此对比说明了一件事:
如果是IO型应用,多线程有优势,
如果是CPU计算型应用,多线程没必要,还有实现锁呢。
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- from threading import Thread class threads_object(Thread): def run(self): function_to_run() class nothreads_object(object): def run(self): function_to_run() def non_threaded(num_iter): funcs = [] for i in range(int(num_iter)): funcs.append(nothreads_object()) for i in funcs: i.run() def threaded(num_threads): funcs = [] for i in range(int(num_threads)): funcs.append(threads_object()) for i in funcs: i.start() for i in funcs: i.join() def function_to_run(): a, b = 0, 1 for i in range(10000): a, b = b, a + b ''' import requests for i in range(10): requests.get("http://10.25.174.41/") ''' def show_results(func_name, results): print("%-23s %4.6f seconds" % (func_name, results)) if __name__ == "__main__": import sys from timeit import Timer repeat = 100 number = 1 number_threads = [1, 2, 4, 8] print('Starting tests') for i in number_threads: t = Timer("non_threaded(%s)" \ % i, "from __main__ import non_threaded") best_result =\ min(t.repeat(repeat=repeat, number=number)) show_results("non_threaded (%s iters) "\ %i, best_result) t = Timer("threaded(%s)" \ % i, "from __main__ import threaded") best_result =\ min(t.repeat(repeat=repeat, number=number)) show_results("threaded (%s iters) "\ %i, best_result) print ('Iterations complete')
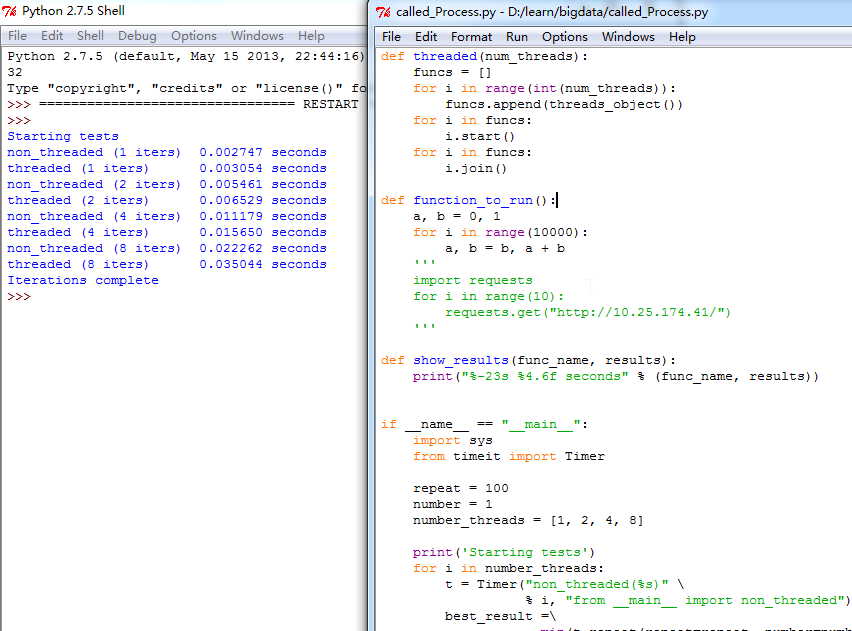




 本文通过对比测试展示了在不同类型的程序中使用多线程的效果。结果显示,在IO密集型应用中多线程能显著提高程序效率;而在CPU计算密集型任务中,多线程可能并无明显优势,甚至因为线程同步开销而降低效率。
本文通过对比测试展示了在不同类型的程序中使用多线程的效果。结果显示,在IO密集型应用中多线程能显著提高程序效率;而在CPU计算密集型任务中,多线程可能并无明显优势,甚至因为线程同步开销而降低效率。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








