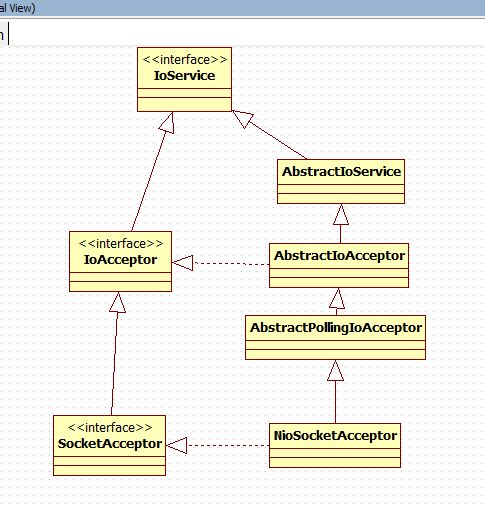
1 NioSocketAcceptor类关系图
1.1 NioSocketAcceptor acceptor = new NioSocketAcceptor(5);
NioSocketAcceptor 初始化顺序
AbstractIoService构造函数
protected AbstractIoService(IoSessionConfig sessionConfig, Executor executor) {
if (sessionConfig == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("sessionConfig");
}
if (getTransportMetadata() == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("TransportMetadata");
}
if (!getTransportMetadata().getSessionConfigType().isAssignableFrom(
sessionConfig.getClass())) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("sessionConfig type: "
+ sessionConfig.getClass() + " (expected: "
+ getTransportMetadata().getSessionConfigType() + ")");
}
// Create the listeners, and add a first listener : a activation listener
// for this service, which will give information on the service state.
listeners = new IoServiceListenerSupport(this);
listeners.add(serviceActivationListener);
// Stores the given session configuration
this.sessionConfig = sessionConfig;
// Make JVM load the exception monitor before some transports
// change the thread context class loader.
ExceptionMonitor.getInstance();
if (executor == null) {
this.executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
createdExecutor = true;
} else {
this.executor = executor;
createdExecutor = false;
}
threadName = getClass().getSimpleName() + '-' + id.incrementAndGet();
}protected AbstractIoAcceptor(IoSessionConfig sessionConfig, Executor executor) {
super(sessionConfig, executor);
defaultLocalAddresses.add(null);
}AbstractPollingIoAcceptor 构造函数
private AbstractPollingIoAcceptor(IoSessionConfig sessionConfig,
Executor executor, IoProcessor<S> processor,
boolean createdProcessor) {
super(sessionConfig, executor);
if (processor == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("processor");
}
this.processor = processor;
this.createdProcessor = createdProcessor;
try {
// Initialize the selector
init();
// The selector is now ready, we can switch the
// flag to true so that incoming connection can be accepted
selectable = true;
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeIoException("Failed to initialize.", e);
} finally {
if (!selectable) {
try {
destroy();
} catch (Exception e) {
ExceptionMonitor.getInstance().exceptionCaught(e);
}
}
}
}NioSocketAcceptor 构造函数
public NioSocketAcceptor(int processorCount) {
super(new DefaultSocketSessionConfig(), NioProcessor.class, processorCount);
((DefaultSocketSessionConfig) getSessionConfig()).init(this);
}1.2 IoFilterChain 过滤链
acceptor.getFilterChain().addLast("logger", new LoggingFilter());
/** AbstractIoService
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
public final DefaultIoFilterChainBuilder getFilterChain() {
if (filterChainBuilder instanceof DefaultIoFilterChainBuilder) {
return (DefaultIoFilterChainBuilder) filterChainBuilder;
}
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Current filter chain builder is not a DefaultIoFilterChainBuilder.");
}
源代码:
public class DefaultIoFilterChainBuilder implements IoFilterChainBuilder {
private final static Logger LOGGER =
LoggerFactory.getLogger(DefaultIoFilterChainBuilder.class);
private final List<Entry> entries;
/**
* Creates a new instance with an empty filter list.
