第一题:
车辆重载:


1 #ifndef BATTERY_H 2 #define BATTERY_H 3 4 class Battery{ 5 public: 6 Battery(int size=70); 7 int getsize()const; 8 private: 9 int batterySize; 10 }; 11 #endif


1 #include"battery.h" 2 3 Battery::Battery(int size):batterySize(size){ 4 } 5 6 int Battery::getsize()const{ 7 return batterySize; 8 }


1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<string> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 #ifndef CAR_H 6 #define CAR_H 7 8 class Car{ 9 public: 10 Car(string maker,string model,int year,int odometer=0); 11 friend ostream&operator<<(ostream &out,const Car &b); 12 void updateOdometer(int new1); 13 string maker,model; 14 int year,odometer; 15 }; 16 17 #endif


1 #include "car.h" 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<string> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 Car::Car(string maker,string model,int year,int odometer):maker(maker),model(model),year(year),odometer(odometer){ 7 } 8 9 ostream&operator<<(ostream &out,const Car &b){ 10 out<<"maker: "<<b.maker<<" model: "<<b.model 11 <<" year: "<<b.year<<" odometer: "<<b.odometer<<endl; 12 return out; 13 } 14 15 void Car::updateOdometer(int new1){ 16 if(new1<odometer) 17 cout<<"wrong!"<<endl; 18 else 19 odometer=new1; 20 }


1 #ifndef ELEC_H 2 #define ELEC_H 3 4 #include<iostream> 5 #include<string> 6 #include"car.h" 7 #include"battery.h" 8 using namespace std; 9 10 class ElectricCar:virtual public Car{ 11 public: 12 ElectricCar(string maker,string model,int year,int odometer=0,Battery battery=70); 13 friend ostream&operator<<(ostream &out,const ElectricCar &c); 14 15 private: 16 Battery battery; 17 18 }; 19 20 #endif


1 #include"electriccar.h" 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<string> 4 #include"battery.h" 5 using namespace std; 6 7 ElectricCar::ElectricCar(string maker,string model,int year,int odometer,Battery battery):Car(maker,model,year,odometer){ 8 battery=battery; 9 } 10 11 ostream&operator<<(ostream &out,const ElectricCar &c){ 12 out<<"maker: "<<c.maker<<" model: "<<c.model 13 <<" year: "<<c.year<<" odometer: "<<c.odometer<<" battery: "<<c.battery.getsize()<<endl; 14 return out; 15 }


