考虑 state_is_tuple
Output, new_state = cell(input, state)
state其实是两个 一个 c state,一个m(对应下图的hidden 或者h) 其中m(hidden)其实也就是输出
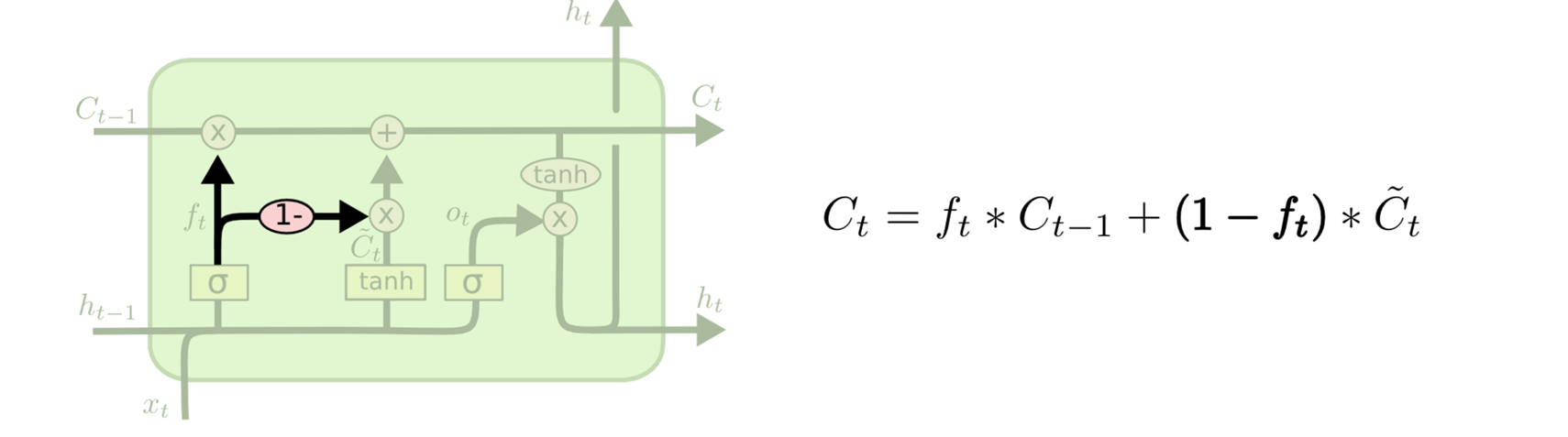
new_state = (LSTMStateTuple(c, m) if self._state_is_tuple
else array_ops.concat(1, [c, m]))
return m, new_state
def basic_rnn_seq2seq(
encoder_inputs, decoder_inputs, cell, dtype=dtypes.float32, scope=None):
with variable_scope.variable_scope(scope or "basic_rnn_seq2seq"):
_, enc_state = rnn.rnn(cell, encoder_inputs, dtype=dtype)
return rnn_decoder(decoder_inputs, enc_state, cell)
def rnn_decoder(decoder_inputs, initial_state, cell, loop_function=None,
scope=None):
with variable_scope.variable_scope(scope or "rnn_decoder"):
state = initial_state
outputs = []
prev = None
for i, inp in enumerate(decoder_inputs):
if loop_function is not None and prev is not None:
with variable_scope.variable_scope("loop_function", reuse=True):
inp = loop_function(prev, i)
if i > 0:
variable_scope.get_variable_scope().reuse_variables()
output, state = cell(inp, state)
outputs.append(output)
if loop_function is not None:
prev = output
return outputs, state
这里decoder用了encoder的最后一个state 作为输入
然后输出结果是decoder过程最后的state 加上所有ouput的集合(也就是hidden的集合)
注意ouputs[-1]其实数值和state里面的m是一致的
当然有可能后面outputs 用dynamic rnn 会补0
encode_feature, state = melt.rnn.encode(
cell,
inputs,
seq_length,
encode_method=0,
output_method=3)
encode_feature.eval()
array([[[ 4.27834410e-03, 1.45841937e-03, 1.25767402e-02,
5.00775501e-03],
[ 6.24437723e-03, 2.60074623e-03, 2.32168660e-02,
9.47457738e-03],
[ 7.59789022e-03, -5.34060055e-05, 1.64511874e-02,
-5.71310846e-03],
[ 0.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00,
0.00000000e+00]]], dtype=float32)
state[1].eval()
array([[ 7.59789022e-03, -5.34060055e-05, 1.64511874e-02,
-5.71310846e-03]], dtype=float32)





















 7255
7255

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