*/
public DefaultIoFilterChainBuilder() {
entries = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<Entry>();
}
/**
* Creates a new copy of the specified {@link DefaultIoFilterChainBuilder}.
*/
public DefaultIoFilterChainBuilder(DefaultIoFilterChainBuilder filterChain) {
if (filterChain == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("filterChain");
}
entries = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<Entry>(filterChain.entries);
}addLast
/**
* @see IoFilterChain#addLast(String, IoFilter)
*/
public synchronized void addLast(String name, IoFilter filter) {
register(entries.size(), new EntryImpl(name, filter));
}
private void register(int index, Entry e) {
if (contains(e.getName())) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Other filter is using the same name: " + e.getName());
}
entries.add(index, e);
}
1.3 IoFilter
1.4 IoSessionConfig
1.4 IoProcess
1.5 acceptor.bind(new InetSocketAddress(this.serverAddr, this.serverPort));
最终会运行AbstractPollingIoAcceptor.bindInternal
AbstractPollingIoAcceptor
protected final Set<SocketAddress> bindInternal(
List<? extends SocketAddress> localAddresses) throws Exception {
// Create a bind request as a Future operation. When the selector
// have handled the registration, it will signal this future.
AcceptorOperationFuture request = new AcceptorOperationFuture(
localAddresses);
// adds the Registration request to the queue for the Workers
// to handle
registerQueue.add(request);
// creates the Acceptor instance and has the local
// executor kick it off.
startupAcceptor();
// As we just started the acceptor, we have to unblock the select()
// in order to process the bind request we just have added to the
// registerQueue.
wakeup();
// Now, we wait until this request is completed.
request.awaitUninterruptibly();
if (request.getException() != null) {
throw request.getException();
}
// Update the local addresses.
// setLocalAddresses() shouldn't be called from the worker thread
// because of deadlock.
Set<SocketAddress> newLocalAddresses = new HashSet<SocketAddress>();
for (H handle:boundHandles.values()) {
newLocalAddresses.add(localAddress(handle));
}
return newLocalAddresses;
}1.5.1 startupAcceptor() 使用线程池执行Acceptor
/**
* This method is called by the doBind() and doUnbind()
* methods. If the acceptor is null, the acceptor object will
* be created and kicked off by the executor. If the acceptor
* object is null, probably already created and this class
* is now working, then nothing will happen and the method
* will just return.
*/
private void startupAcceptor() {
// If the acceptor is not ready, clear the queues
// TODO : they should already be clean : do we have to do that ?
if (!selectable) {
registerQueue.clear();
cancelQueue.clear();
}
// start the acceptor if not already started
Acceptor acceptor = acceptorRef.get();
if (acceptor == null) {
acceptor = new Acceptor();
if (acceptorRef.compareAndSet(null, acceptor)) {
executeWorker(acceptor);
}
}
}Acceptor() 实现了Runnable接口 不停的执行
/**
* This class is called by the startupAcceptor() method and is
* placed into a NamePreservingRunnable class.
* It's a thread accepting incoming connections from clients.
* The loop is stopped when all the bound handlers are unbound.
*/
private class Acceptor implements Runnable {
public void run() {
assert (acceptorRef.get() == this);
int nHandles = 0;
while (selectable) {
try {
// Detect if we have some keys ready to be processed
// The select() will be woke up if some new connection
// have occurred, or if the selector has been explicitly
// woke up
int selected = select();
// this actually sets the selector to OP_ACCEPT,
// and binds to the port on which this class will
// listen on
nHandles += registerHandles();
// Now, if the number of registred handles is 0, we can
// quit the loop: we don't have any socket listening
// for incoming connection.
if (nHandles == 0) {
acceptorRef.set(null);
if (registerQueue.isEmpty() && cancelQueue.isEmpty()) {
assert (acceptorRef.get() != this);
break;
}
if (!acceptorRef.compareAndSet(null, this)) {
assert (acceptorRef.get() != this);
break;
}
assert (acceptorRef.get() == this);
}
if (selected > 0) {
// We have some connection request, let's process
// them here.
