1. 以 Hibernate Shards 数据的水平、垂直切割(一)- Hibernate测试环境的项目为基础
2. Hibernate Shards使用了 commons logging,下载个项目最新的release版本。这里用的版本为1.1.1
3. 在 Hibernate Shards 数据的水平、垂直切割(一)- Hibernate测试环境中,我们在mysql中建立了一个hbshards数据库,为了测试shards再建立一个hbshards2的数据库,contact表的结构一样
4. 将Hibernate Shards发布包中的hibernate-shards.jar放到lib目录
项目引用添加hibernate-shards.jar
将commons logging发布包中的commons-logging-1.1.1.jar放到lib目录
CLASSPATH中添加hibernate-shards.jar、commons-logging-1.1.1.jar
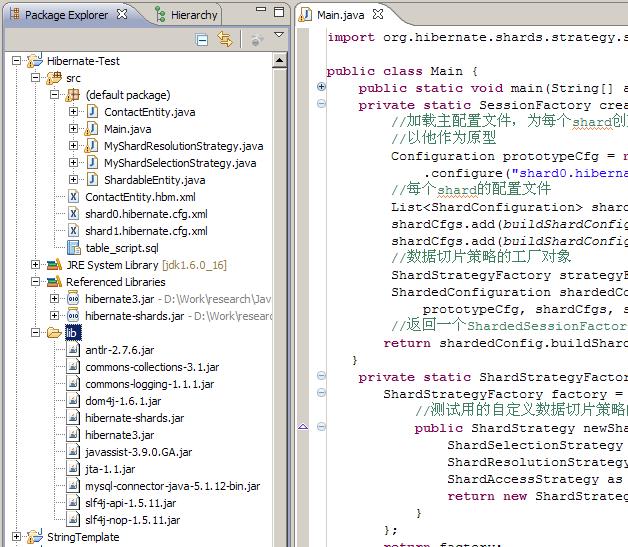
Hibernate Shards测试项目
出于结构上的简单考虑,定义一个ShardableEntity的接口,让ContactEntity实现这个接口:
public interface ShardableEntity {
public String getIdentifier();
}
public class ContactEntity implements ShardableEntity {
public String getIdentifier(){
return this._id;
}
//other code omitted is the same with previous post
}因为我们需要将contact的数据以切片的形式存入2个数据库中,因此需要配置这2个数据库的信息。Hibernate Shards通过定义2个hibernate的配置文件解决这个问题:
shard0.hibernate.cfg.xml:
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost/hbshards</property>
<property name="connection.username">root</property>
<property name="connection.password">dev</property>
<property name="connection.pool_size">10</property>
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLInnoDBDialect</property>
<property name="hbm2ddl.auto">validate</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.shard_id">0</property>
<property name="hibernate.shard.enable_cross_shard_relationship_checks">false</property>
<mapping resource="ContactEntity.hbm.xml" />
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration> shard1.hibernate.cfg.xml:
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost/hbshards2</property>
<property name="connection.username">root</property>
<property name="connection.password">dev</property>
<property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLInnoDBDialect</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.shard_id">1</property>
<property name="hibernate.shard.enable_cross_shard_relationship_checks">false</property>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration> 其中shard0.hibernate.cfg.xml作为主要的配置文件,针对每个shard创建的SessionFactory对象,除了数据库连接信息的配置之外,都来自shard0.hibernate.cfg.xml
针对其他每个shard创建的SessionFactory,数据库连接信息从相应的配置文件(例如shard1.hibernate.cfg.xml)中读取,读取的内容包括connection.url、connection.username、connection.password、connection.datasource。为了hibernate加载其他shard的配置文件时不抛异常,在其他shard的配置文件中我们还是把必要的配置属性写上去了
hibernate.connection.shard_id属性为每个shard定义一个id,必须有一个shard_id为0的shard,其他的shard_id可以定义为任意整数
我们假定contact的id都是由数字组成的一个8位长度的字符串
对contact的切割策略简单定义为: contact id第一个字符为0-4的存入shard0中,为5-9的存入shard1中
为了实现这一策略,我们需要实现hibernate shards的2个接口
ShardResolutionStrategy接口的实现:
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import org.hibernate.shards.strategy.resolution.ShardResolutionStrategy;
import org.hibernate.shards.strategy.selection.ShardResolutionStrategyData;
import org.hibernate.shards.ShardId;
/*
* a simple ShardResolutionStrategy implementation for our ContactEntity
*/
public class MyShardResolutionStrategy implements ShardResolutionStrategy {
private List<ShardId> _shardIds;
public MyShardResolutionStrategy(List<ShardId> shardIds){
this._shardIds = shardIds;
}
public List selectShardIdsFromShardResolutionStrategyData(
ShardResolutionStrategyData arg0){
List ids = new ArrayList();
String id = (String)arg0.getId();
if(id==null || id.isEmpty()) ids.add(this._shardIds.get(0));
