41、题目要求 : 问候脚本
编写一个问候程序,它执行时能根据系统当前的时间向用户输出问候信息。假设从半夜到中午为早晨,中午到下午六点为下午,下午六点到半夜为晚上。
参考答案
#!/bin/bash
d=`date +%H`
if [ $d -ge 0 -a $d -lt 7 ]
then
tag=1
elif [ $d -ge 7 -a $d -lt 12 ]
then
tag=2
elif [ $d -ge 12 -a $d -lt 18 ]
then
tag=3
else
tag=4
fi
case $tag in
1)
echo "早晨好"
;;
2)
echo "上午好"
;;
3)
echo "下午好"
;;
4)
echo "晚上好"
;;
*)
echo "脚本出错啦"
;;
esac
实例 :
执行脚本,查看运行结果,脚本没有问题。date命令查看系统当前的时间
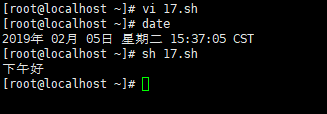
注意 :
[ $d -ge 0 -a $d -lt 7 ] #大于等于0,小于7
[ $d -ge 7 -a $d -lt 12 ] #大于等于7,小于12
[ $d -ge 12 -a $d -lt 18 ] #大于等于12,小于18
d=`date -d -10 hours +%H` #时间后退10个小时,就变成了脚本执行的结果早上好
42、题目要求 : 菜单脚本
写一个shell脚本,实现简单的弹出式菜单功能,用户能根据显示的菜单项从键盘选择执行对应的命令。
参考答案
#!/bin/bash
PS3="Please input your choice(1-4): "
select i in w ls pwd quit
do
case $i in
w)
w
;;
ls)
ls
;;
pwd)
pwd
;;
quit)
exit
;;
*)
echo "Please input 1-3."
;;
esac
done
参考答案2
#!/bin/bash
echo -e "1) w\n2) ls\n3) pwd\n4) quit"
while :
do
read -p "Please input your choice(1-4): " c
case $c in
1)
w
;;
2)
ls
;;
3)
pwd
;;
4)
exit
;;
*)
echo "Please input 1-4."
;;
esac
done
实例 :
执行脚本,输入数字,执行对应的命令。
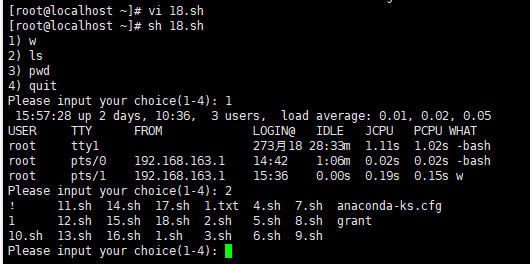
注意 :
w\n2) ls\n3) pwd\n4) #使用 数字去代替命令w,ls,pwd
43、题目要求 : 检查用户是否登录
写一个shell脚本,执行中每隔5分钟检查指定的用户是否登录系统,用户名从命令行输入,如果指定的用户已经登录,则显示相关信息。
参考答案
#!/bin/bash
while :
do
if w|sed '1'd|awk '{print $1}'|grep -qw "$1"
then
echo "用户$1 已经登录系统."
exit
fi
sleep 300
done
实例 :
查看当前的用户
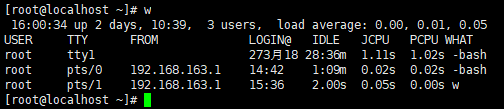
执行脚本,输入用户名,查看该用户有没有登录。

注意 :
if w|sed '1'd|awk '{print $1}'|grep -qw "$1" #查找并去掉出显示出来的第一行,
44、题目要求 : 检查系统是否入侵
先普及一个小常识,我们用ps aux可以查看到进程的PID,而每个PID都会在/proc内产生。如果查看到的pid在proc内是没有的,则进程被人修改了,这就代表系统很有可能已经被入侵过了。 请用上面知识编写一个shell,定期检查下自己的系统是否被人入侵过
参考答案
#!/bin/bash
pp=$$
ps -elf |sed '1'd > /tmp/pid.txt
for pid in `awk -v ppn=$pp '$5!=ppn {print $4}' /tmp/pid.txt`
do
if ! [ -d /proc/$pid ]
then
echo "系统中并没有pid为$pid的目录,需要检查。"
fi
done
实例 :
使用命令ls -l /proc,查看文件的pid,然后通过pid,查看进程。
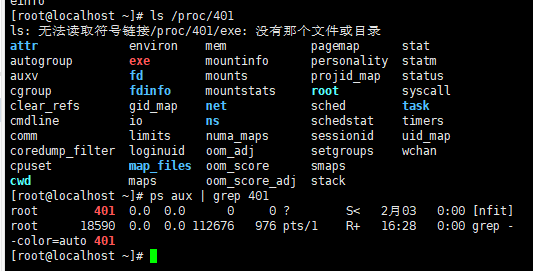
打印出,含有pid的行
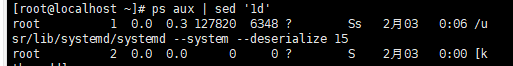
