element being zeroed. 23 */ 24 spin_lock_irqsave(&idp->lock, flags); 25 __move_to_free_list(idp, p); 26 spin_unlock_irqrestore(&idp->lock, flags); 27 } 28 29 static void __move_to_free_list(struct idr *idp, struct idr_layer *p) 30 { 31 p->ary[0] = idp->id_free; 32 idp->id_free = p; 33 idp->id_free_cnt++; 34 }
第一次循环结果
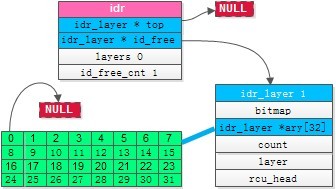
第二次循环结果
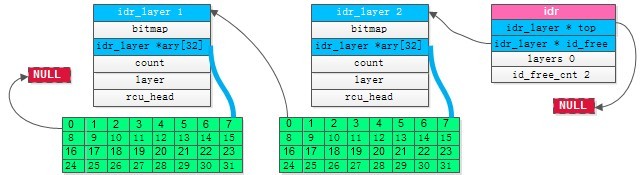
接着
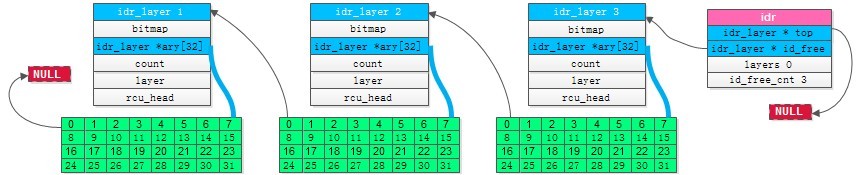
最后得到一条链(循环IDR_FREE_MAX次)
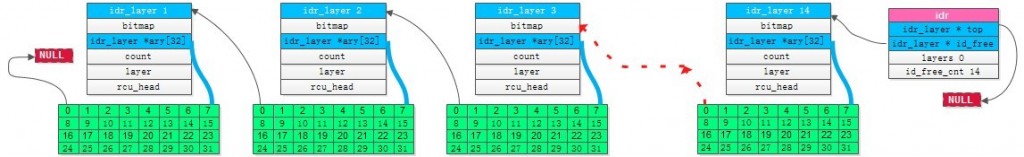
四、构建树并申请ID, 绑定地址
idr_get_new和idr_get_new_above函数


/* 申请0~0x7fffffff之间的id */ int idr_get_new(struct idr *idp, void *ptr, int *id) { int rv; rv = idr_get_new_above_int(idp, ptr, 0); /* * This is a cheap hack until the IDR code can be fixed to * return proper error values. */ if (rv < 0) return _idr_rc_to_errno(rv); *id = rv; return 0; } /* 申请starting_id~0x7fffffff之间的id */ int idr_get_new_above(struct idr *idp, void *ptr, int starting_id, int *id) { int rv; rv = idr_get_new_above_int(idp, ptr, starting_id); /* * This is a cheap hack until the IDR code can be fixed to * return proper error values. */ if (rv < 0) return _idr_rc_to_errno(rv); *id = rv; return 0; }
为什么只能到0x7fffffff呢, 到后面就知道了.
idr_get_new和idr_get_new_above两个函数都是调用idr_get_new_above_int函数:


1 static int idr_get_new_above_int(struct idr *idp, void *ptr, int starting_id) 2 { 3 /* MAX_LEVEL = 7 */ 4 struct idr_layer *pa[MAX_LEVEL]; 5 int id; 6 7 /* 从idr->top中寻找可用的最小ID */ 8 id = idr_get_empty_slot(idp, starting_id, pa); 9 if (id >= 0) { 10 /* 11 * 将ID与对象地址ptr绑定, 并且标记 12 * pa[0]->ary[id & IDR_MASK] =(struct idr_layer *)ptr; 13 */ 14 rcu_assign_pointer(pa[0]->ary[id & IDR_MASK], 15 (struct idr_layer *)ptr); 16 pa[0]->count++; 17 idr_mark_full(pa, id); 18 } 19 20 return id; 21 }
idr_get_empty_slot函数.


