Question: Median of Two Sorted Arrays
My Answer in C
int* UnionTwoArrays(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int* nums2, int nums2Size) { // UnionTwoArrays
int* ans;
ans = (int*)malloc((nums1Size+nums2Size+1) * sizeof(int));
int p1 = 0, p2 = 0, p = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums1Size+nums2Size; i++) {
if (p1 >= nums1Size) { // if out of bound
ans[p] = nums2[p2]; p2++; p++; continue;
} else if (p2 >= nums2Size) {
ans[p] = nums1[p1]; p1++; p++; continue;
}
if (nums1[p1] < nums2[p2]) { // normal judge
ans[p] = nums1[p1]; p1++; p++;
} else {
ans[p] = nums2[p2]; p2++; p++;
}
}
return ans;
}
double findMedianSortedArrays(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int* nums2, int nums2Size) {
int* unionarrays = (int*)malloc((nums1Size+nums2Size+1) * sizeof(int));
unionarrays = UnionTwoArrays(nums1, nums1Size, nums2, nums2Size);
double ans = 0; int index = (nums1Size+nums2Size)/2;
if ((nums1Size+nums2Size)%2 == 0) {
ans = (unionarrays[index]+unionarrays[index-1])*1.0/2;
} else {
ans = unionarrays[index];
}
return ans;
}Test Environment
//
// main.cpp
// Median of Two Sorted Arrays
//
// Created by wasdns on 17/2/4.
// Copyright © 2017年 wasdns. All rights reserved.
//
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <algorithm>
int* UnionTwoArrays(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int* nums2, int nums2Size) {···}
double findMedianSortedArrays(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int* nums2, int nums2Size) {···}
void PrintArrays(int* p, int n) { // Print Arrays
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", p[i]); printf("\n");
}
int main() {
int n1, n2;
scanf("%d%d", &n1, &n2);
int* p1; int* p2;
p1 = (int*)malloc(n1*(sizeof(int)));
p2 = (int*)malloc(n2*(sizeof(int)));
for (int i = 0; i < n1; i++) {
scanf("%d", &p1[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n2; i++) {
scanf("%d", &p2[i]);
}
PrintArrays(p1, n1);
PrintArrays(p2, n2);
PrintArrays(UnionTwoArrays(p1, n1, p2, n2), n1+n2);
printf("%lf\n", findMedianSortedArrays(p1, n1, p2, n2));
return 0;
}Better Solutions
Better Solutions: Share my O(log(min(m,n)) solution with explanation
Details
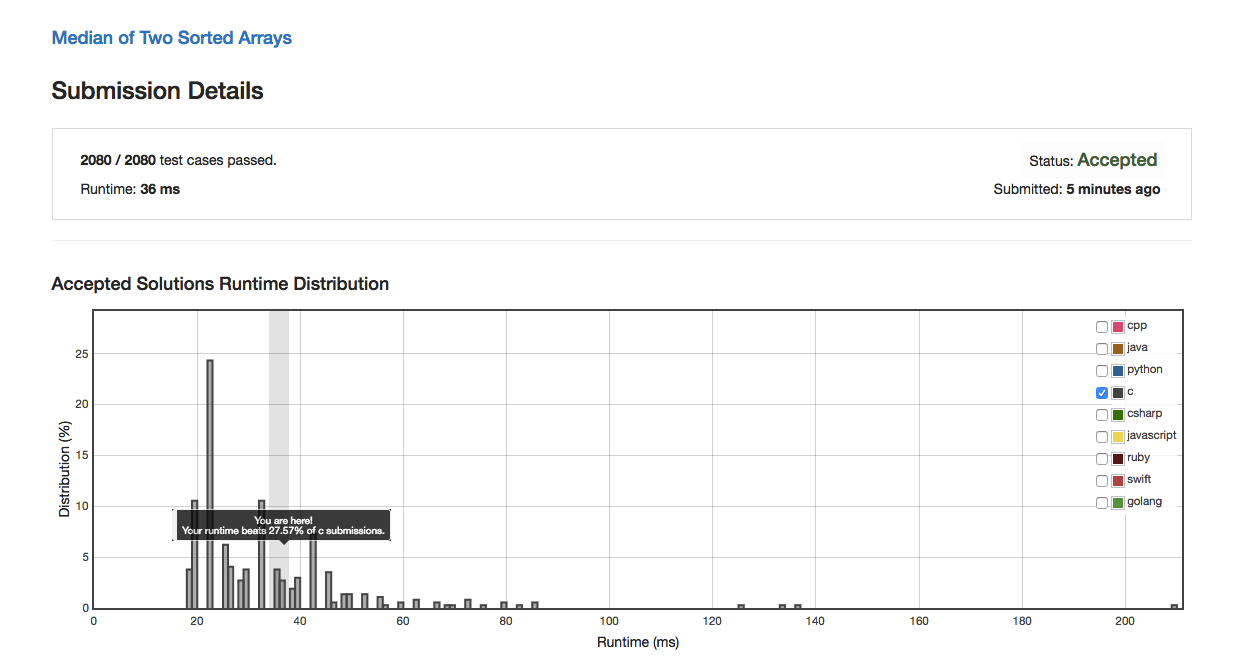
Feelings and Review
看到本题马上反映到归并排序的合并思想,将两个字符串合并之后再找中间值,合并的时候维护两个指针指向两个字符串的元素,并考虑两种情况:1.两个字符串等长时(或者还没有遍历到字符串尾),比较两个指针指向元素的大小,判断之后移动指针;2.两个字符串不等长时,如A字符串长度小于B字符串,则需要在遍历完A字符串之后将B字符串后续的字符接上。
当然,如此暴力的solution时间复杂度为O(n+m)。本题自然还有效率更高的解法 => 上文引用的Better Solutions => 时间复杂度O(log(min(n+m))),使用的方法很巧妙,是二分的变种,值得思索!
2017/2/4




 本文提供了一种通过合并两个有序数组来查找中位数的C语言实现方案。该方法首先将两个数组合并成一个新的有序数组,然后根据数组总长度的奇偶性找到中位数。此外,还讨论了更高效的O(log(min(m,n)))解决方案。
本文提供了一种通过合并两个有序数组来查找中位数的C语言实现方案。该方法首先将两个数组合并成一个新的有序数组,然后根据数组总长度的奇偶性找到中位数。此外,还讨论了更高效的O(log(min(m,n)))解决方案。

















 291
291

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








