LDAP:
的英文全称是Lightweight Directory Access Protocol,简称为LDAP。LDAP是轻量目录访问协议[1],它是基于X.500标准的,但是简单多了并且可以根据需要定制。LDAP目录中可以存储各种类型的数据:电子邮件地址、邮件路由信息、人力资源数据、公用密匙、联系人列表,等等.
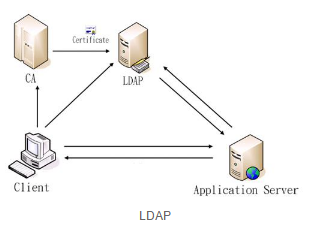
简单的说来,LDAP是一个得到关于人或者资源的集中、静态数据的快速方式,用来发布目录信息到许多不同资源的协议。通常它都作为一个集中的地址本使用,类似于我们所使用诸如NIS(Network Information Service)、DNS (Domain Name Service)等网络目录,也类似于你在花园中所看到的树木。
LDAP和关系数据库是两种不同层次的概念,后者是存贮方式(同一层次如网格数据库,对象数据库),前者是存贮模式和访问协议。LDAP是一个比关系数据库抽象层次更高的存贮概念,与关系数据库的查询语言SQL属同一级别。LDAP最基本的形式是一个连接数据库的标准方式。该数据库为读查询作了优化。因此它可以很快地得到查询结果,不过在其它方面,例如更新,就慢得多。从另一个意义上 LDAP是实现了指定的数据结构的存贮,它是一种特殊的数据库。但是LDAP和一般的数据库不同,明确这一点是很重要的。 LDAP对查询进行了优化,与写性能相比LDAP的读性能要优秀很多。
服务器
LDAP服务器可以用“推”或“拉”的方法复制部分或全部数据,例如:可以把数据“推”到远程的办公室,以增加数据的安全性。复制技术是内置在LDAP服务器中的而且很容易配置。如果要在DBMS中使用相同的复制功能,数据库厂商就会要你支付额外的费用,而且也很难管理。
什么时候该用LDAP存储数据?
如果下面每一个问题的答案都是"是",那么把数据存在LDAP中就是一个好主意。
l 需要在任何平台上都能读取数据吗?
l 每一个单独的记录项是不是每一天都只有很少的改变?
信息模型:描述LDAP的信息表示方式
在LDAP中信息以树状方式组织,在树状信息中的基本数据单元是条目,而每个条目由属性构成,属性中存储有属性值;LDAP中的信息模式,类似于面向对象的概念,在LDAP中每个条目必须属于某个或多个对象类(Object Class),每个Object Class由多个属性类型组成,每个属性类型有所对应的语法和匹配规则;对象类和属性类型的定义均可以使用继承的概念。每个条目创建时,必须定义所属的对象类,必须提供对象类中的必选属性类型的属性值,在LDAP中一个属性类型可以对应多个值。
在LDAP中把对象类、属性类型、语法和匹配规则统称为Schema,在LDAP中有许多系统对象类、属性类型、语法和匹配规则,这些系统Schema在LDAP标准中进行了规定,同时不同的应用领域也定义了自己的Schema,同时用户在应用时,也可以根据需要自定义Schema。
LDAP中为了加快查询的速度,针对不同的数据类型,可以提供不同的匹配方法,如针对字符串类型的相等、模糊、大于小于均提供自己的匹配规则。
过滤器和语法
LDAP是一个查询为主的记录结构,无论是何种查询方式,最终都由过滤器缺点查询的条件。过滤器相当于SQL中的WHERE子句。任何LDAP的类过滤和字符串都必须放在括号内,如(objectclass=*),指列出所有类型的记录(不过分类)。
可以使用=,>=,<=,~=(约等于)进行比较,如(number<=100)。合并条件是最怪的,必须把操作符放在两个操作对象的前面而不是中间,单一操作对象用括号括起来。如
l A与B,不是A&B,而是(&(A)(B))。
l 或使用"|"表示;
l 非使用"!"表示。
l 对于"与",或"或"在操作符后可以跟多个条件表达式,但非后则只参是单个表达式。
目录优势:
1.LDAP目录服务可以有效地解决众多网络服务的用户账户问题。
2.LDAP目录服务规定了统一的身份信息数据库、身份认证机制和接口,实现了资源和信息的统一管理,保证了数据的一致性和完整性。
3.LDAP目录服务是以树状的层次结构来描述数据信息的,此种模型适应了众多行业应用的业务组织结构。[3]
LDAP 使用说明
- LDAP 支持 使用 LADP 与 Windows AD 的用户作为 jumpserver 登录用户
- 已经存在的用户不能与要登录的 LDAP 用户有用户名和邮箱同名, 具有唯一性
