由前两篇博客大概了解了SS的启动初始化和表单登陆的过程
- 在初始化过程中,Security会加载用户配置的权限信息,比如:
http.authorizeRequests()
// .antMatchers("/")
// .permitAll() // 请求路径"/"允许访问
// .anyRequest()
// .authenticated() // 其它请求都不需要校验才能访问
.antMatchers("/home")
.hasRole("LOGOPR")
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login") // 定义登录的页面"/login",允许访问
.permitAll()
.failureUrl("/login?#error=1111")
// .failureHandler(failHander)
.and()
.logout() // 默认的"/logout", 允许访问
.permitAll();
}这里面就包含了请求及对应的权限,比如/home需要LOGOPR角色,等等
- 表单登陆成功之后,SS中就存储了当前用户的信息,也就包括了用户的权限
那么在访问的时候,SS就能根据访问路径的权限与访问用户的权限进行比对,符合则通过,不符合就抛出异常重定向到指定界面
看看访问授权的时序图:
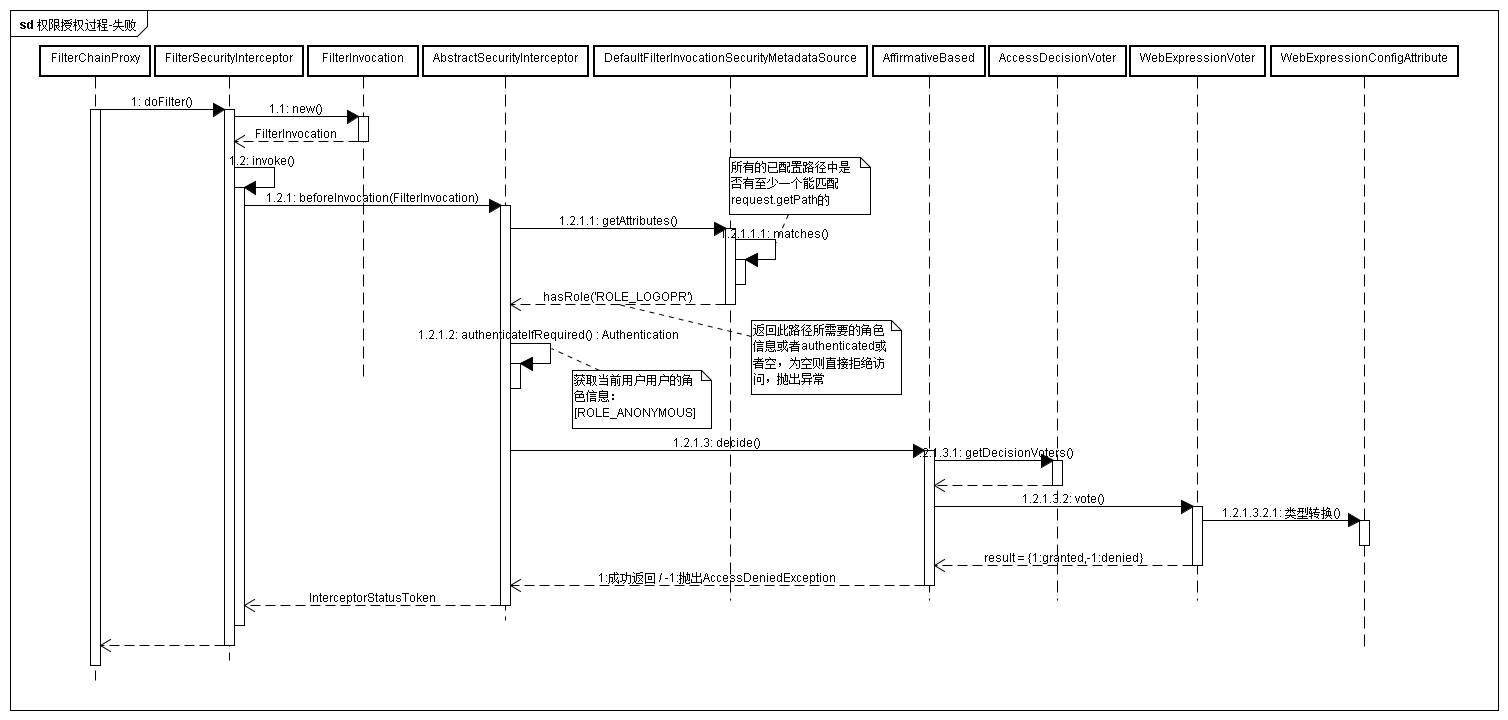
代码的调用比较复杂,上图简单化了,主要是一个授权的过程,下面就根据源码来瞧瞧吧!
