Sometimes, you have created two models. They have the same parent class like this:
public class Person
{
public int PersonId { get; set; }
public string PersonName { get; set; }
}
public class InsidePerson : Person
{
public string Title { get; set; }
public string Department { get; set; }
}
public class OutsidePerson : Person
{
public string CompanyName { get; set; }
}After you execute the command Update-Database in nuget command line, Entity Framework will create one table named people:
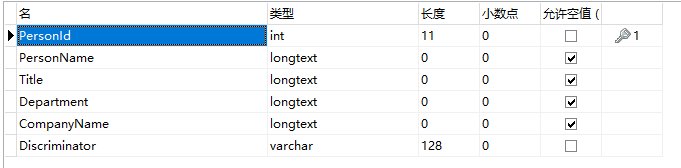
The Discriminator column is created for discriminating what model dose current row represent. this model creating type is called TPH(Table per Hierarchy Inheritance). Let's do a test. Add some codes in main function:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
using (MyDbContext db = new MyDbContext())
{
Person insidePerson1 = new InsidePerson()
{
PersonName = "InsidePerson1",
Title = "Manager",
Department = "development"
};
db.People.Add(insidePerson1);
InsidePerson insidePerson2 = new InsidePerson()
{
PersonName = "InsidePerson2",
Title = "Manager",
Department = "development"
};
db.People.Add(insidePerson2);
InsidePerson insidePerson3 = new InsidePerson()
{
PersonName = "InsidePerson3",
Title = "Manager",
Department = "development"
};
db.InsidePeople.Add(insidePerson3);
Person outsidePerson1 = new OutsidePerson()
{
PersonName = "outsidePerson1",
CompanyName = "Tencent"
};
db.People.Add(outsidePerson1);
db.SaveChanges();
}
}Let's look at the database:
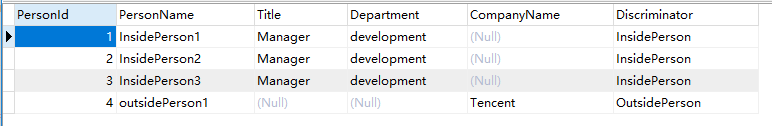
If you don't like the discriminator column which entity framework auto create, you can define your column by adding these codes in OnModelCreating function of DbContext class:
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
modelBuilder.Entity<Person>()
.Map<InsidePerson>(p => p.Requires("PersonType").HasValue(1))
.Map<OutsidePerson>(p => p.Requires("PersonType").HasValue(2));
}Then, execute the command Add-Migration AddPesonTypeColumn2PeopleTable and Update-Database in nuget command line. Now, look at the database again:
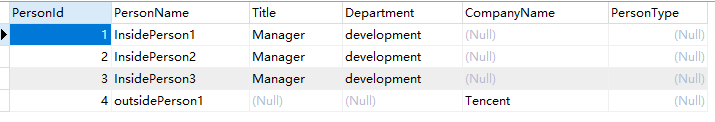
We can find the Entity Framework can't insert any value into PersonType column of existed rows. It's a little sad. Now, We insert some new data by coding:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
using (MyDbContext db = new MyDbContext())
{
Person insidePerson4 = new InsidePerson()
{
PersonName = "InsidePerson4",
Title = "Manager",
Department = "development"
};
db.People.Add(insidePerson4);
Person outsidePerson2 = new OutsidePerson()
{
PersonName = "outsidePerson2",
CompanyName = "Baidu"
};
db.People.Add(outsidePerson2);
db.SaveChanges();
}
}Look at the databas again:
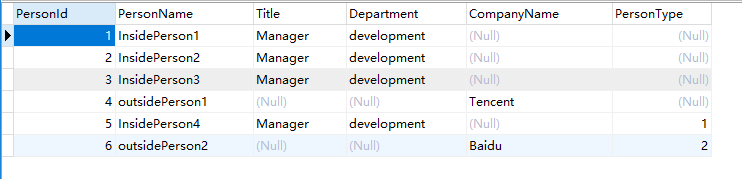
That's all.























 101
101

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