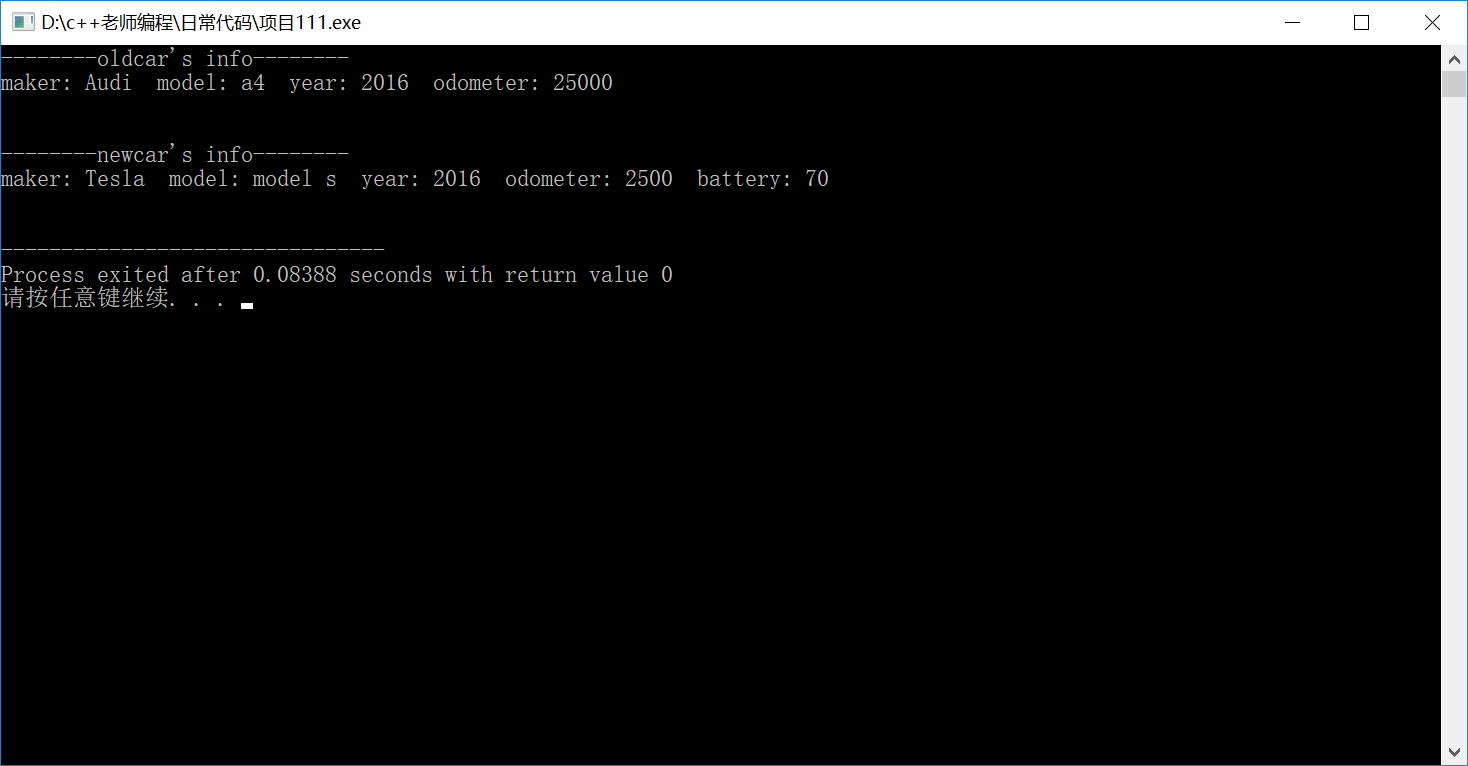
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include "car.h" 4 #include "electricCar.h" 5 6 int main() { 7 // 测试Car类 8 Car oldcar("Audi","a4",2016); 9 cout << "--------oldcar's info--------" << endl; 10 oldcar.updateOdometer(25000); 11 cout << oldcar << endl; 12 // 测试ElectricCar类 13 ElectricCar newcar("Tesla","model s",2016); 14 newcar.updateOdometer(2500); 15 cout << "\n--------newcar's info--------\n"; 16 cout << newcar << endl; 17 18 return 0; 19 }
第二题:


1 #ifndef ARRAY_INT_H 2 #define ARRAY_INT_H 3 4 class ArrayInt { 5 public: 6 ArrayInt(int n, int value = 0); 7 ~ArrayInt(); 8 int& operator[](int num); 9 // 补足:将运算符[]重载为成员函数的声明 10 // ××× 11 void print(); 12 private: 13 int *p; 14 int size; 15 }; 16 17 #endif


1 #include "arrayInt.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <cstdlib> 4 using std::cout; 5 using std::endl; 6 7 ArrayInt::ArrayInt(int n, int value) : size(n) { 8 p = new int[size]; 9 10 if (p == nullptr) { 11 cout << "fail to mallocate memory" << endl; 12 exit(0); 13 } 14 15 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) 16 p[i] = value; 17 } 18 19 ArrayInt::~ArrayInt() { 20 delete[] p; 21 } 22 23 void ArrayInt::print() { 24 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) 25 cout << p[i] << " "; 26 cout << endl; 27 } 28 29 // 补足:将运算符[]重载为成员函数的实现 30 // ××× 31 32 int& ArrayInt::operator[](int num) { 33 return p[num]; 34 }