- LDAP 设置说明
LDAP地址 ldap://serverurl:389 或者 ldaps://serverurl:636(需要勾选ssl) # 此处是设置LDAP的服务器,推荐使用IP, 防止解析问题 绑定DN cn=administrator,cn=Users,dc=jumpserver,dc=org # 这里是设置认证用户的信息, jumpserver会使用这个用户去校验ldap的信息是否正确 密码 # 上面认证用户的密码 用户OU ou=jumpserver,dc=jumpserver,dc=org # 这里是设置用来登录jumpserver的组织单元, 比如我要用某个ou的用户来登录jumpserver # 多OU用法 ou=jumpserver,dc=jumpserver,dc=org | ou=user,dc=jumpserver,dc=org | ou=xxx,dc=jumpserver,dc=org 用户过滤器 (cn=%(user)s) # 这里是设置筛选ldap用户的哪些属性, 不能有多余的空格 LADP属性映射 {"username": "cn", "name": "sn", "email": "mail"} username name email 是jumpserver的用户属性(不可更改) cn sn mail 是ldap的用户属性(可自定义) # 这里的意思是, 把ldap用户的属性映射到jumpserver上 使用SSL # 勾选后 LDAP地址 需要设置成 ldaps://serverurl:636 启动LDAP认证 # 如果需要使用 LDAP或域用户 登录 jumpserver,则必选
- 补充
-
DN 一定要是完整的DN, 不能跳过OU, 可以使用其他工具查询 如:cn=admin,ou=aaa,dc=jumpserver,dc=org,必须要写成cn=admin,ou=aaa,dc=jumpserver,dc=org 不能缩写成cn=admin,dc=jumpserver,dc=org 用户OU 用户OU可以只写顶层OU, 不写子OU 如:ou=aaa,ou=bbb,ou=ccc,dc=jumpserver,dc=org,可以只写ou=ccc,dc=jumpserver,dc=org,根据需求自行修改 用户过滤器 筛选用户的规则, 点击测试连接就是根据这个规则到用户OU里面去检索用户, 可以自定义规则 如:(uid=%(user)s) 或 (sAMAccountName=%(user)s) 等, 这里的属性需要与下面的属性映射设置一致 LADP属性映射 username name email 这三项不可修改删除, 属性映射的字段必须存在, 且登录用户名和邮件不可以重复 如:{"username": "uid", "name": "sn", "email": "mail"} 或 {"username": "sAMAccountName", "name": "cn", "email": "mail"} "username": "uid" 这里的 uid 必须和上面的 (uid=%(user)s) 这里的 uid 一致 如果上面是(sAMAccountName=%(user)s) 那么下面也应该修改为{"username": "sAMAccountName", username 是 jumpserver 的用户用户名, name 是 jumpserver 的用户名称, mail 是 jumpserver 用户的邮箱 属性映射的意思是把ldap的什么属性来作为jumpserver的用户用户名, 把ldap的什么属性作为jumpserver的用户名称, 把ldap的什么属性作为jumpserver的用户邮箱




 本文介绍了LDAP(轻量目录访问协议)的基本概念、特点及其在实际场景中的应用。LDAP是一种用于查询、浏览和搜索目录信息的标准协议,适用于需要跨平台访问且更新频率较低的数据存储场景。
本文介绍了LDAP(轻量目录访问协议)的基本概念、特点及其在实际场景中的应用。LDAP是一种用于查询、浏览和搜索目录信息的标准协议,适用于需要跨平台访问且更新频率较低的数据存储场景。
















 27
27

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








