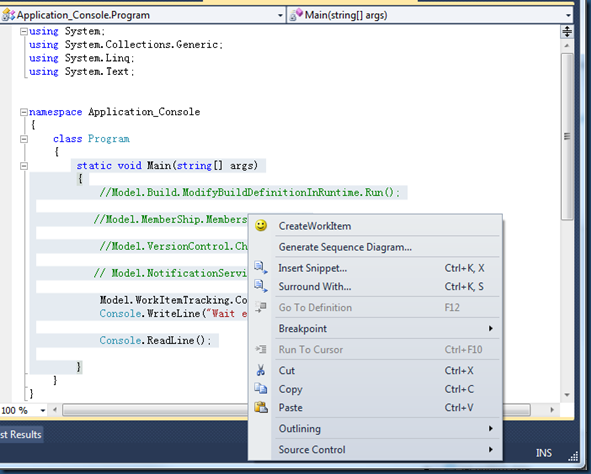
Some developers or testers may find that it will be more convenient that they could create a bug in code editor. Select a method, right click and create a work item.
Following steps and sample codes is for VS2010 and .NET4.0.
1 Create a VS Add-in project
2 Add new entry to the context menu of code editor.
The add-in class Connect will implement interface IDTExtensibility2
1: namespace Extensibility2: {3: [Guid("B65AD801-ABAF-11D0-BB8B-00A0C90F2744")]4: [TypeLibType(4160)]5: public interface IDTExtensibility26: {7: [DispId(3)]8: void OnAddInsUpdate(ref Array custom);9: [DispId(5)]10: void OnBeginShutdown(ref Array custom);11: [DispId(1)]12: void OnConnection(object Application, ext_ConnectMode ConnectMode, object AddInInst, ref Array custom);13: [DispId(2)]14: void OnDisconnection(ext_DisconnectMode RemoveMode, ref Array custom);15: [DispId(4)]16: void OnStartupComplete(ref Array custom);17: }18: }
Implement method OnConnection with following code
1: public void OnConnection(object application, ext_ConnectMode connectMode, object addInInst, ref Array custom)2: {3: _applicationObject = (DTE2)application;4: _addInInstance = (AddIn)addInInst;5: if(connectMode == ext_ConnectMode.ext_cm_UISetup)6: {7: object []contextGUIDS = new object[] { };8: Commands2 commands = (Commands2)_applicationObject.Commands;9: string toolsMenuName = "";10:11:12: //Place the command on the tools menu.13: //Find the MenuBar command bar, which is the top-level command bar holding all the main menu items:14: Microsoft.VisualStudio.CommandBars.CommandBar menuBarCommandBar = ((Microsoft.VisualStudio.CommandBars.CommandBars)_applicationObject.CommandBars)["Editor Context Menus"];15:16: //Find the Tools command bar on the MenuBar command bar:17: CommandBarControl toolsControl = menuBarCommandBar.Controls[toolsMenuName];18: CommandBarPopup toolsPopup = (CommandBarPopup)toolsControl;19:20: //This try/catch block can be duplicated if you wish to add multiple commands to be handled by your Add-in,21: // just make sure you also update the QueryStatus/Exec method to include the new command names.22: try23: {24: //Add a command to the Commands collection:25: Command command = commands.AddNamedCommand2(_addInInstance, "CreateWorkItem", "CreateWorkItem", "Executes the command for CreateWorkItem", true, 59, ref contextGUIDS, (int)vsCommandStatus.vsCommandStatusSupported + (int)vsCommandStatus.vsCommandStatusEnabled, (int)vsCommandStyle.vsCommandStylePictAndText, vsCommandControlType.vsCommandControlTypeButton);26:27: //Add a control for the command to the tools menu:28: if((command != null) && (toolsPopup != null))29: {30: command.AddControl(toolsPopup.CommandBar, 1);31:32: }33: }34: catch(System.ArgumentException)35: {36: //If we are here, then the exception is probably because a command with that name37: // already exists. If so there is no need to recreate the command and we can38: // safely ignore the exception.39: }40: }41: }
3 Handle the command when the menu is clicked
The add-in class Connect will implement interface IDTCommandTarget
1: public interface IDTCommandTarget2: {3: [DispId(2)]4: void Exec(string CmdName, vsCommandExecOption ExecuteOption, ref object VariantIn, ref object VariantOut, ref bool Handled);5: [DispId(1)]6: void QueryStatus(string CmdName, vsCommandStatusTextWanted NeededText, ref vsCommandStatus StatusOption, ref object CommandText);7: }
When the menu is click, the method Exec is called.
In the Exec command, show a dialog to choose work item type.
