1. 轮询全局变量
2. 使用事件驱动
A. 信号量
(1) 二进制信号量(resource/binary semaphore)< 互斥锁 Mutex( Mutual exclusion ) >
信号量只有二进制的0或1
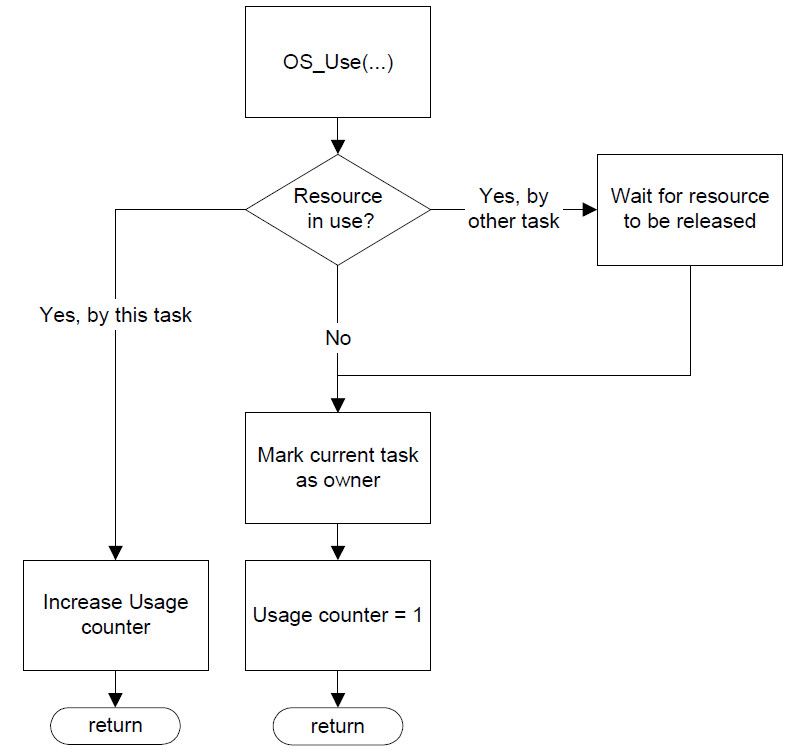
OS_Use() Claims a resource and blocks it for other tasks
OS_Unuse() Releases a semaphore currently in use by a task.
OS_Request() Requests a specified semaphore, blocks it for other tasks if it is available. Continues execution in any case.
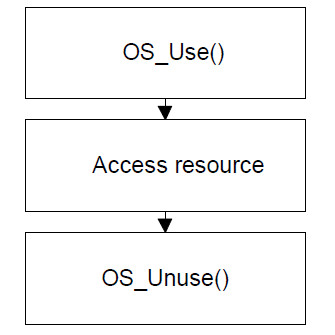
Claims a resource and blocks it for other tasks.
Requests a specified semaphore and blocks it for other tasks if it is available.
Continues execution in any case

(2) 计数信号量(counting/general semaphore)
信号量是一个任意的整数
OS_SignalCSema() Increments the counter of a semaphore
OS_WaitCSema() Decrements the counter of a semaphore.
OS_CSemaRequest() Decrements the counter of a semaphore, if available.
B. 消息
(1) 邮箱 - 1..127 字节的消息 ( 消息字节数 -- 固定的)
OS_PutMail() Stores a new message of a predefined size in a mailbox.
OS_WaitMail() Waits until a mail is available, but does not retrieve the message from the mailbox.
OS_GetMail() Retrieves a message of a predefined size from a mailbox.
OS_PeekMail() Reads a mail from a mailbox without removing it
(2) 队列 - 大于 127 字节的消息 ( 消息字节数 -- 可变的 )
OS_Q_Put() Stores a new message of given size in a queue.
OS_Q_PutBlocked() Stores a new message of given size in a queue. Blocks the calling task when queue is full.
OS_Q_GetPtr() Retrieves a message from a queue.
OS_Q_GetPtrCond() Retrieves a message from a queue, if one message is available or returns without suspension.
OS_Q_GetPtrTimed() Retrieves a message from a queue within a specified time, if one message is available.
OS_Q_Purge() Deletes the last retrieved message in a queue.
C. 事件
(1) 任务事件 - 每一个任务有 1 字节 事件掩码 ( 8 个事件 )
OS_SignalEvent() Signals event(s) to a specified task.
OS_WaitEvent() Waits for one of the events specified in the bitmask and clears the event memory after an event occurs.
OS_WaitSingleEvent() Waits for one of the events specified as bitmask and clears only that event after it occurs.
OS_WaitEvent_Timed() Waits for the specified events for a given time, and clears the event memory after an event occurs.
OS_WaitSingleEventTimed() Waits for the specified events for a given time; after an event occurs, only that event is cleared.
(2) 事件对象 - the signaling function does not need to know which task is waiting for the event to occur
OS_EVENT_Wait() Waits for an event.
OS_EVENT_WaitTimed() Waits for an event with timeout and resets the event after it occurs.
OS_EVENT_Set() Sets the events, or resumes waiting tasks.
OS_EVENT_Reset() Resets the event to none-signaled state.
OS_EVENT_Pulse() Sets the event, resumes waiting tasks, if any,and then resets the event.
OS_EVENT_Get() Returns the state of an event object.




 本文深入探讨了信号量和消息机制在操作系统中的应用,包括二进制信号量、计数信号量、邮箱、队列、事件等核心概念及其工作原理。
本文深入探讨了信号量和消息机制在操作系统中的应用,包括二进制信号量、计数信号量、邮箱、队列、事件等核心概念及其工作原理。

















 205
205

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








