1.1 File类
File类在java中表示(带路径的)文件或者目录。
1.1.1 File常用属性和方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 给定路径创建File对象
// File file = new File("D:"+File.separator+"javatest"+File.separator+"a.txt");
File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\b.mp3");
System.out.println(file);
// 文件基本属性
System.out.println(file.canExecute());
System.out.println(file.canRead());
System.out.println(file.canWrite());
// 文件的创建、删除
if(!file.exists()) {
boolean r;
try {
r = file.createNewFile();
if(r) {
System.out.println("文件创建成功");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 删除文件
file.delete();
}创建文件时会抛出检查时异常IOException
1.1.2 File的路径相关
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\a");
// File file = new File("a.txt");
// 获取file的绝对路径
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());
// 获取file的创建时的路径字符串
System.out.println(file.getPath());
// 获取文件或者目录的名字
System.out.println(file.getName());
// 获取文件或者目录的父目录
System.out.println(file.getParent());
}注意:如果file是相对路径,相对路径的当前路径是工程目录
1.1.3 目录的创建
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\c\\d\\e");
if(!file.exists()) {
boolean r;
try {
// 一次只能创建一个目录
// r = file.mkdir();
r = file.mkdirs();
if(r) {
System.out.println("目录创建成功");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
1.1.4 目录的遍历
list():返回一个file表示的目录中的子目录或者文件,字符串数组类型
listFiles():返回一个file表示的目录中的子目录或者文件,File数组类型
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 需求:遍历d:\javatest目录
// list()
File file = new File("d:\\javatest");
/*
String[] list = file.list();
for (String str : list) {
System.out.print(str);
File f = new File(file.getPath()+"\\"+str);
if(f.isDirectory()) {
System.out.println(" 目录");
}else {
System.out.println(" 文件");
}
}*/
// listFiles();
File[] listFiles = file.listFiles();
for (File f : listFiles) {
System.out.print(f.getName());
if(f.isDirectory()) {
System.out.println(" 目录");
}else {
System.out.println(" 文件");
}
}
}
1.2 IO流
1.2.1 流
流(stream):流是一连串流动的数据(字节、字符),以先进先出的方式发送的信息的通道中
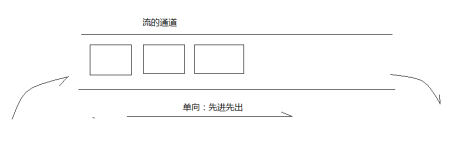
1.2.2 输入流和输出流
输入流
数据从源数据源流入程序的过程称为输入流。可以理解为从源数据源读取数据到程序的过程
输出流
数据从程序流出到目的地的过程称为输出流。可以理解为把数据从程序写入目的地的过程
数据源一般指提供数据的原始媒介,一般常见有文件、数据库、云端、其他硬件等能提供数据的媒介。
1.2.3 流的分类
按照流向分为输入流和输出流
按照处理单元分为字节流和字符流
按照功能分为节点流和转换流。
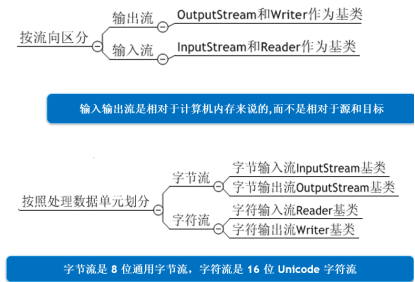
1.2.4 InputStream/OutputStream
InputStream 是所有字节输入流的抽象父类,提供了read 读取一个字节,read(byte[] buf) 读取一定量的字节到缓冲区数组 buf中。
OutputStream 是所有字节输出流的抽象父类,提供了write() 写入一个字节,write(byte[] buf) 写入一定量的字节到输出流
FileInputStream 文件字节输入流,专门用于从文件中读取字节到程序内存中。FileOutputStream 文件字节输出流,专门用于从内存中写入字节到文件中。
需求:从文件读取一个字节
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 需求:读取一个文件中的一个字节
File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\a.txt");
// 【1】创建管道
FileInputStream in = null;
try {
in = new FileInputStream(file);
// 【2】从管道读取一个字节
/*
int t;
t = in.read();
t = in.read();
t = in.read();
t = in.read();
*/
// System.out.println(t);
// 循环读取一个字节
int t;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while( (t=in.read()) != -1 ) {
sb.append((char)t);
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 【3】关闭流管道
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
一次读取多个字节
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 需求:一次读取多个字节
File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\a.txt");
// 【1】创建管道
FileInputStream in = null;
try {
in = new FileInputStream(file);
// 【2】从管道读取多个字节到缓冲区
/*
byte[] buf = new byte[5];
int len;
len = in.read(buf);
len = in.read(buf);
len = in.read(buf);
len = in.read(buf);
for(byte b:buf) {
System.out.print((char)b+"\t");
}
System.out.println(len);
*/
// 通过循环读取文件
byte[] buf = new byte[5];
int len;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while( (len=in.read(buf)) != -1 ) {
// 读取的内容是原始二进制流,需要根据编码的字符集解码成对于字符
String str = new String(buf,0,len);
sb.append(str);
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 【3】关闭流管道
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
需求:按照指定编码写入文件
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException,IOException {
File oriFile = new File("d:\\javatest\\logo.jpg");
File toFile = new File("logo.jpg");
long totalLen = oriFile.length(); // 文件大小