else{
//our shard selection is identified by the
//first char(number) in contact id
//0-4 => shards0, 5-9 => shards1
Integer i = new Integer(id.substring(0, 1));
ids.add(this._shardIds.get(i/5));
}
return ids;
}
}import java.util.List;
import org.hibernate.shards.ShardId;
import org.hibernate.shards.strategy.selection.ShardSelectionStrategy;
/*
* a simple ShardSelectionStrategy implementation for our ContactEntity
*/
public class MyShardSelectionStrategy implements ShardSelectionStrategy {
private List<ShardId> _shardIds;
public MyShardSelectionStrategy(List<ShardId> shardIds){
this._shardIds=shardIds;
}
public ShardId selectShardIdForNewObject(Object obj) {
if(obj instanceof ShardableEntity) {
String id = ((ShardableEntity)obj).getIdentifier();
if(id==null || id.isEmpty()) return this._shardIds.get(0);
Integer i = new Integer(id.substring(0, 1));
//our shard selection is identified by the
//first char(number) in contact id
//0-4 => shards0, 5-9 => shards1
return this._shardIds.get(i/5);
}
//for non-shardable entities we just use shard0
return this._shardIds.get(0);
}
}import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.hibernate.shards.*;
import org.hibernate.shards.cfg.*;
import org.hibernate.shards.strategy.*;
import org.hibernate.shards.strategy.access.*;
import org.hibernate.shards.strategy.resolution.*;
import org.hibernate.shards.strategy.selection.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HibernateShardsTest(args);
}
private static SessionFactory createSessionFactory() {
//加载主配置文件,为每个shard创建SessionFactory对象时将
//以他作为原型
Configuration prototypeCfg = new Configuration()
.configure("shard0.hibernate.cfg.xml");
//每个shard的配置文件
List<ShardConfiguration> shardCfgs = new ArrayList<ShardConfiguration>();
shardCfgs.add(buildShardConfig("shard0.hibernate.cfg.xml"));
shardCfgs.add(buildShardConfig("shard1.hibernate.cfg.xml"));
//数据切片策略的工厂对象
ShardStrategyFactory strategyFactory = buildShardStrategyFactory();
ShardedConfiguration shardedConfig = new ShardedConfiguration(
prototypeCfg, shardCfgs, strategyFactory);
//返回一个ShardedSessionFactory对象
return shardedConfig.buildShardedSessionFactory();
}
private static ShardStrategyFactory buildShardStrategyFactory() {
ShardStrategyFactory factory = new ShardStrategyFactory() {
//测试用的自定义数据切片策略的工厂类
public ShardStrategy newShardStrategy(List<ShardId> shardIds) {
ShardSelectionStrategy ss = new MyShardSelectionStrategy(shardIds);
ShardResolutionStrategy rs = new MyShardResolutionStrategy(shardIds);
ShardAccessStrategy as = new SequentialShardAccessStrategy();
return new ShardStrategyImpl(ss, rs, as);
}
};
return factory;
}
private static ShardConfiguration buildShardConfig(String configFile) {
Configuration config = new Configuration().configure(configFile);
return new ConfigurationToShardConfigurationAdapter(config);
}
private static void HibernateShardsTest(String[] args){
String loginId = "RicCC@cnblogs.com";
String password = "123";
if(args!=null && args.length==2){
loginId = args[0];
password = args[1];
}
SessionFactory factory = null;
try{
factory = createSessionFactory();
ShardsTestCreate(factory);
ShardsTestLogin(factory, loginId, password);
ShardsTestDelete(factory);
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(factory!=null) factory.close();
}
}
private static void ShardsTestCreate(SessionFactory factory){