以上面的代码为例,访问/home需要LOGOPR权限,登陆用户默认拥有ROLE_USER权限
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
FilterInvocation fi = new FilterInvocation(request, response, chain);
invoke(fi);
}
//invoke
public void invoke(FilterInvocation fi) throws IOException, ServletException {
if ((fi.getRequest() != null)
&& (fi.getRequest().getAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED) != null)
&& observeOncePerRequest) {
// filter already applied to this request and user wants us to observe
// once-per-request handling, so don't re-do security checking
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
} else {
// first time this request being called, so perform security checking
if (fi.getRequest() != null && observeOncePerRequest) {
fi.getRequest().setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED, Boolean.TRUE);
}
InterceptorStatusToken token = super.beforeInvocation(fi);
try {
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
} finally {
super.finallyInvocation(token);
}
super.afterInvocation(token, null);
}
}看到代码中调用父类AbstractSecurityInterceptor的beforeInvocation(),调用前,返回一个InterceptorStatusToken,后续还会调用afterInvocation,那么继续跟进beforeInvocation:
protected InterceptorStatusToken beforeInvocation(Object object) {
Assert.notNull(object, "Object was null");
final boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
if (!getSecureObjectClass().isAssignableFrom(object.getClass())) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Security invocation attempted for object "
+ object.getClass().getName()
+ " but AbstractSecurityInterceptor only configured to support secure objects of type: "
+ getSecureObjectClass());
}
Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes = this.obtainSecurityMetadataSource()
.getAttributes(object);
if (attributes == null || attributes.isEmpty()) {
if (rejectPublicInvocations) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Secure object invocation "
+ object
+ " was denied as public invocations are not allowed via this interceptor. "
+ "This indicates a configuration error because the "
+ "rejectPublicInvocations property is set to 'true'");
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Public object - authentication not attempted");
}
publishEvent(new PublicInvocationEvent(object));
return null; // no further work post-invocation
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Secure object: " + object + "; Attributes: " + attributes);
}
if (SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() == null) {
credentialsNotFound(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractSecurityInterceptor.authenticationNotFound",
"An Authentication object was not found in the SecurityContext"),
object, attributes);
}
Authentication authenticated = authenticateIfRequired();
// Attempt authorization
try {
this.accessDecisionManager.decide(authenticated, object, attributes);
}
catch (AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException) {
publishEvent(new AuthorizationFailureEvent(object, attributes, authenticated,
accessDeniedException));
throw accessDeniedException;
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Authorization successful");
}
if (publishAuthorizationSuccess) {
publishEvent(new AuthorizedEvent(object, attributes, authenticated));
}
// Attempt to run as a different user
Authentication runAs = this.runAsManager.buildRunAs(authenticated, object,
attributes);
if (runAs == null) {
if (debug) {
logger.debug("RunAsManager did not change Authentication object");
}
// no further work post-invocation
return new InterceptorStatusToken(SecurityContextHolder.getContext(), false,
attributes, object);
}
else {
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Switching to RunAs Authentication: " + runAs);
}
SecurityContext origCtx = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext());
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(runAs);
// need to revert to token.Authenticated post-invocation
return new InterceptorStatusToken(origCtx, true, attributes, object);
}
