java8中加入了这个CompletableFuture对象,据说用起来会比较爽,Stream和CompletableFuture的设计都遵循了类似的模式:它们都使用了Lambda表达式以及流水线的思想。看oracle给出的说明,对于下面这样的查询数据库的操作
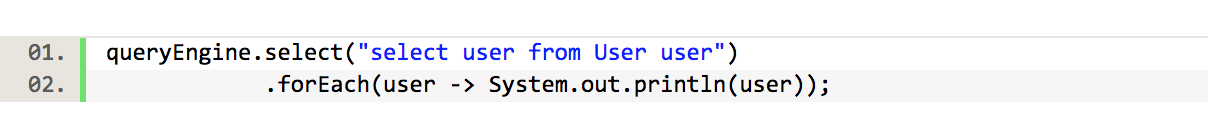
但是假设查询的数据库操作比较慢,我们想另起一个线程去执行,等执行完成的时候,打印出来结果,以前我们可以使用Callable,用ExcutorService执行。
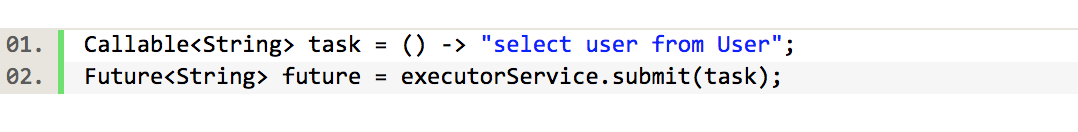

但是这里有个问题是,当调用future的get()方法获取结果,但是会阻塞当前调用的线程;它很难直接表述多个Future 结果之间的依赖性,实际开发中,我们经常需要达成这种目的,原来的Future接口的方法并不多。CompletionStage就应运而生了,然后我们重写上面的执行方法:
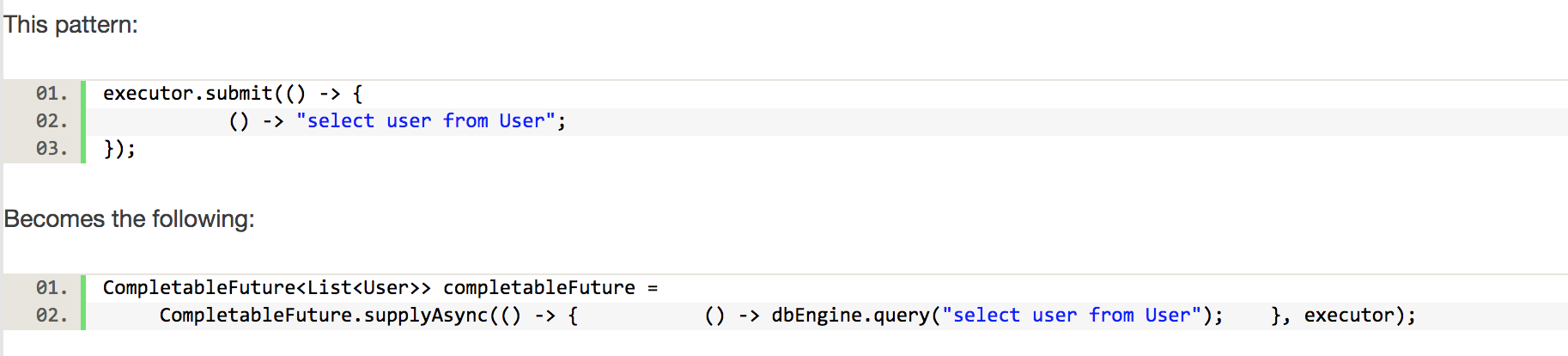
用CompletableFuture(实现了CompletionStage接口)的supplyAsync()方法取代了ExecutorService的submit(),而且可以把Executor作为第二个参数,提供执行的线程池的选择,没有阻塞当前线程。当然CompletableFuture也实现了Future接口,所以也同样可以使用get进行阻塞获取值。task可以是正在运行,或者已经完成返回结果,或者异常。

