我们首先来看下面的一个案例:
这里是 HelloWorld.java 文件的内容:
package
com.yiibai;
public
class
HelloWorld {
private
String message;
public
void
setMessage(String message){
this
.message = message;
}
public
void
getMessage(){
System.out.println(
"Your Message : "
+ message);
}
public
void
init(){
System.out.println(
"Bean is going through init."
);
}
public
void
destroy(){
System.out.println(
"Bean will destroy now."
);
}
}
|
这是实现BeanPostProcessor,之前和之后的任何bean的初始化它打印一个bean的名字非常简单的例子
这里是InitHelloWorld.java文件的内容:
package
com.yiibai;
import
org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import
org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
public
class
InitHelloWorld
implements
BeanPostProcessor {
public
Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean,
String beanName)
throws
BeansException {
System.out.println(
"BeforeInitialization : "
+ beanName);
return
bean;
// you can return any other object as well
}
public
Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean,
String beanName)
throws
BeansException {
System.out.println(
"AfterInitialization : "
+ beanName);
return
bean;
// you can return any other object as well
}
}
|
以下是MainApp.java 文件的内容。在这里,需要注册一个关闭挂钩registerShutdownHook() 是在AbstractApplicationContext类中声明的方法。这将确保正常关闭,并调用相关的destroy方法。
package
com.yiibai;
import
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext;
import
org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public
class
MainApp {
public
static
void
main(String[] args) {
AbstractApplicationContext context =
new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"Beans.xml"
);
HelloWorld obj = (HelloWorld) context.getBean(
"helloWorld"
);
obj.getMessage();
context.registerShutdownHook();
}
}
|
下面是init和destroy方法需要的配置文件beans.xml文件:
<?
xml
version
=
"1.0"
encoding
=
"UTF-8"
?>
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
<
bean
id
=
"helloWorld"
class
=
"com.yiibai.HelloWorld"
init-method
=
"init"
destroy-method
=
"destroy"
>
<
property
name
=
"message"
value
=
"Hello World!"
/>
</
bean
>
<
bean
class
=
"com.yiibai.InitHelloWorld"
/>
</
beans
>
|
创建源代码和bean配置文件完成后,让我们运行应用程序。如果一切顺利,这将打印以下信息:
BeforeInitialization : helloWorld
Bean is going through init.
AfterInitialization : helloWorld
Your Message : Hello World!
Bean will destroy now.
|
我们来看下spring管理bean的生命周期:
在对应未初始化之前先调用 postProcessBeforeInitialization方法
然后对bean进行初始化,通过set方法设置对象的成员属性之后,对象就初始化完成。这里对象实现了InitialingBean接口,就会执行接口方法afterPropertsets方法。该方法在bean所有属性的set方法执行完毕后执行。是bean初始化成功的标志位,表示bean初始化接受
bean初始化成功之后,如果设置了init-method属性就执行该bean对象的方法
接下来执行postProcessAfterInitialization
最后执行destroy-method方法。
我们来看bean的生命周期的执行过程