Session session = null;
Transaction transaction = null;
System.out.println("===Create Contacts===");
try{
session = factory.openSession();
transaction = session.beginTransaction();
session.save(new ContactEntity("01111111","RicCC@cnblogs.com"
, "123", "Richie", "RicCC@cnblogs.com"));
session.save(new ContactEntity("91111111","a@cnblogs.com"
, "123", "AAA", "a@cnblogs.com"));
session.save(new ContactEntity("81111111","b@cnblogs.com"
, "123", "BBB", "b@cnblogs.com"));
session.save(new ContactEntity("31111111","c@cnblogs.com"
, "123", "CCC", "c@cnblogs.com"));
transaction.commit();
}catch(Exception e){
if(transaction!=null) transaction.rollback();
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(session!=null) session.close();
}
}
private static void ShardsTestLogin(SessionFactory factory
, String loginId, String password){
Session session = null;
ContactEntity c = null;
System.out.println("\n===Login Test===");
try{
session = factory.openSession();
List contacts = session.createQuery("from ContactEntity where LoginId=:loginId")
.setString("loginId", loginId)
.list();
if(contacts.isEmpty())
System.out.println("Contact \"" + loginId + "\" not found!");
else{
c = (ContactEntity)contacts.get(0);
if(c.getPassword().equals(password))
System.out.println("Contact \"" + loginId + "\" login successful");
else
System.out.println("Password is incorrect (should be: "
+ c.getPassword() + ", but is: " + password + ")");
}
System.out.println("\n===Get Contact by Id===");
c = (ContactEntity)session.get(ContactEntity.class, "81111111");
System.out.println(c.toString());
c = (ContactEntity)session.get(ContactEntity.class, "31111111");
System.out.println(c.toString());
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(session!=null) session.close();
}
}
private static void ShardsTestDelete(SessionFactory factory){
Session session = null;
Transaction transaction = null;
System.out.println("\n===Delete Contacts===");
try{
session = factory.openSession();
transaction = session.beginTransaction();
List contacts = session.createQuery("from ContactEntity").list();
Iterator it = contacts.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
session.delete(it.next());
}
transaction.commit();
}catch(Exception e){
if(transaction!=null) transaction.rollback();
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(session!=null) session.close();
}
}
}
运行测试
用Eclipse编译class文件,将生成的所有class文件以及相关的配置、映射文件 拷贝到lib目录中,运行Main.class结果如下:
D:\Work\research\Java\Hibernate-Test\lib>java Main
===Create Contacts===
Hibernate: insert into CONTACT (EMAIL, NAME, LOGIN_ID, PASSWORD, ID) values (?,?, ?, ?, ?)
Hibernate: insert into CONTACT (EMAIL, NAME, LOGIN_ID, PASSWORD, ID) values (?,?, ?, ?, ?)
Hibernate: insert into CONTACT (EMAIL, NAME, LOGIN_ID, PASSWORD, ID) values (?,?, ?, ?, ?)
Hibernate: insert into CONTACT (EMAIL, NAME, LOGIN_ID, PASSWORD, ID) values (?,?, ?, ?, ?)
===Login Test===
Hibernate: select contactent0_.ID as ID0_, contactent0_.EMAIL as EMAIL0_, contactent0_.NAME as NAME0_, contactent0_.LOGIN_ID as LOGIN4_0_, contactent0_.PASSWORD as PASSWORD0_ from CONTACT contactent0_ where contactent0_.LOGIN_ID=?
Hibernate: select contactent0_.ID as ID0_, contactent0_.EMAIL as EMAIL0_, contactent0_.NAME as NAME0_, contactent0_.LOGIN_ID as LOGIN4_0_, contactent0_.PASSWORD as PASSWORD0_ from CONTACT contactent0_ where contactent0_.LOGIN_ID=?