long cpyedLen = 0; // 已复制完成的大小
float progress = 0.0f;
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(oriFile);
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(toFile);
// 一次读取1kb
byte[] buf = new byte[512];
int len;
while( (len=in.read(buf)) != -1) {
out.write(buf, 0, len);
cpyedLen += len;
progress = cpyedLen*1.0f/totalLen;
System.out.println(progress);
}
in.close();
out.close();
System.out.println("复制完成!");
}
1.2.5 Reader/Writer
Reader 是字符输入流的抽象父类,提供了
read 一次读取一个字符
read(char[] cbuf) 一次读取多个字符到字符缓冲区cbuf,返回长度表示读取的字符个数。
Writer 是字符输出流的抽象父类,提供了
write
write(char[] cbuf)
write(string)
FileReader 文件字符输入流,专门用于读取默认字符编码文本性文件。
FileWriter 文件字符输出流,专门用于写入默认字符编码的文本性文件。为了提高效率,FileWriter内部存在一个字节缓冲区,用于对待写入的字符进行统一编码到字节缓冲区,一定要在关闭流之前,调用flush方法刷新缓冲区。
需求:一次读取一个字符/多个字符到cbuf
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\d.txt");
FileReader reader = new FileReader(file);
// 【1】一次读取一个字符
/*
int c;
c = reader.read();
c = reader.read();
c = reader.read();
c = reader.read();
c = reader.read();
System.out.println((char)c);
*/
// 【2】一次读取多个字符到cbuf中
/*
char[] cbuf = new char[2];
int len;
len = reader.read(cbuf);
len = reader.read(cbuf);
len = reader.read(cbuf);
len = reader.read(cbuf);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(cbuf));
System.out.println(len);
*/
char[] cbuf = new char[2];
int len;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while( (len=reader.read(cbuf)) != -1 ) {
sb.append(cbuf,0,len);
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
需求:写入字符到文件中
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\f.txt");
FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(file);
// 【1】一次写入一个字符
/*writer.write('中');
writer.write('国');*/
// 【2】一次写入多个字符
/*char[] cbuf = {'h','e','l','l','o','中','国'};
writer.write(cbuf);*/
// 【3】一次写入一个字符串
String str = "hello你好";
writer.write(str);
// 刷新字节缓冲区
writer.flush();
// 关闭流通道
writer.close();
System.out.println("写入完成");
}
1.2.6 BufferedReader/BufferedWriter
BufferedReader 继承于Reader,提供了read,read(char[] cbuf);readLine() 用于读取一行文本,实现对文本的高效读取。
BufferedReader 初始化时需要一个reader,本质上BufferedReader在reader的基础上增加readLine()的功能。
BufferedWriter继承于Writer,提供了write,write(char[] cbuf);write(string)
newline() 写入一个行分隔符。
需求:读取一首诗
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 按行读取gbk文本性文件
File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\i.txt");
// 【1】创建管道
FileReader reader = new FileReader(file);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(reader);
// 【2】读取一行
/*
String line = br.readLine();
line = br.readLine();
line = br.readLine();
line = br.readLine();
*/
String line;
while( (line=br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
}
需求:以gbk编码写入一首诗到文件
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\j.txt");
// 【1】创建gbk管道
FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(file);
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(writer);
// 【2】写入一行
bw.write("窗前明月光,");
bw.newLine();
bw.write("疑似地上霜。");
// for win
// bw.write("\r\n");
// for unix/linux/mac
// bw.write("\n");
bw.write("举头望明月,");
bw.newLine();
// 【3】flush
bw.flush();
// 【4】关闭管道
bw.close();
writer.close();
}
需求:以utf8编码高效写入文件
/**
* 以utf8写入一首诗
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("d:\\javatest\\j-utf8.txt");
// 【1】创建utf8管道
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file);
OutputStreamWriter writer = new OutputStreamWriter(out, "UTF-8");
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(writer);
// 【2】写入一行
bw.write("窗前明月光,");
bw.newLine();
bw.write("疑似地上霜。");
// for win
bw.write("\r\n");
// for unix/linux/mac
// bw.write("\n");
bw.write("举头望明月,");
bw.newLine();
// 【3】flush
bw.flush();
// 【4】关闭管道
bw.close();
writer.close();
}
}




 该博客主要介绍Java中的File类和IO流。File类可表示带路径的文件或目录,涉及常用属性、方法、路径相关、目录创建与遍历。IO流包括输入流和输出流,按流向、处理单元、功能分类,还介绍了InputStream/OutputStream、Reader/Writer、BufferedReader/BufferedWriter等抽象父类及相关需求实现。
该博客主要介绍Java中的File类和IO流。File类可表示带路径的文件或目录,涉及常用属性、方法、路径相关、目录创建与遍历。IO流包括输入流和输出流,按流向、处理单元、功能分类,还介绍了InputStream/OutputStream、Reader/Writer、BufferedReader/BufferedWriter等抽象父类及相关需求实现。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