}先调用DefaultFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource的getAttributes方法,返回一个Collection<ConfigAttribute>,是一个ConfigAttribute集合,代码比较简单:
public Collection<ConfigAttribute> getAttributes(Object object) {
final HttpServletRequest request = ((FilterInvocation) object).getRequest();
for (Map.Entry<RequestMatcher, Collection<ConfigAttribute>> entry : requestMap
.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getKey().matches(request)) {
return entry.getValue();
}
}
return null;
}注意requestMap,如下:

{
ExactUrl [processUrl='/login?#error=1111']=[permitAll],
ExactUrl [processUrl='/login']=[permitAll],
ExactUrl [processUrl='/login']=[permitAll],
ExactUrl [processUrl='/login?logout']=[permitAll],
Ant [pattern='/home']=[hasRole('ROLE_LOGOPR'),
Ant [pattern='/logout', POST]=[permitAll],]
}
可以看到这个requestMap保存的就是在自定义HttpSecurity的配置的路径-权限信息,遍历此Map,和请求的request进行匹配,请求的路径是/home,匹配成功,如下:
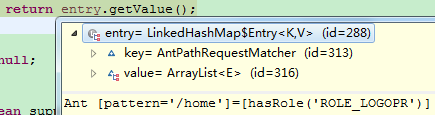
返回的value:
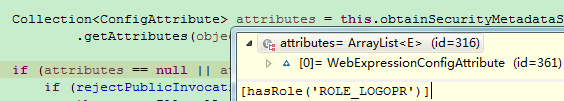
可以看到,/home匹配的权限信息就是上面配置的ROLE_LOGOPR
继续跟进,直到:
Authentication authenticated = authenticateIfRequired();
从方法命名(是否必须授权)可以看出,这里就是返回授权用户的方法,从登陆流程就直到,登陆成功的结果就是产生一个Authentication对象的过程,返回的对象如下:
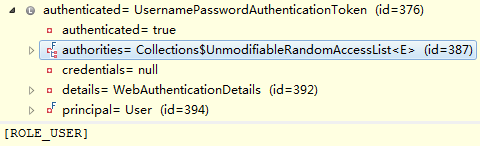
org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken@b43690ca:
Principal: org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User@f02988d6:
Username: username;
Password: [PROTECTED];
Enabled: true;
AccountNonExpired: true;
credentialsNonExpired: true;
AccountNonLocked: true;
Granted Authorities: ROLE_USER;
Credentials: [PROTECTED];
Authenticated: true;
Details: org.springframework.security.web.authentication.WebAuthenticationDetails@21a2c:
RemoteIpAddress: 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1;
SessionId: A08566CA24D4246E04EFC436D3738400;
Granted Authorities: ROLE_USER
这个时候,访问请求的路径及权限,登陆用户的信息都已经获取了,下面就是决定是否能访问了!!!
执行:this.accessDecisionManager.decide(authenticated, object, attributes);
调用AffirmativeBased的decide方法:
public void decide(Authentication authentication, Object object,
Collection<ConfigAttribute> configAttributes) throws AccessDeniedException {
int deny = 0;
for (AccessDecisionVoter voter : getDecisionVoters()) {
int result = voter.vote(authentication, object, configAttributes);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Voter: " + voter + ", returned: " + result);
}
switch (result) {
case AccessDecisionVoter.ACCESS_GRANTED:
return;
case AccessDecisionVoter.ACCESS_DENIED:
deny++;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
if (deny > 0) {
throw new AccessDeniedException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractAccessDecisionManager.accessDenied", "Access is denied"));
}
// To get this far, every AccessDecisionVoter abstained
checkAllowIfAllAbstainDecisions();
}通过遍历一个投票器集合来决定int deny的值,由其判断授权的结果!
查看投票器集合,仅有一个WebExpressionVoter,调用其vote方法:
public int vote(Authentication authentication, FilterInvocation fi,
Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes) {
assert authentication != null;
assert fi != null;
assert attributes != null;
WebExpressionConfigAttribute weca = findConfigAttribute(attributes);
if (weca == null) {
return ACCESS_ABSTAIN;
}
EvaluationContext ctx = expressionHandler.createEvaluationContext(authentication,
fi);
ctx = weca.postProcess(ctx, fi);
return ExpressionUtils.evaluateAsBoolean(weca.getAuthorizeExpression(), ctx) ? ACCESS_GRANTED
: ACCESS_DENIED;
}由attributes生成WebExpressionConfigAttribute对象weca,由authentication生成EvaluationContext对象ctx,关键调用:ctx = weca.postProcess(ctx, fi);
返回更新后的ctx:
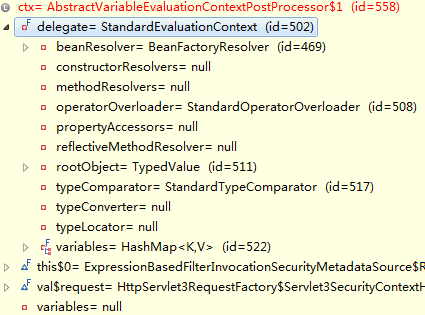
后续主要调用spring的方法,后面再跟进
执行WebExpressionVoter完毕,返回int结果为-1,那么deny++,deny=1,代码抛出异常:
if (deny > 0) {
throw new AccessDeniedException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractAccessDecisionManager.accessDenied", "Access is denied"));
}异常捕获,直到doFilter结束。。。
先暂停!







 本文详细解析了Spring Security框架中的权限验证过程,包括初始化配置、表单登录、权限信息加载等核心步骤,并深入探讨了权限匹配和投票决策机制。
本文详细解析了Spring Security框架中的权限验证过程,包括初始化配置、表单登录、权限信息加载等核心步骤,并深入探讨了权限匹配和投票决策机制。

















 1911
1911

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