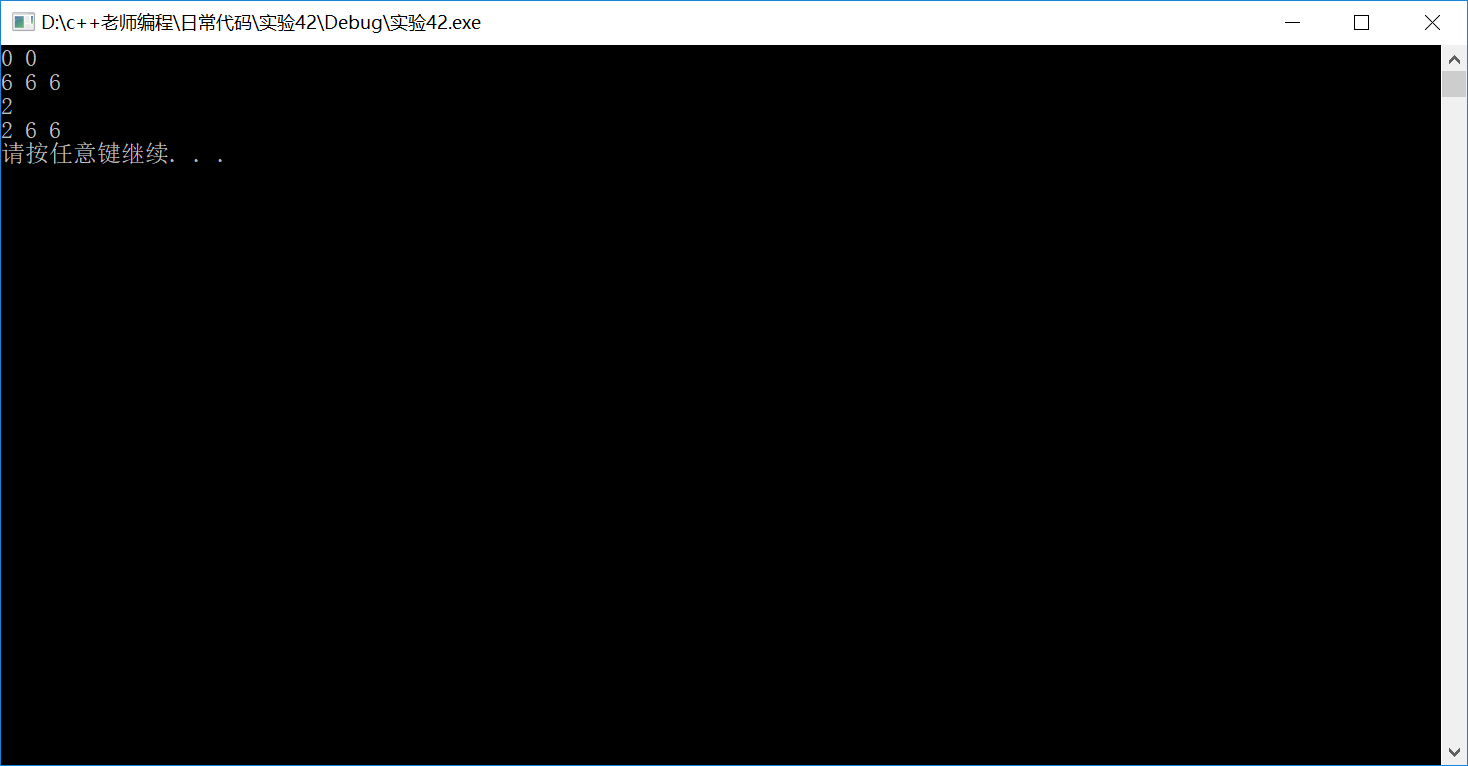
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 #include "arrayInt.h" 5 6 int main() { 7 // 定义动态整型数组对象a,包含2个元素,初始值为0 8 ArrayInt a(2); 9 a.print(); 10 11 // 定义动态整型数组对象b,包含3个元素,初始值为6 12 ArrayInt b(3, 6); 13 b.print(); 14 15 // 通过对象名和下标方式访问并修改对象元素 16 b[0] = 2; 17 cout << b[0] << endl; 18 b.print(); 19 20 system("pause"); 21 22 return 0; 23 }
写这篇实验的时候前前后后用了不少的时间,我发现对一些基础知识的某一个点的不理解会导致写程序的时候被卡住 ,然后改正过来的时候又会感觉,哇原来这么简单,我怎么会在这个上面花费这么多时间呢。
评论:
https://www.cnblogs.com/GeorgeWan/
https://www.cnblogs.com/wyy0204/
https://www.cnblogs.com/wyf-blogs/




















 3085
3085

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








