Golang加密系列的最后一篇,嗯,RSA涉及的概念太多,弄了好久才搞清楚。。。
代码的结构如下图
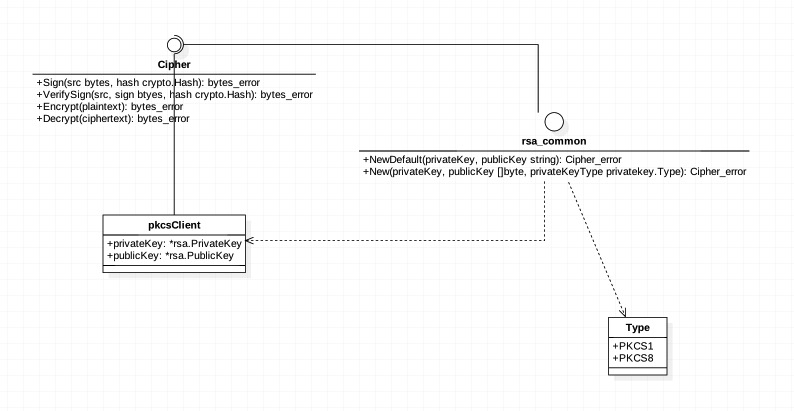
PS:StarUML这玩意在Mac上所有连到Interface的线都变成直线了...我很惆怅...
定义一个对外开放的接口
package rsa
import "crypto"
type Cipher interface {
Encrypt(plaintext []byte) ([]byte, error)
Decrypt(ciphertext []byte) ([]byte, error)
Sign(src []byte, hash crypto.Hash) ([]byte, error)
Verify(src []byte, sign []byte, hash crypto.Hash) error
}RSA也是一个块加密算法,总是在一个固定大小的块(block)上进行操作。但跟AES等不同的是,RSA 的block size是跟key length 以及所使用的填充模式有关的。填充方式有以下几种。
1、RSA_PKCS1_PADDING 填充模式,最常用的模式。
输入block长度 : block size比RSA 钥模长(modulus) 短至少11个字节, 也就是RSA_size(rsa) – 11
输出结果长度 : 和modulus一样长
例如,对于1024bit的密钥,blockSize = 1024/8 – 11 = 117 字节
2、RSA_PKCS1_OAEP_PADDING
输入block长度:RSA_size(rsa) – 41
输出结果长度 : 和modulus一样长
3、RSA_NO_PADDING
不填充
解密的时候,如果密文长度过长,也需要切分成多个块进行解密,block size 和 key length 是相等的。
这里仅支持了第一种填充方式。
package rsa
func pkcs1Padding(src []byte, keySize int) [][]byte {
srcSize := len(src)
blockSize := keySize - 11
var v [][]byte
if srcSize <= blockSize {
v = append(v, src)
} else {
groups := len(src) / blockSize
for i := 0; i < groups; i++ {
block := src[:blockSize]
v = append(v, block)
src = src[blockSize:]
if len(src) < blockSize {
v = append(v, src)
}
}
}
return v
}
func unPadding(src []byte, keySize int) [][]byte {
srcSize := len(src)
blockSize := keySize
var v [][]byte
if srcSize == blockSize {
v = append(v, src)
} else {
groups := len(src) / blockSize
for i := 0; i < groups; i++ {
block := src[:blockSize]
v = append(v, block)
src = src[blockSize:]
}
}
return v
}定义私有的pkcsClient ,实现Cipher接口, PKCS格式的私钥都使用这个client
package rsa
import (
"bytes"
"crypto"
"crypto/rand"
"crypto/rsa"
)
type pkcsClient struct {
privateKey *rsa.PrivateKey
publicKey *rsa.PublicKey
}
func (this *pkcsClient) Encrypt(plaintext []byte) ([]byte, error) {
blocks := pkcs1Padding(plaintext, this.publicKey.N.BitLen()/8)
buffer := bytes.Buffer{}
for _, block := range blocks {
ciphertextPart, err := rsa.EncryptPKCS1v15(rand.Reader, this.publicKey, block)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
buffer.Write(ciphertextPart)
}
return buffer.Bytes(), nil
}
func (this *pkcsClient) Decrypt(ciphertext []byte) ([]byte, error) {
ciphertextBlocks := unPadding(ciphertext, this.privateKey.N.BitLen()/8)
buffer := bytes.Buffer{}
for _, ciphertextBlock := range ciphertextBlocks {
plaintextBlock, err := rsa.DecryptPKCS1v15(rand.Reader, this.privateKey, ciphertextBlock)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
buffer.Write(plaintextBlock)
}
return buffer.Bytes(), nil
}
func (this *pkcsClient) Sign(src []byte, hash crypto.Hash) ([]byte, error) {
h := hash.New()
h.Write(src)
hashed := h.Sum(nil)
return rsa.SignPKCS1v15(rand.Reader, this.privateKey, hash, hashed)
}
func (this *pkcsClient) Verify(src []byte, sign []byte, hash crypto.Hash) error {
h := hash.New()
h.Write(src)
hashed := h.Sum(nil)
return rsa.VerifyPKCS1v15(this.publicKey, hash, hashed, sign)
}将私钥类型定义成枚举类型
package privatekey
type Type int64
const (
PKCS1 Type = iota
PKCS8
)定义一个New/NewDefault函数,用于创建client
package rsa
import (
"crypto/rsa"
"crypto/x509"
"encoding/pem"
"errors"
"github.com/89hmdys/toast/rsa/privatekey"
)