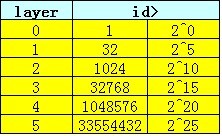
1 static int idr_get_empty_slot(struct idr *idp, int starting_id, 2 struct idr_layer **pa) 3 { 4 struct idr_layer *p, *new; 5 int layers, v, id; 6 unsigned long flags; 7 8 id = starting_id; 9 build_up: 10 p = idp->top; 11 layers = idp->layers; 12 /* 第一次申请ID时,p都为null,看图A */ 13 if (unlikely(!p)) { 14 if (!(p = get_from_free_list(idp))) 15 return -1; 16 p->layer = 0; 17 layers = 1; 18 } 19 /* 20 * 当申请ID比目前分配的空间数还大时,开辟新层 21 * 比如目前是2层结构, 可以分配的空间数为32^2=1024,最大ID为1023, 现在需要申请的ID为1050, 22 * 则需要开辟1层变成3层结构,这样可以分配的空间数为32^3, 最大ID变为32^3 - 1 23 * 看图B 24 */ 25 while ((layers < (MAX_LEVEL - 1)) && (id >= (1 << (layers*IDR_BITS)))) { 26 layers++; 27 if (!p->count) { 28 /* 29 *这里不知道怎么进去的 30 */ 31 p->layer++; 32 continue; 33 } 34 /* 从idp->id_free中取出一个idr_layer结构失败 */ 35 if (!(new = get_from_free_list(idp))) { 36 /* 37 * The allocation failed. If we built part of 38 * the structure tear it down. 39 */ 40 spin_lock_irqsave(&idp->lock, flags); 41 for (new = p; p && p != idp->top; new = p) { 42 p = p->ary[0]; 43 new->ary[0] = NULL; 44 new->bitmap = new->count = 0; 45 __move_to_free_list(idp, new); 46 } 47 spin_unlock_irqrestore(&idp->lock, flags); 48 return -1; 49 } 50 new->ary[0] = p; 51 new->count = 1; 52 new->layer = layers-1; 53 if (p->bitmap == IDR_FULL) 54 __set_bit(0, &new->bitmap); 55 p = new; 56 } 57 /* idp->top = p */ 58 rcu_assign_pointer(idp->top, p); 59 idp->layers = layers; 60 /* 以上部分主要处理layer相关,以下部分主要处理id相关 */ 61 v = sub_alloc(idp, &id, pa); 62 if (v == IDR_NEED_TO_GROW) 63 goto build_up; 64 return(v); 65 }
图a:
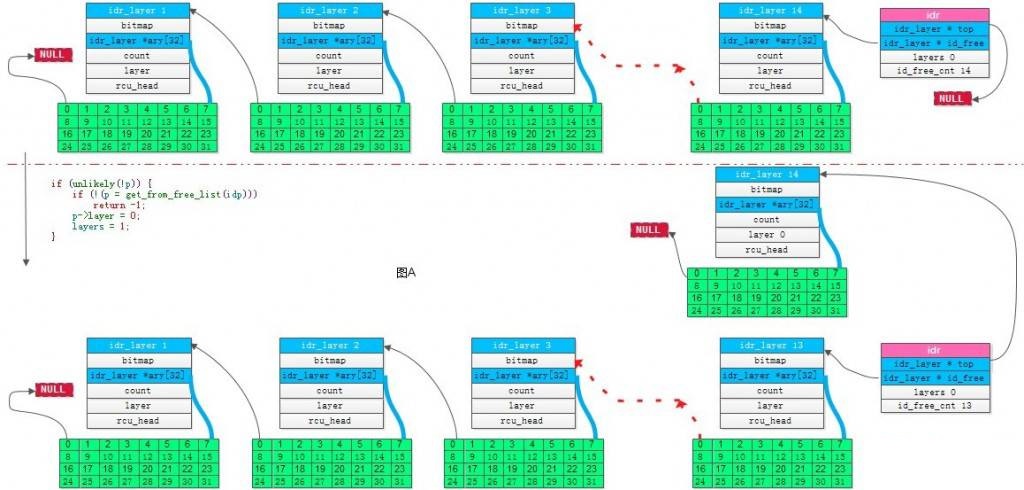
图b:
get_from_free_list函数.


1 static struct idr_layer *get_from_free_list(struct idr *idp) 2 { 3 struct idr_layer *p; 4 unsigned long flags; 5 6 spin_lock_irqsave(&idp->lock, flags); 7 /* 从空闲节点链中取出1个节点 */ 8 if ((p = idp->id_free)) { 9 idp->id_free = p->ary[0]; 10 idp->id_free_cnt--; 11 p->ary[0] = NULL; 12 } 13 spin_unlock_irqrestore(&idp->lock, flags); 14 return(p); 15 }
sub_alloc函数, 里面就有判断如果id>=0x80000000是无法申请的.