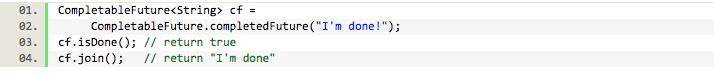
创建一个已完成的CompletableFuture,看起来很奇怪,为什么这么写,据说对于用于测试环境是很有用的,暴露不太写单元测试了。
从task创建一个CompletableFuture,这里有两种方式从一个Runnable或者supplier,当然还有第二参数是线程池的方法,runAsync()易于理解,注意它需要Runnable,因此它返回CompletableFuture<Void>作为Runnable不返回任何值。如果你需要处理异步操作并返回结果,使用Supplier<U>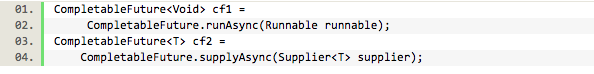
如果没有提供ExecutorService,会使用fork/join pool框架执行,这种方式也用于streams的并行操作,后续我们写的demo也是类似。关键的入参只有一个Function,它是函数式接口,所以使用Lambda表示起来会更加优雅。task可以是Function,Consumer或者Runnable。
public static void useWithThread() throws Exception{
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = new CompletableFuture();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//模拟执行耗时任务
System.out.println("task doing...");
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//告诉completableFuture任务已经完成
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread());
completableFuture.complete(121);
}
}).start();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread());
//获取任务结果,如果没有完成会一直阻塞等待
//如果发生异常 会被限制在执行任务的线程的范围内,最终会杀死该线程,而这会导致等待 get 方法返回结果的线程永久地被阻塞。
//客户端可以使用重载版本的 get 方法,它使用一个超时参数来避免发生这样的情况
Integer result=completableFuture.get();
//使用这种方法至少能防止程序永久地等待下去,超时发生时,程序会得到通知发生了 Timeout-Exception 。
// 不过,也因为如此,你不能指定执行任务的线程内到底发生了什么问题。
// Integer result=completableFuture.get(100, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("计算结果:"+result);
}
public static void useWithThreadCompleteException() throws Exception{
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture=new CompletableFuture();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
//模拟执行耗时任务
System.out.println("task doing...");
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
throw new RuntimeException("抛异常了");
}catch (Exception e) {
//告诉completableFuture任务发生异常了
completableFuture.completeExceptionally(e);
}
}
}).start();
String result=completableFuture.get(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("计算结果:"+result);
}
public static void useExceptionally() {
String result = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (1 == 1) {
throw new RuntimeException("测试一下异常情况");
}
return "s1";
}).exceptionally(e -> {
System.out.println(e.toString());
return "hello world";
}).join();
System.out.println(result);
}
/**
*方法接受一个生产者(Supplier)作为参数,返回一个 CompletableFuture
对象。生产者方法会交由 ForkJoinPool池中的某个执行线程( Executor )运行,
但是你也可以使用 supplyAsync 方法的重载版本,传递第二个参数指定线程池执行器执行生产者方法。
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void usesupplyAsync() throws Exception {
//supplyAsync内部使用ForkJoinPool线程池执行任务
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
//模拟执行耗时任务
System.out.println("task doing...");
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//返回结果
return "hello xin";
});
System.out.println("计算结果:"+completableFuture.get(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
}
public static void useAnyofAndAllof() throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture1=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
//模拟执行耗时任务
System.out.println("task1 doing...");
try {
Thread.sleep(10000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//返回结果
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread());
return "hello";
});
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture2=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
//模拟执行耗时任务
System.out.println("task2 doing...");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//返回结果
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread());
return "world";
});
/**
* 该方法接收一个 CompletableFuture 对象构成的数组,返回由第一个执行完毕的
* CompletableFuture 对象的返回值构成的 CompletableFuture<Object>
*/
CompletableFuture<Object> anyResult=CompletableFuture.anyOf(completableFuture1,completableFuture2);
System.out.println("第一个完成的任务结果:"+anyResult.get());
//allOf 工厂方法接收一个由CompletableFuture 构成的数组,数组中的所有
// Completable-Future 对象执行完成之后,它返回一个 CompletableFuture<Void> 对象。
// 这意味着,如果你需要等待多个 CompletableFuture 对象执行完毕,对 allOf 方法返回的
//CompletableFuture 执行 join 操作可以等待CompletableFuture执行完成
CompletableFuture<Void> allResult=CompletableFuture.allOf(completableFuture1,completableFuture2);
//阻塞等待所有任务执行完成
allResult.join();
System.out.println("所有任务执行完成");
}
/**
* //等第一个任务完成后,将任务结果传给参数result,执行后面的任务并返回一个代表任务的completableFuture
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void useThenCompose() throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture1=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
//模拟执行耗时任务
System.out.println("task1 doing...");
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//返回结果
return "hello";
}).thenCompose(result->CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
//模拟执行耗时任务
System.out.println("task2 doing...");
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//返回结果
return result+" world";
}));
System.out.println(completableFuture1.get(10,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
}
/**
* public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombine(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);
public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);
public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn,Executor executor);
* 将第一个任务与第二个任务组合一起执行,都执行完成后,将两个任务的结果合并
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void useThenCombine() throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//模拟执行耗时任务
System.out.println("task1 doing...");
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//返回结果
return 100;
}).thenCombine(
//第二个任务
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//模拟执行耗时任务
System.out.println("task2 doing...");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//返回结果
return 200;
}),
//合并函数
(result1, result2) -> result1 + result2);
System.out.println(completableFuture1.get(10,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
}
public static void usethenAccept() throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//模拟执行耗时任务