//默认客户端,pkcs8私钥格式,pem编码
func NewDefault(privateKey, publicKey string) (Cipher, error) {
blockPri, _ := pem.Decode([]byte(privateKey))
if blockPri == nil {
return nil, errors.New("private key error")
}
blockPub, _ := pem.Decode([]byte(publicKey))
if blockPub == nil {
return nil, errors.New("public key error")
}
return New(blockPri.Bytes, blockPub.Bytes, privatekey.PKCS8)
}
func New(privateKey, publicKey []byte, privateKeyType privatekey.Type) (Cipher, error) {
priKey, err := genPriKey(privateKey, privateKeyType)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
pubKey, err := genPubKey(publicKey)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return &pkcsClient{privateKey: priKey, publicKey: pubKey}, nil
}
func genPubKey(publicKey []byte) (*rsa.PublicKey, error) {
pub, err := x509.ParsePKIXPublicKey(publicKey)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return pub.(*rsa.PublicKey), nil
}
func genPriKey(privateKey []byte, privateKeyType privatekey.Type) (*rsa.PrivateKey, error) {
var priKey *rsa.PrivateKey
var err error
switch privateKeyType {
case privatekey.PKCS1:
{
priKey, err = x509.ParsePKCS1PrivateKey([]byte(privateKey))
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
}
case privatekey.PKCS8:
{
prkI, err := x509.ParsePKCS8PrivateKey([]byte(privateKey))
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
priKey = prkI.(*rsa.PrivateKey)
}
default:
{
return nil, errors.New("unsupport private key type")
}
}
return priKey, nil
}最后,看看如何使用上面的代码来进行加密/解密,签名验签
package rsa_test
import (
"crypto"
"encoding/base64"
"encoding/hex"
"fmt"
"testing"
"toast/rsa"
)
var cipher rsa.Cipher
func init() {
client, err := rsa.NewDefault(`-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----
私钥信息
-----END PRIVATE KEY-----`, `-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----
公钥信息
-----END PUBLIC KEY-----`)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
cipher = client
}
func Test_DefaultClient(t *testing.T) {
cp, err := cipher.Encrypt([]byte("测试加密解密"))
if err != nil {
t.Error(err)
}
cpStr := base64.URLEncoding.EncodeToString(cp)
fmt.Println(cpStr)
ppBy, err := base64.URLEncoding.DecodeString(cpStr)
if err != nil {
t.Error(err)
}
pp, err := cipher.Decrypt(ppBy)
fmt.Println(string(pp))
}
func Test_Sign_DefaultClient(t *testing.T) {
src := "测试签名验签"
signBytes, err := cipher.Sign([]byte(src), crypto.SHA256)
if err != nil {
t.Error(err)
}
sign := hex.EncodeToString(signBytes)
fmt.Println(sign)
signB, err := hex.DecodeString(sign)
errV := cipher.Verify([]byte(src), signB, crypto.SHA256)
if errV != nil {
t.Error(errV)
}
fmt.Println("verify success")
}关于RSA相关的一些概念,参见我的另一篇博客.pem引发的血案
这里还有一个已经编写好的AES/RSA加解密的包,可以直接引用,github地址:https://github.com/89hmdys/toast
2月14日补充,
近期公司对接了一个保险平台,对数据进行RSA加密的时候发现当待加密数据长度超过了秘钥长度时,会报错(比如生成了1024bit/128byte的秘钥,那么待加密的数据长度只能是<=128byte,而输出的数据长度是和秘钥长度相等的)
找了些资料,发现rsa加密如果数据过长的时候,需要对数据进行分片,根据所选择的填充方式的不同,每片的数据长度也不一样。例如选择PKCS1填充方式的时候,数据长度=秘钥长度-MIN(11)。




 本文深入探讨了Golang中RSA加密的实现细节,包括密钥处理、数据分片及填充方式的选择,并提供了完整的示例代码。
本文深入探讨了Golang中RSA加密的实现细节,包括密钥处理、数据分片及填充方式的选择,并提供了完整的示例代码。

















 821
821

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