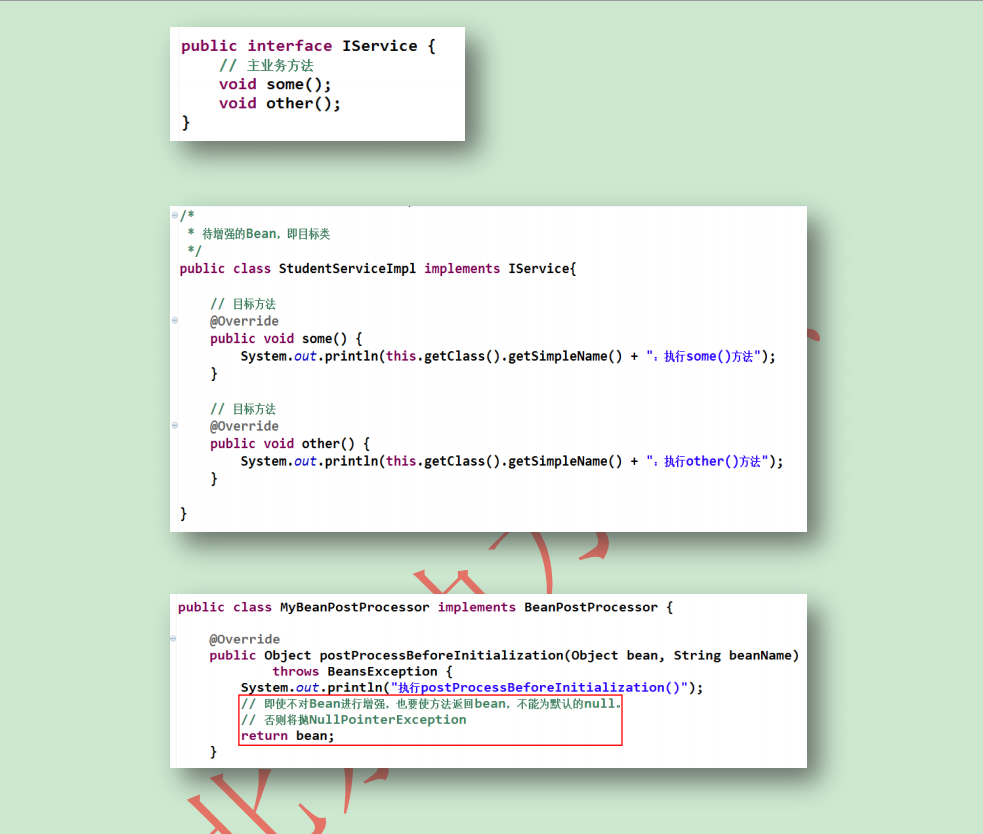
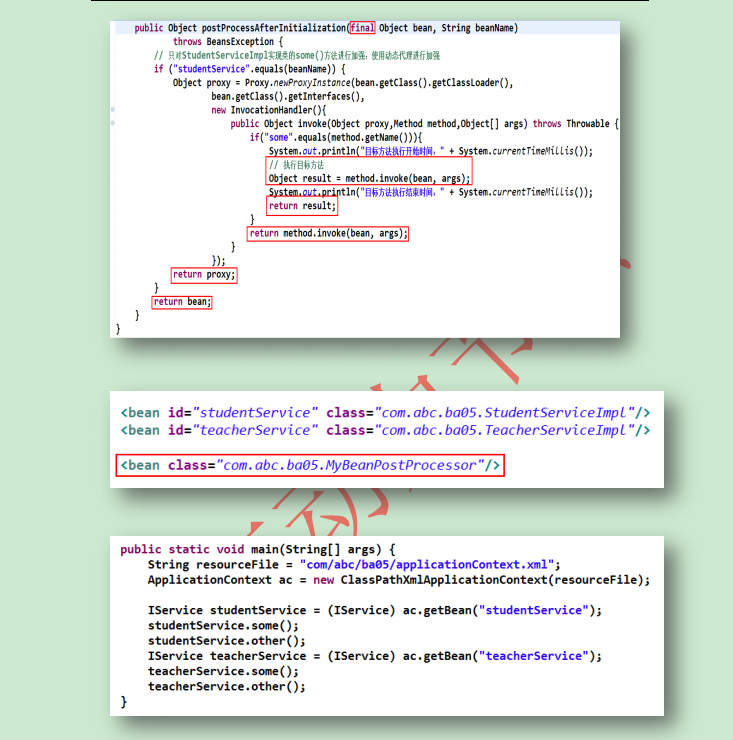
第二点:bean后处理器的作用
Bean后处理器的基本要求是实现BeanPostProcessor接口。通过实现postProcessBeforeInitialization() 和 postProcessAfterInitialization() 方法,可以在初始化回调方法前后处理所有Bean。可以实现对指定
bean对应方法的业务进行增强





 本文详细介绍了Spring框架中Bean的生命周期,包括初始化前、初始化中及销毁等关键阶段,并通过示例代码展示了BeanPostProcessor接口如何增强Bean的功能。
本文详细介绍了Spring框架中Bean的生命周期,包括初始化前、初始化中及销毁等关键阶段,并通过示例代码展示了BeanPostProcessor接口如何增强Bean的功能。
















 1375
1375

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