1 static int sub_alloc(struct idr *idp, int *starting_id, struct idr_layer **pa) 2 { 3 int n, m, sh; 4 struct idr_layer *p, *new; 5 int l, id, oid; 6 unsigned long bm; 7 8 id = *starting_id; 9 restart: 10 p = idp->top; 11 l = idp->layers; 12 pa[l--] = NULL; 13 while (1) { 14 /* 15 * 从根节点开始寻找直到到达叶子节点 16 */ 17 18 /* n = 0~31 */ 19 n = (id >> (IDR_BITS*l)) & IDR_MASK; 20 21 bm = ~p->bitmap; 22 m = find_next_bit(&bm, IDR_SIZE, n); 23 /* 顶层位图已满,需要再开辟1层 */ 24 if (m == IDR_SIZE) { 25 l++; 26 oid = id; 27 id = (id | ((1 << (IDR_BITS * l)) - 1)) + 1; 28 29 if (id >= 1 << (idp->layers * IDR_BITS)) { 30 *starting_id = id; 31 return IDR_NEED_TO_GROW; 32 } 33 p = pa[l]; 34 BUG_ON(!p); 35 36 /* If we need to go up one layer, continue the 37 * loop; otherwise, restart from the top. 38 */ 39 sh = IDR_BITS * (l + 1); 40 if (oid >> sh == id >> sh) 41 continue; 42 else 43 goto restart; 44 } 45 /* 改变ID */ 46 if (m != n) { 47 sh = IDR_BITS*l; 48 id = ((id >> sh) ^ n ^ m) << sh; 49 } 50 /* 如果id>=0x80000000,无法申请 */ 51 if ((id >= MAX_ID_BIT) || (id < 0)) 52 return IDR_NOMORE_SPACE; 53 if (l == 0) 54 break; 55 /* 56 * Create the layer below if it is missing. 57 */ 58 if (!p->ary[m]) { 59 new = get_from_free_list(idp); 60 if (!new) 61 return -1; 62 new->layer = l-1; 63 rcu_assign_pointer(p->ary[m], new); 64 p->count++; 65 } 66 pa[l--] = p; 67 p = p->ary[m]; 68 } 69 70 pa[l] = p; 71 return id; 72 }
find_next_bit函数.


1 /* find_next_bit就是从地址addr处的size位2进制数据中,从第offset位向左开始寻找下一个置1位 2 */ 3 unsigned long find_next_bit(const unsigned long *addr, unsigned long size, 4 unsigned long offset) 5 { 6 const unsigned long *p = addr + BITOP_WORD(offset); 7 /* result 是32的倍数 */ 8 unsigned long result = offset & ~(BITS_PER_LONG-1); 9 unsigned long tmp; 10 11 12 if (offset >= size) 13 return size; 14 size -= result; 15 /* offset =0~31, 这个offset 加上 result 等于 输入参数的offset */ 16 offset %= BITS_PER_LONG; 17 /* 查找低32位 */ 18 if (offset) { 19 tmp = *(p++); 20 tmp &= (~0UL << offset); 21 if (size < BITS_PER_LONG) 22 goto found_first; 23 if (tmp) 24 goto found_middle; 25 size -= BITS_PER_LONG; 26 result += BITS_PER_LONG; 27 } 28 29 /* size是32的倍正整数, 32位一次寻找置1位 */ 30 while (size & ~(BITS_PER_LONG-1)) { 31 if ((tmp = *(p++))) 32 goto found_middle; 33 result += BITS_PER_LONG; 34 size -= BITS_PER_LONG; 35 } 36 /* 走到这里就是整个数已无置1位, 返回最开始的size值 */ 37 if (!size) 38 return result; 39 40 /* 走到这里size一开始就不是32的倍数, 比如是37位数, 低32位已无置1位, 后面寻找高5位的置1位 */ 41 tmp = *p; 42 43 found_first: 44 tmp &= (~0UL >> (BITS_PER_LONG - size)); 45 if (tmp == 0UL) /* Are any bits set? */ 46 return result + size; /* Nope. */ 47 found_middle: 48 return result + __ffs(tmp); 49 }
五、利用ID寻找地址
idr_find函数.


1 void *idr_find(struct idr *idp, int id) 2 { 3 int n; 4 struct idr_layer *p; 5 6 p = rcu_dereference_raw(idp->top); 7 if (!p) 8 return NULL; 9 n = (p->layer+1) * IDR_BITS; 10 11 /* id最大为0x7fffffff */ 12 id &= MAX_ID_MASK; 13 14 if (id >= (1 << n)) 15 return NULL; 16 BUG_ON(n == 0); 17 18 /* 一直到叶子节点 */ 19 while (n > 0 && p) { 20 n -= IDR_BITS; 21 BUG_ON(n != p->layer*IDR_BITS); 22 p = rcu_dereference_raw(p->ary[(id >> n) & IDR_MASK]); 23 } 24 return((void *)p); 25 }




 本文深入解析了IDR(Identifier Resource)的数据结构及其操作方法,包括初始化、分配ID、构建32叉树等过程,并详细解释了相关函数的工作原理。
本文深入解析了IDR(Identifier Resource)的数据结构及其操作方法,包括初始化、分配ID、构建32叉树等过程,并详细解释了相关函数的工作原理。
















 2089
2089

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