processHandles(selectedHandles());
}
// check to see if any cancellation request has been made.
nHandles -= unregisterHandles();
} catch (ClosedSelectorException cse) {
// If the selector has been closed, we can exit the loop
break;
} catch (Throwable e) {
ExceptionMonitor.getInstance().exceptionCaught(e);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e1) {
ExceptionMonitor.getInstance().exceptionCaught(e1);
}
}
}
// Cleanup all the processors, and shutdown the acceptor.
if (selectable && isDisposing()) {
selectable = false;
try {
if (createdProcessor) {
processor.dispose();
}
} finally {
try {
synchronized (disposalLock) {
if (isDisposing()) {
destroy();
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
ExceptionMonitor.getInstance().exceptionCaught(e);
} finally {
disposalFuture.setDone();
}
}
}
}NioSocketAcceptor
/**
* Check if we have at least one key whose corresponding channels is
* ready for I/O operations.
*
* This method performs a blocking selection operation.
* It returns only after at least one channel is selected,
* this selector's wakeup method is invoked, or the current thread
* is interrupted, whichever comes first.
*
* @return The number of keys having their ready-operation set updated
* @throws IOException If an I/O error occurs
* @throws ClosedSelectorException If this selector is closed
*/
@Override
protected int select() throws Exception {
return selector.select();
}请问
/**
* Sets up the socket communications. Sets items such as:
* <p/>
* Blocking
* Reuse address
* Receive buffer size
* Bind to listen port
* Registers OP_ACCEPT for selector
*/
private int registerHandles() {
for (;;) {
// The register queue contains the list of services to manage
// in this acceptor.
AcceptorOperationFuture future = registerQueue.poll();
if (future == null) {
return 0;
}
// We create a temporary map to store the bound handles,
// as we may have to remove them all if there is an exception
// during the sockets opening.
Map<SocketAddress, H> newHandles = new ConcurrentHashMap<SocketAddress, H>();
List<SocketAddress> localAddresses = future.getLocalAddresses();
try {
// Process all the addresses
for (SocketAddress a : localAddresses) {
H handle = open(a);
newHandles.put(localAddress(handle), handle);
}
// Everything went ok, we can now update the map storing
// all the bound sockets.
boundHandles.putAll(newHandles);
// and notify.
future.setDone();
return newHandles.size();
} catch (Exception e) {
// We store the exception in the future
future.setException(e);
} finally {
// Roll back if failed to bind all addresses.
if (future.getException() != null) {
for (H handle : newHandles.values()) {
try {
close(handle);
} catch (Exception e) {
ExceptionMonitor.getInstance().exceptionCaught(e);
}
}
// TODO : add some comment : what is the wakeup() waking up ?
wakeup();
}
}
}
}接上图open方法 jdk自带的NIO
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
protected ServerSocketChannel open(SocketAddress localAddress)
throws Exception {
// Creates the listening ServerSocket
ServerSocketChannel channel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
boolean success = false;
try {
// This is a non blocking socket channel
channel.configureBlocking(false);
// Configure the server socket,
ServerSocket socket = channel.socket();
// Set the reuseAddress flag accordingly with the setting
socket.setReuseAddress(isReuseAddress());
// and bind.
socket.bind(localAddress, getBacklog());
// Register the channel within the selector for ACCEPT event
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
success = true;
} finally {
if (!success) {
close(channel);
}
}
return channel;
}Acceptor接收数据
if (selected > 0) {
// We have some connection request, let's process
// them here.
processHandles(selectedHandles());
}/**
* This method will process new sessions for the Worker class. All
* keys that have had their status updates as per the Selector.selectedKeys()
* method will be processed here. Only keys that are ready to accept
* connections are handled here.