Contact "RicCC@cnblogs.com" login successful
===Get Contact by Id===
Hibernate: select contactent0_.ID as ID0_0_, contactent0_.EMAIL as EMAIL0_0_, contactent0_.NAME as NAME0_0_, contactent0_.LOGIN_ID as LOGIN4_0_0_, contactent0_.PASSWORD as PASSWORD0_0_ from CONTACT contactent0_ where contactent0_.ID=?
{ Id="81111111", LoginId="b@cnblogs.com", Name="BBB", EMail="b@cnblogs.com" }
Hibernate: select contactent0_.ID as ID0_0_, contactent0_.EMAIL as EMAIL0_0_, contactent0_.NAME as NAME0_0_, contactent0_.LOGIN_ID as LOGIN4_0_0_, contactent0_.PASSWORD as PASSWORD0_0_ from CONTACT contactent0_ where contactent0_.ID=?
{ Id="31111111", LoginId="c@cnblogs.com", Name="CCC", EMail="c@cnblogs.com" }
===Delete Contacts===
Hibernate: select contactent0_.ID as ID0_, contactent0_.EMAIL as EMAIL0_, contactent0_.NAME as NAME0_, contactent0_.LOGIN_ID as LOGIN4_0_, contactent0_.PASSWORD as PASSWORD0_ from CONTACT contactent0_
Hibernate: select contactent0_.ID as ID0_, contactent0_.EMAIL as EMAIL0_, contactent0_.NAME as NAME0_, contactent0_.LOGIN_ID as LOGIN4_0_, contactent0_.PASSWORD as PASSWORD0_ from CONTACT contactent0_
Hibernate: delete from CONTACT where ID=?
Hibernate: delete from CONTACT where ID=?
Hibernate: delete from CONTACT where ID=?
Hibernate: delete from CONTACT where ID=?
1. 通过id加载实体的时候,hibernate shards使用ShardSelectionStrategy来决定应当从哪个shard加载数据
2. 新增数据的时候,hibernate shards使用ShardResolutionStrategy来决定应当将数据insert到哪个shard中
这里为什么不能使用ShardSelectionStrategy呢?因为与id的生成机制相关,比如说可以让数据库来生成id(hibernate中的native方式),例如自增id,在shard的应用场景下可以简单的给每个shard一个起止范围,只是在insert数据的时候必须通过特定的算法决定将数据insert到哪个shard中,这样的情况下ShardSelectionStrategy是无法运用的。而对于assigned等类似的id生成机制,还是可以运用ShardSelectionStrategy策略的
3. 执行hql或者Criteria查询的时候,则使用ShardAccessStrategy从shard中查询数据
上面示例中的buildShardStrategyFactory方法中,我们使用了hibernate shards项目提供的SequentialShardAccessStrategy策略,这个策略在所有shards中逐个执行查询语句,然后对各个结果进行合并
基于上面几点,我们可以对上面测试运行后的输出做出解释了:
两个使用了hql的地方,都产生了两次sql查询,这是因为使用了SequentialShardAccessStrategy缘故,他从我们定义的两个shard中分别执行sql查询,合并结果集返回给调用者
把测试代码中的删除语句注释掉,运行测试后查询数据库,可以确认数据都是正确的insert在相应的shard中的
总结
上面演示了hibernate shards的基本用法,总体来看使用上非常简单,只需要针对实施shard的实体使用hibernate shards提供的ShardedSessionFactory即可
使用hibernate shards也存在一些限制,但大部分都是使用shards后的一些设计要求,或者是目前的it技术背景下对shards设计上的约束,在后面一篇中再详细整理一下这方面内容
文中使用的测试项目源文件在这里: 下载。引用到的jar文件需要从相关项目网站去下载




 本文介绍HibernateShards在Java项目的具体应用,包括环境搭建、数据库分片策略实现及测试代码示例。
本文介绍HibernateShards在Java项目的具体应用,包括环境搭建、数据库分片策略实现及测试代码示例。

















 145
145

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