打印出只含有pid的行
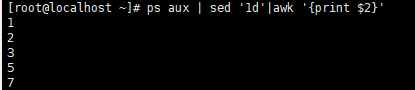
注意 :
脚本要把ps、sed、awk中的PID过滤掉,只剩下进程的pid。
ps -elf |sed '1'd > /tmp/pid.txt #列出pid,并删除第一行,将结果写入/tmp/pid.txt
for pid in `awk -v ppn=$pp '$5!=ppn {print $4}' /tmp/pid.txt` #awk显示出来的pid在第四列,把第四列过滤掉;把ps -elf显示出来的第四列,打印出来。-v : 引用的意思,$5!=ppn {print $4} : $5不等于ppn $4
45、题目要求 : 三行并一行
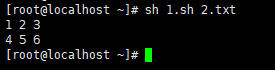
想办法把文本里面每三行内容合并到一行 例如:1.txt内容
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
处理后应该是
1 2 3
4 5 6
7
【核心要点】
while read 逐行遍历
echo -n 不换行
参考答案
#!/bin/bash
n=1
cat $1 |while read line
do
n1=$[$n%3]
if [ $n1 -eq 0 ]
then
echo "$line"
else
echo -n "$line "
fi
n=$[$n+1]
done实例 :
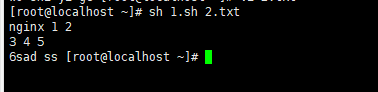
脚本执行结果
注意 :
n1=$[$n%3] #$n能够被3整除
$n1 -eq 0 #-eq等于 0,换行。
46、题目要求 : 网卡和ip(1)、网卡和ip(2)
写一个getinterface.sh 脚本可以接受选项[i,I],完成下面任务:
1)使用格式:getinterface.sh [-i interface | -I ip]
2)当用户使用-i选项时,显示指定网卡的IP地址;当用户使用-I选项时,显示其指定ip所属的网卡。
例: sh getinterface.sh -i eth0 或者
sh getinterface.sh -I 192.168.0.1
3)当用户使用除[-i | -I]选项时,显示[-i interface | -I ip]此信息。
4)当用户指定信息不符合时,显示错误。(比如指定的eth0没有,而是eth1时)
【核心要点】
两个参数$1只能是-i或者-I , $2只能是网卡名字或者IP地址
把网卡名字和IP地址写到一个临时文件里备用
参考答案
#!/bin/bash
ip add |awk -F ': ' '$1 ~ "^[1-9]" {print $2}' > /tmp/ifs.txt
get_ip()
{
ip add show dev $1 |grep inet |awk '{print $2}' |awk -F '/' '{print $1}'
}
for eth in `cat /tmp/ifs.txt`
do
myip=`get_ip $eth`
if [ -z "$myip" ]
then
echo $eth
else
echo $eth $myip
fi
done > /tmp/if_ip.txt
if [ $# -ne 2 ]
then
echo "请输入正确的格式: bash $0 -i 网卡 或者 bash $0 -I ip"
exit
fi
if [ $1 == "-i" ]
then
if awk '{print $1}' /tmp/if_ip.txt |grep -qw $2
then
eth=$2
ip1=`awk -v aeth=$eth '$1==aeth' /tmp/if_ip.txt|sed "s/$eth //"`
echo "网卡$2的ip是 $ip1"
else
echo "你指定的网卡不对,系统中的网卡有:`cat /tmp/ifs.txt|xargs`"
exit
fi
elif [ $1 == "-I" ]
then
if grep -qw " $2 " /tmp/if_ip.txt
then
eth=`grep -w " $2 " /tmp/if_ip.txt|awk '{print $1}'`
echo "IP $2对应的网卡是$eth"
else
echo "你指定的ip不对,系统中的IP有:`ip add |grep inet |awk '{print $2}'|awk -F '/' '{print $1}'|xargs`"
exit