1: public void Exec(string commandName, vsCommandExecOption executeOption, ref object varIn, ref object varOut, ref bool handled)2: {3: handled = false;4: if(executeOption == vsCommandExecOption.vsCommandExecOptionDoDefault)5: {6: if (commandName == "CreateWorkItem.Connect.CreateWorkItem")7: {8: Microsoft.VisualStudio.TeamFoundation.TeamFoundationServerExt tfsExt9: = (Microsoft.VisualStudio.TeamFoundation.TeamFoundationServerExt)_applicationObject.GetObject("Microsoft.VisualStudio.TeamFoundation.TeamFoundationServerExt");10:11: //Confirm that TFS is connected12: if ((tfsExt == null)13: || (tfsExt.ActiveProjectContext == null)14: || (tfsExt.ActiveProjectContext.DomainUri == null)15: || (tfsExt.ActiveProjectContext.ProjectUri == null))16: {17: MessageBox.Show("Please Connect to TFS first and select a Team Project");18: }19:20: WorkItemTypeSelect witselect = new WorkItemTypeSelect();21: witselect._applicationObject = _applicationObject;22: witselect.ShowDialog();23:24: handled = true;25: return;26: }27: }28: }
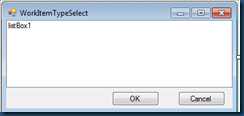
The UI of the dialog is like
The codes are
1: using System;2: using System.Collections.Generic;3: using System.ComponentModel;4: using System.Data;5: using System.Drawing;6: using System.Linq;7: using System.Text;8: using System.Windows.Forms;9: using EnvDTE80;10: using Microsoft.TeamFoundation.Client;11: using Microsoft.VisualStudio.TeamFoundation.WorkItemTracking;12: using Microsoft.TeamFoundation.WorkItemTracking.Client;13:14: namespace CreateWorkItem15: {16: public partial class WorkItemTypeSelect : Form17: {18: public DTE2 _applicationObject { get; set; }19: Microsoft.VisualStudio.TeamFoundation.TeamFoundationServerExt tfsExt;20: DocumentService witDocumentService;21: TfsTeamProjectCollection tfsProjectCollection;22: WorkItemStore wiStore;23:24: public WorkItemTypeSelect()25: {26: InitializeComponent();27: }28:29: private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)30: {31:32: WorkItem wi = new WorkItem(wiStore.Projects[tfsExt.ActiveProjectContext.ProjectName].WorkItemTypes[listBox1.SelectedItem.ToString()]);33:34: wi.Title = listBox1.SelectedItem.ToString();35:36: dynamic selection = _applicationObject.ActiveDocument.Selection;37: wi.Description = selection.Text;38:39: IWorkItemDocument widoc = null;40: widoc = witDocumentService.CreateWorkItem(wi,41: new object());42: try43: {44: witDocumentService.ShowWorkItem(widoc);45: }46: finally47: {48: widoc.Release(this);49: }50: this.Close();51: }52:53: private void WorkItemTypeSelect_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)54: {55: tfsExt = (Microsoft.VisualStudio.TeamFoundation.TeamFoundationServerExt)_applicationObject.GetObject("Microsoft.VisualStudio.TeamFoundation.TeamFoundationServerExt");56:57: witDocumentService = (DocumentService)_applicationObject.GetObject("Microsoft.VisualStudio.TeamFoundation.WorkItemTracking.DocumentService");58:59: tfsProjectCollection = TfsTeamProjectCollectionFactory.GetTeamProjectCollection(new Uri(tfsExt.ActiveProjectContext.DomainUri));60:61: wiStore = tfsProjectCollection.GetService<WorkItemStore>();62:63: listBox1.Items.Clear();64: foreach (WorkItemType wit in wiStore.Projects[tfsExt.ActiveProjectContext.ProjectName].WorkItemTypes)65: {66: listBox1.Items.Add(wit.Name);67: }68:69:70: }71: }72: }
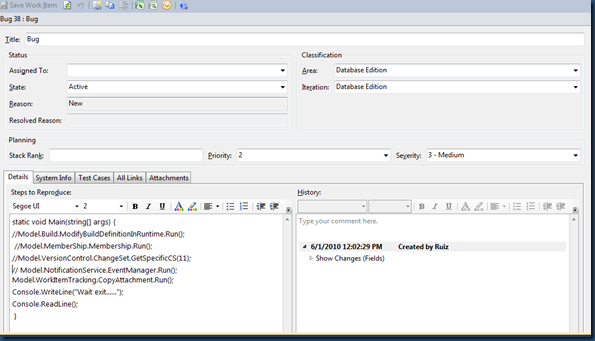
Note that in MSF for Agile 5, description is not displayed in Bug work item, you can
set the field Microsoft.VSTS.TCM.ReproSteps.
The final result is
 VS2010中创建Bug工作项
VS2010中创建Bug工作项




 本文介绍如何在Visual Studio 2010中通过代码编辑器快速创建Bug工作项。通过实现VS Add-in项目并在代码编辑器上下文菜单中添加新条目,用户可以选择方法并右键创建工作项。文章详细介绍了实现步骤及关键代码。
本文介绍如何在Visual Studio 2010中通过代码编辑器快速创建Bug工作项。通过实现VS Add-in项目并在代码编辑器上下文菜单中添加新条目,用户可以选择方法并右键创建工作项。文章详细介绍了实现步骤及关键代码。
















 1483
1483

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