System.out.println("task1 doing...");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//返回结果
return 100;
});
//注册完成事件
completableFuture1.thenAccept(result->System.out.println("task1 done,result:"+result));
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture2=
//第二个任务
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//模拟执行耗时任务
System.out.println("task2 doing...");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//返回结果
return 2000;
});
//注册完成事件
completableFuture2.thenAccept(result->System.out.println("task2 done,result:"+result));
//将第一个任务与第二个任务组合一起执行,都执行完成后,将两个任务的结果合并
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture3 = completableFuture1.thenCombine(completableFuture2,
//合并函数
(result1, result2) -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result1 + result2;
});
System.out.println(completableFuture3.get());
}
/**
* public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn,Executor executor);
*/
public static void useThenApply() {
String result = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread());
return "hello";}
).thenApplyAsync(s -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread());return s + " world";}).join();
System.out.println(result);
}
/**
*public CompletionStage<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action,Executor executor);
*/
public static void useThenAccept(){
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "hello").thenAccept(s -> System.out.println(s+" world"));
}
/**
*public CompletionStage<Void> thenRun(Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action,Executor executor);
*/
public static void useThenRun() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread());
return "hello";
}).thenRun(() -> {
System.out.println(" world");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread());
}).get();
}
/* public <U> CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBoth(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action);
public <U> CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action);
public public<U> CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action, Executor executor);
*/
public static void useThenAcceptBoth() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "hello";
}).thenAcceptBoth(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "world";
}), (s1, s2) -> System.out.println(s1 + " " + s2)).get();
}
/*
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterBoth(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action,Executor executor);
*/
public static void useRunAfterBoth() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "s1";
}).runAfterBothAsync(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "s2";
}), () -> System.out.println("hello world")).get();
}
/* public <U> CompletionStage<U> applyToEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Function<? super T, U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Function<? super T, U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Function<? super T, U> fn,Executor executor);
*/
public static void useApplyToEither() {
String result = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "s1";
}).applyToEither(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "hello world";
}), s -> s).join();
System.out.println(result);
}
/*
public CompletionStage<Void> acceptEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletionStage<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletionStage<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Consumer<? super T> action,Executor executor);
*/
public static void useAcceptEither() {
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "s1";
}).acceptEither(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "hello world";
}), System.out::println);
while (true){}
}
/*
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterEither(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action,Executor executor);
*/
public static void useRunAfterEither() {
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "s1";
}).runAfterEither(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "s2";
}), () -> System.out.println("hello world"));
while (true) {
}
}
/**
* public CompletionStage<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action);
public CompletionStage<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action);
public CompletionStage<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action,Executor executor);
当运行完成时,对结果的记录。这里的完成时有两种情况,一种是正常执行,返回值。
另外一种是遇到异常抛出造成程序的中断。这里为什么要说成记录,
因为这几个方法都会返回CompletableFuture,当Action执行完毕后它的结果返回原始的CompletableFuture的计算结果或者返回异常。
所以不会对结果产生任何的作用
*/
public static void useWhenComplete() {
String result = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (1 == 1) {
throw new RuntimeException("测试一下异常情况");
}
return "s1";
}).whenComplete((s, t) -> {
System.out.println(s);
System.out.println(t.getMessage());
}).exceptionally(e -> {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
return "hello world";
}).join();
System.out.println(result);
}
/*
public <U> CompletionStage<U> handle(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn,Executor executor);
*/
public static void handle() {
String result = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//出现异常
if (1 == 1) {
throw new RuntimeException("测试一下异常情况");
}
return "s1";
}).handle((s, t) -> {
if (t != null) {
return "hello world";
}
return s;
}).join();
System.out.println(result);
}
写的代码也在https://github.com/woshiyexinjie/java-godliness
参考内容:
http://www.jianshu.com/p/6f3ee90ab7d3
http://www.jianshu.com/p/4897ccdcb278







 本文详细介绍了Java 8中引入的CompletableFuture类,通过丰富的示例代码展示了如何使用CompletableFuture实现异步编程,包括创建、组合任务及处理异常等多种场景。
本文详细介绍了Java 8中引入的CompletableFuture类,通过丰富的示例代码展示了如何使用CompletableFuture实现异步编程,包括创建、组合任务及处理异常等多种场景。

















 3251
3251

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