* <p/>
* Session objects are created by making new instances of SocketSessionImpl
* and passing the session object to the SocketIoProcessor class.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void processHandles(Iterator<H> handles) throws Exception {
while (handles.hasNext()) {
H handle = handles.next();
handles.remove();
// Associates a new created connection to a processor,
// and get back a session
S session = accept(processor, handle);
if (session == null) {
break;
}
//初始化session
initSession(session, null, null);
// add the session to the SocketIoProcessor 过滤链处理数据入口
session.getProcessor().add(session);
}
}processHandles 的accept 获取SocketChannel 封装成NioSocketSessionprotected NioSession accept(IoProcessor<NioSession> processor,
ServerSocketChannel handle) throws Exception {
SelectionKey key = handle.keyFor(selector);
if ((key == null) || (!key.isValid()) || (!key.isAcceptable()) ) {
return null;
}
// accept the connection from the client
SocketChannel ch = handle.accept();
if (ch == null) {
return null;
}
return new NioSocketSession(this, processor, ch);
}processor
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
public final void add(S session) {
if (disposed || disposing) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Already disposed.");
}
// Adds the session to the newSession queue and starts the worker
newSessions.add(session);
startupProcessor();
}
/**
* Starts the inner Processor, asking the executor to pick a thread in its
* pool. The Runnable will be renamed
*/
private void startupProcessor() {
Processor processor = processorRef.get();
if (processor == null) {
processor = new Processor();
if (processorRef.compareAndSet(null, processor)) {
executor.execute(new NamePreservingRunnable(processor, threadName));
}
}
// Just stop the select() and start it again, so that the processor
// can be activated immediately.
wakeup();
}主要接收数据处理代码逻辑
/**
* The main loop. This is the place in charge to poll the Selector, and to
* process the active sessions. It's done in
* - handle the newly created sessions
* -
*/
private class Processor implements Runnable {
public void run() {
assert (processorRef.get() == this);
int nSessions = 0;
lastIdleCheckTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (;;) {
try {
// This select has a timeout so that we can manage
// idle session when we get out of the select every
// second. (note : this is a hack to avoid creating
// a dedicated thread).
long t0 = System.currentTimeMillis();
int selected = select(SELECT_TIMEOUT);
long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
long delta = (t1 - t0);
if ((selected == 0) && !wakeupCalled.get() && (delta < 100)) {
// Last chance : the select() may have been
// interrupted because we have had an closed channel.
if (isBrokenConnection()) {
LOG.warn("Broken connection");
// we can reselect immediately
// set back the flag to false
wakeupCalled.getAndSet(false);
continue;
} else {
LOG.warn("Create a new selector. Selected is 0, delta = "
+ (t1 - t0));
// Ok, we are hit by the nasty epoll
// spinning.
// Basically, there is a race condition
// which causes a closing file descriptor not to be
// considered as available as a selected channel, but
// it stopped the select. The next time we will
// call select(), it will exit immediately for the same
// reason, and do so forever, consuming 100%
// CPU.
// We have to destroy the selector, and
// register all the socket on a new one.
registerNewSelector();
}
// Set back the flag to false
wakeupCalled.getAndSet(false);
// and continue the loop
continue;
}
// Manage newly created session first
nSessions += handleNewSessions();
updateTrafficMask();
// Now, if we have had some incoming or outgoing events,
// deal with them
if (selected > 0) {
//LOG.debug("Processing ..."); // This log hurts one of the MDCFilter test...
process();
}
// Write the pending requests
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
flush(currentTime);
// And manage removed sessions
nSessions -= removeSessions();
// Last, not least, send Idle events to the idle sessions
notifyIdleSessions(currentTime);
// Get a chance to exit the infinite loop if there are no
// more sessions on this Processor
if (nSessions == 0) {
processorRef.set(null);
if (newSessions.isEmpty() && isSelectorEmpty()) {
// newSessions.add() precedes startupProcessor
assert (processorRef.get() != this);
break;
}
assert (processorRef.get() != this);
if (!processorRef.compareAndSet(null, this)) {
// startupProcessor won race, so must exit processor
assert (processorRef.get() != this);
break;
}
assert (processorRef.get() == this);
}
// Disconnect all sessions immediately if disposal has been
// requested so that we exit this loop eventually.