fi
else
echo "请输入正确的格式: bash $0 -i 网卡 或者 bash $0 -I ip"
fi
实例 :
查看系统中有哪些网卡
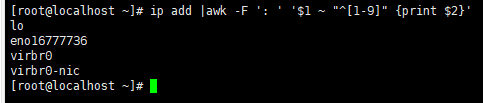
查看lo网卡第二行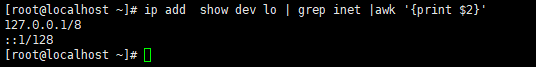
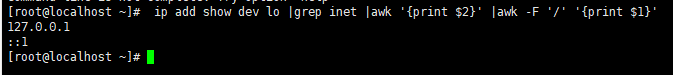
注意 :
ip add |awk -F ': ' '$1 ~ "^[1-9]" {print $2}' > /tmp/ifs.txt #将网卡和网卡IP对应的关系,写入到 /tmp/ifs.txt 文件中
ip add show dev $1 |grep inet |awk '{print $2}' |awk -F '/' '{print $1}' #只显示网卡的IP地址。
if awk '{print $1}' /tmp/if_ip.txt |grep -qw $2 #
if [ -z "$myip" ] #如果这个变量为空,
47、题目要求 : 随机3位数
写一个脚本产生随机3位的数字,并且可以根据用户的输入参数来判断输出几组。 比如,脚本名字为 number3.sh。
执行方法:
1)bash number3.sh 会产生一组3位数字。
2)bash number3.sh 10 会产生10组3位数字。
参考答案
#!/bin/bash
get_number()
{
for i in `seq 0 2`
do
a[$i]=$[$RANDOM%10]
done
echo ${a[@]}|sed s'/ //g'
}
if [ $# -eq 0 ]
then
get_number
elif [ $# -eq 1 ]
then
n=`echo $1|sed 's/[0-9]//g'`
if [ -n "$n" ]
then
echo "给定的参数必须是一个数字"
exit
fi
for i in `seq 1 $1`
do
get_number
done |xargs
else
echo "格式不对,正确的是格式是sh $0 [n],这里的n是一个数字。"
fi
实例 :
脚本运行结果
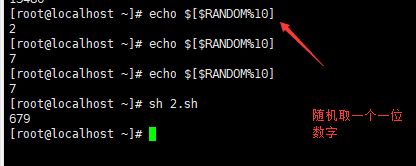
注意 :
if [ -n "$n" ] #如果-n不为空,说明“给定的参数必须是一个数字”
elif [ $# -eq 1 ] #eq 等于1
48、题目要求 : 是否安装包
写一个shell,先判断是否安装httpd和mysql,没有安装进行安装,安装了检查是否启动服务,若没有启动则需要启动服务。
说明 :操作系统为cnetos6,httpd和mysql全部为rpm包安装
【核心要点】
rpm -q 包名 判断是否安装
service xxx start #启动
参考答案
#!/bin/bash
if_install()
{
rpm -q $1 >/dev/null 2>/dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ]
then
echo "$1已经安装"
return 0
else
echo "$1没有安装"
return 1
fi
}
if_install httpd
if [ $? -eq 0 ]
then
if ! pgrep httpd >/dev/null
then
service httpd start
fi
else
yum install -y httpd
fi
if_install mysql-server
if [ $? -eq 0 ]
then
if ! pgrep mysqld >/dev/null
then
service mysqld start
fi
else
yum install -y mysql-server
fi
实例 :
查看软件是否安装
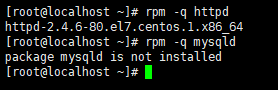
脚本执行的过程
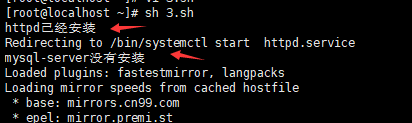
注意 :
rpm -q $1 >/dev/null 2>/dev/null #判断是否安装,如果安装写入/dev/null,未安装;$1就是包名
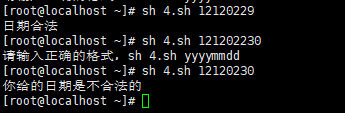
49、题目要求 : 日期是否合法
用shell脚本判断输入的日期是否合法。
比如20170110就是合法日期,20171332就不合法。
参考答案
#!/bin/bash
