四、0-1背包问题
问题表述:给定n种物品和一背包。物品i的重量是wi,其价值为pi,背包的容量为C。问应如何选择装入背包的物品,使得装入背包中物品的总价值最大?
0-1背包问题是一个特殊的整数规划问题。
解空间:
可行性约束函数:
上界函数:
考虑一个右子树的时候,设
r:是当前未考虑的剩余物品的总价值(remainder)
cp:是当前的价值(current price)
bestp:是当前得到的最优价值(best price)
那么,满足:
但是,上界r太松。
一个更加紧的上界:
将剩余物品按照单位重量价值排序,然后依次装入物品,直到装不下,再将剩余物品的一部分放入背包。(r_n <= r)
实现
/* 主题:0-1背包问题
* 作者:chinazhangjie
* 邮箱:chinajiezhang@gmail.com
* 开发语言:C++
* 开发环境:Mircosoft Virsual Studio 2008
* 时间: 2010.10.25
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
class goods {
public:
int weight; // 重量
int price; // 价格
goods() : weight(0),price(0)
{}
};
bool goods_greater(const goods& lhs,const goods& rhs)
{
return (lhs.price / lhs.weight) > (rhs.price / rhs.weight);
}
class knapsack
{
public:
knapsack (int c,const vector<goods>& gl)
: capacity (c), curr_price(0), best_price (0), curr_weight(0){
goods_list = gl;
total_layers = gl.size();
curr_path.resize (total_layers);
best_path.resize (total_layers);
}
void backtrack () {
__backtrack (0);
cout << "path: " ;
copy (best_path.begin(),best_path.end(),ostream_iterator<int> (cout, " "));
cout << endl;
cout << "best_price: " << best_price << endl;
}
private:
// 计算上界
int __bound (int layers) {
int cleft = capacity - curr_weight;
int result = curr_price;
// 将layer之后的物品进行按单位价格降序排序
vector<goods> tmp = goods_list;
sort (tmp.begin() + layers, tmp.end(),goods_greater);
// 以物品单位重量价值递减序装入物品
while (layers < total_layers && tmp[layers].weight <= cleft) {
cleft -= tmp[layers].weight;
result += tmp[layers].price;
++ layers;
}
// 装满背包
if (layers < total_layers) {
result += (tmp[layers].price / tmp[layers].weight) * cleft;
}
return result;
}
void __backtrack (int layers) {
// 到达叶子结点,更新最优价值
if (layers >= total_layers) {
if (curr_price > best_price || best_price == 0) {
best_price = curr_price;
copy (curr_path.begin(), curr_path.end(), best_path.begin());
}
return ;
}
// 左剪枝(能放的下)
if (curr_weight + goods_list[layers].weight <= capacity) {
curr_path[layers] = 1;
curr_weight += goods_list[layers].weight;
curr_price += goods_list[layers].price;
__backtrack (layers + 1);
curr_weight -= goods_list[layers].weight;
curr_price -= goods_list[layers].price;
}
// 右剪枝
if (__bound (layers + 1) > best_price || best_price == 0 ) {
curr_path[layers] = 0;
__backtrack (layers + 1);
}
/*curr_path[layers] = 0;
__backtrack (layers + 1);*/
}
private:
vector<goods> goods_list; // 货物信息列表
int capacity; // 背包承载量
int curr_price; // 当前价格
int curr_weight; // 当前重量
int best_price; // 当前得到的最优价值
int total_layers; // 总层数
vector<int> curr_path; // 当前路径
vector<int> best_path; // 最优价值下的路径
};
int main()
{
const int size = 3;
vector<goods> gl(size);
gl[0].weight = 10;
gl[0].price = 1;
gl[1].weight = 8;
gl[1].price = 4;
gl[2].weight = 5;
gl[2].price = 5;
knapsack ks(16, gl);
ks.backtrack ();
return 0;
}
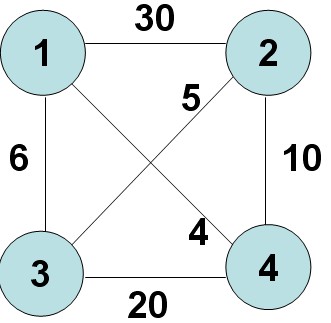
五、旅行售货员问题
问题表述:在图中找到一个权最小的周游路线
解空间:排列树
剪枝策略:
当前路径的权重+下一个路径的权重 < 当前的最小权重,则搜索该路径
实现:
/* 主题:旅行售货员问题
* 作者:chinazhangjie
* 邮箱:chinajiezhang@gmail.com
* 开发语言:C++
* 开发环境:Mircosoft Virsual Studio 2008
* 时间: 2010.10.26
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <iterator>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class traveling
{
public:
static const int NOEDGE = -1 ;
public:
traveling (const vector<vector<int> >& ug)
: curr_cost (0), best_cost (-1) {
node_count = ug.size ();
undigraph = ug;
curr_solution.resize (node_count);
for (int i = 0; i < node_count; ++ i) {
curr_solution[i] = i;
}
best_solution.resize (node_count);
}
void backtrack () {
__backtrack (1);
cout << best_cost << endl;
}
private:
void __backtrack (int layers) {
if (layers >= node_count) {
if (undigraph[curr_solution[node_count - 1]][curr_solution[0]] == NOEDGE){
return ;
}
int total_cost = curr_cost +
undigraph[curr_solution[node_count - 1]][curr_solution[0]] ;
if (total_cost < best_cost || best_cost == -1) {
// 更新最优费用和最优路径
best_cost = total_cost;
copy (curr_solution.begin(),
curr_solution.end(),
best_solution.begin());
}
return ;
}
for (int i = layers; i < node_count; ++ i) {
// 剪枝
if (undigraph[curr_solution[layers - 1]][curr_solution[i]] != NOEDGE &&
( curr_cost + undigraph[curr_solution[layers - 1]][curr_solution[i]]
< best_cost || best_cost == -1 )) {
// 搜索子树
swap (curr_solution[layers],curr_solution[i]);
curr_cost +=
undigraph[curr_solution[layers - 1]][curr_solution[layers]];
__backtrack (layers + 1);
curr_cost -=
undigraph[curr_solution[layers - 1]][curr_solution[layers]];
swap (curr_solution[layers],curr_solution[i]);
}
}
}
int node_count; // 结点个数
int curr_cost; // 当前费用
int best_cost; // 当前
vector<int> curr_solution; // 当前解决方案
vector<int> best_solution; // 最优解决方案
vector<vector<int> > undigraph; // 无向图(采用矩阵存储)
};
int main()
{
int size = 4;
vector<vector<int> > ug(size);
for (int i = 0;i < size; ++ i) {
ug[i].resize (size);
}
ug[0][0] = -1;
ug[0][1] = 30;
ug[0][2] = 6;
ug[0][3] = 4;
ug[1][0] = 30;
ug[1][1] = -1;
ug[1][2] = 5;
ug[1][3] = 10;
ug[2][0] = 6;
ug[2][1] = 5;
ug[2][2] = -1;
ug[2][3] = 20;
ug[3][0] = 4;
ug[3][1] = 10;
ug[3][2] = 20;
ug[3][3] = -1;
traveling t(ug);
t.backtrack();
return 0;
}
参考书籍 《算法设计与分析(第二版)》 王晓东 编著
授课教师 张阳教授




















 1238
1238

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