if (isDisposing()) {
for (Iterator<S> i = allSessions(); i.hasNext();) {
scheduleRemove(i.next());
}
wakeup();
}
} catch (ClosedSelectorException cse) {
// If the selector has been closed, we can exit the loop
break;
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionMonitor.getInstance().exceptionCaught(t);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e1) {
ExceptionMonitor.getInstance().exceptionCaught(e1);
}
}
}
try {
synchronized (disposalLock) {
if (disposing) {
doDispose();
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionMonitor.getInstance().exceptionCaught(t);
} finally {
disposalFuture.setValue(true);
}
}
}过滤链:
private void process() throws Exception {
for (Iterator<S> i = selectedSessions(); i.hasNext();) {
S session = i.next();
process(session);
i.remove();
}
}
/**
* Deal with session ready for the read or write operations, or both.
*/
private void process(S session) {
// Process Reads
if (isReadable(session) && !session.isReadSuspended()) {
read(session);
}
// Process writes
if (isWritable(session) && !session.isWriteSuspended()) {
// add the session to the queue, if it's not already there
if (session.setScheduledForFlush(true)) {
flushingSessions.add(session);
}
}
}
private void read(S session) {
IoSessionConfig config = session.getConfig();
int bufferSize = config.getReadBufferSize();
IoBuffer buf = IoBuffer.allocate(bufferSize);
final boolean hasFragmentation = session.getTransportMetadata()
.hasFragmentation();
try {
int readBytes = 0;
int ret;
try {
if (hasFragmentation) {
while ((ret = read(session, buf)) > 0) {
readBytes += ret;
if (!buf.hasRemaining()) {
break;
}
}
} else {
ret = read(session, buf);
if (ret > 0) {
readBytes = ret;
}
}
} finally {
buf.flip();
}
if (readBytes > 0) {
//处理逻辑
IoFilterChain filterChain = session.getFilterChain();
filterChain.fireMessageReceived(buf);
buf = null;
if (hasFragmentation) {
if (readBytes << 1 < config.getReadBufferSize()) {
session.decreaseReadBufferSize();
} else if (readBytes == config.getReadBufferSize()) {
session.increaseReadBufferSize();
}
}
}
if (ret < 0) {
scheduleRemove(session);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
if (e instanceof IOException) {
if (!(e instanceof PortUnreachableException)
|| !AbstractDatagramSessionConfig.class.isAssignableFrom(config.getClass())
|| ((AbstractDatagramSessionConfig) config).isCloseOnPortUnreachable()) {
scheduleRemove(session);
}
}
IoFilterChain filterChain = session.getFilterChain();
filterChain.fireExceptionCaught(e);
}
}调用过滤连: DefaultIoFilterChain
public void fireMessageReceived(Object message) {
if (message instanceof IoBuffer) {
session.increaseReadBytes(((IoBuffer) message).remaining(), System
.currentTimeMillis());
}
Entry head = this.head;
callNextMessageReceived(head, session, message);
}
private void callNextMessageReceived(Entry entry, IoSession session,
Object message) {
try {
IoFilter filter = entry.getFilter();
NextFilter nextFilter = entry.getNextFilter();
filter.messageReceived(nextFilter, session,
message);
} catch (Throwable e) {
fireExceptionCaught(e);
}
}业务处理handler总是最后处理




 本文详细解析了NioSocketAcceptor的工作流程,包括初始化、绑定、接收连接及数据处理等关键步骤,并深入探讨了其内部实现机制。
本文详细解析了NioSocketAcceptor的工作流程,包括初始化、绑定、接收连接及数据处理等关键步骤,并深入探讨了其内部实现机制。

















 415
415

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