if [ $# -ne 1 ] || [ ${#1} -ne 8 ]
then
echo "请输入正确的格式,sh $0 yyyymmdd"
exit 1
fi
y=`echo ${1:0:4}`
m=`echo ${1:4:2}`
d=`echo ${1:6:2}`
if echo $d|grep -q "^0"
then
d=`echo ${1:6:2}|sed 's/^0//'`
fi
if cal $m $y >/dev/null 2>/dev/null
then
if ! cal $m $y|grep -qw "$d"
then
echo "你给的日期是不合法的"
else
echo "日期合法"
fi
else
echo "你给的日期不合法"
fi
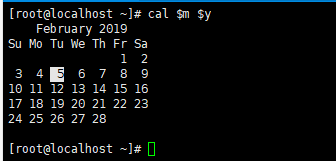
实例 :
查看系统时间,月和年。
修改系统时间为指定的时间
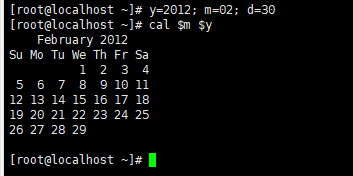
取前三个,取前四个
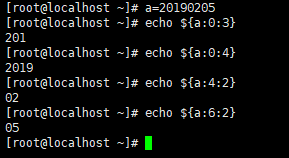
脚本执行的结果
注意 :
if [ $# -ne 1 ] || [ ${#1} -ne 8 ] # $#不等于1 或者 ${#1} 不等于8,提示 : “请输入正确的格式,sh $0 yyyymmdd”
if echo $d|grep -q "^0" #查找不以0开头的
if ! cal $m $y|grep -qw "$d" #
if cal $m $y >/dev/null 2>/dev/null #日历月和年,正确和错误都输入到/dev/null
50、题目要求 : 监控流量
写一个监控网卡的脚本,需要满足以下要求:
-
每10分钟检测一次指定网卡的流量。
-
如果流量为0,则重启网卡。
【核心要点】
sar -n DEV # 查看dev网卡的流量
ifdown xxx; ifup xxx #下载的速度,和上传的速度
参考答案
#!/bin/bash
LANG=en
sar -n DEV 1 10|grep -w "$1" > /tmp/sar.tmp
in=`grep "Average:" /tmp/sar.tmp|awk '{print $5}'|sed 's/\.//'`
out=`grep "Average:" /tmp/sar.tmp|awk '{print $6}'|sed 's/\.//'`
if [ $in == "000" ] && [ $out == "000" ]
then
ifdown $1
ifup $1
fi实例 :
10秒一次网卡流量监测
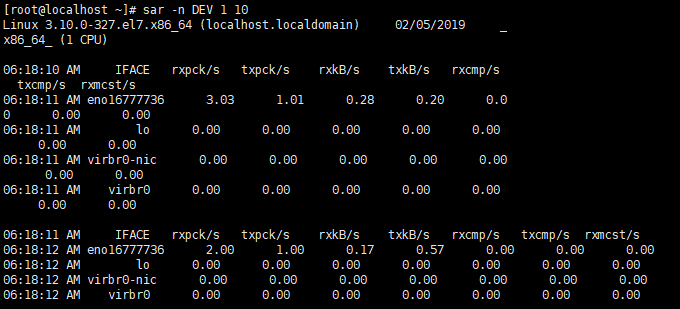
查看lo网卡的流量,10秒一次网卡流量监测,average为0时,需要重启网卡。
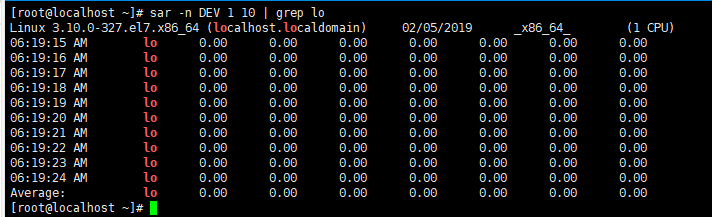
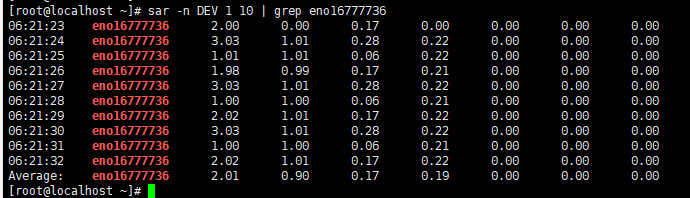
脚本执行的结果
注意 :
sar -n DEV 1 10|grep -w "$1" > /tmp/sar.tmp #把网卡流量的每10秒统计一次的结果的第一行,写入到 /tmp/sar.tmp
in=`grep "Average:" /tmp/sar.tmp|awk '{print $5}'|sed 's/\.//'` #进入的流量的第五行,输入到/tmp/sar.tmp,去掉前面的小数点。
out=`grep "Average:" /tmp/sar.tmp|awk '{print $6}'|sed 's/\.//'` #输出的流量的第六行,输入到/tmp/sar.tmp,去掉前面的小数点。
if [ $in == "000" ] && [ $out == "000" ] #当进入的和输出的,都为0时,重启网卡。
来源 :https://github.com/aminglinux/shell100/blob/master/13.md







 本文集提供了多个实用的Shell脚本示例,涵盖时间问候、菜单交互、用户登录检测、系统安全检查、网络状态监控等场景,帮助读者深入理解Shell脚本的编写技巧。
本文集提供了多个实用的Shell脚本示例,涵盖时间问候、菜单交互、用户登录检测、系统安全检查、网络状态监控等场景,帮助读者深入理解Shell脚本的编写技巧。

















 817
817

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








