- java 异常机制的特点
1、把各种不同的类型的异常情况进行分类,用java类来表示异常情况,称为异常类
2、异常流程的代码和正常流程的代码分离,提高程序的可读性,简化结构
3、可以灵活的处理异常,如当前方法有能力处理异常,就捕获并且处理它 try...catch... ,
否则只需要抛出异常 throws exception,由方法调用者来处理它。 - java虚拟机方法调用栈
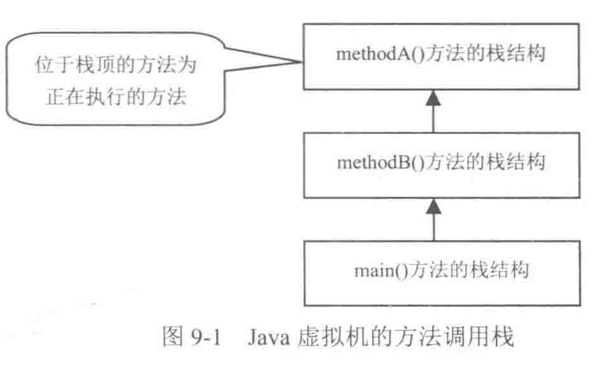
-
package Exception; /** * Created by yg on 2019/1/26. */ public class ExceptionDemo { public void methodA(int money) throws SpecialException { if (money < 0) throw new SpecialException("异常啦~~~"); System.out.println("--- methodA,这里执行不到"); // throw new 一抛出,后面剩下的代码都不会执行啦... } public void methodB1(int money) throws SpecialException { methodA(money); System.out.println("--- methodb"); } // public void methodB2(int money) { // // try { // methodA(money); // } catch (SpecialException e) { // System.out.println("--- 这个异常我可以自己处理,就不让别人擦屁股"); // e.printStackTrace(); // } // } // public static void main(String args[]) { // try { // new ExceptionDemo().methodB1(-1); // } catch (SpecialException e) { // e.printStackTrace(); // 异常处理了,仅仅是打印而已,总比不写任何处理好啊.. // } // } public static void main(String args[]) throws SpecialException { System.out.println("---我仅仅抛出异常了,可我已经是主线程了," + "系统会自动调用异常对象的 pringStackTrace())方法,打印来自方法调用栈的异常信息"); new ExceptionDemo().methodB1(-1); } // public static void main(String args[]) { // new ExceptionDemo().methodB2(-1); // } } - finally 关键字,顾名思义,最终一定要做点什么事情, 不管 try代码中是否出现异常,都会执行finally代码块!!!
public void methodB2(int money) { try { methodA(money); } catch (SpecialException e) { System.out.println("--- 被methodB 捕获了,继续执行下面的代码"); e.printStackTrace(); } finally { System.out.println("--- 我处理完异常了!!!"); } }不建议用下面这个写法,缺点有两个: 1、程序太松散,可读性差 2、万一 catch 里面继续抛出异常,就会被跳过去,不执行 "--- 我处理完异常了!!!"。 public void methodB2(int money) { try { methodA(money); } catch (SpecialException e) { System.out.println("--- 被methodB 捕获了,继续执行下面的代码"); e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("--- 我处理完异常了!!!"); }finally 来个案例分析吧 public class ExceptionDemo { public void methodA(int money) throws SpecialException { if (money < 0) throw new SpecialException("异常啦~~~"); System.out.println("--- methodA,这里执行不到"); } public void methodB3(int money) throws SpecialException { try { methodA(money); } catch (SpecialException e) { System.out.println("--- 第1步:被methodB 捕获了,继续执行下面的代码"); if (money < 0) { System.out.println("--- 第2步:我草,我又抓了一个异常,继续抛出"); throw e; } } finally { System.out.println("--- 第3步:catch完调用finally"); // try catch 执行完 立马执行自己的finally代码块,不用管catch里面继续抛出的异常. } System.out.println("--- 我处理完异常了!!!"); 这句不执行,为啥?catch里面又抛出异常了啊!!! } public static void main(String args[]) { try { new ExceptionDemo().methodB3(-1); } catch (SpecialException e) { System.out.println("--- 第4步:终于来问这里了方式"); } finally { System.out.println("--- 第5步:我还得屁股擦一擦"); } } } 执行结果如下: --- 第1步:被methodB 捕获了,继续执行下面的代码 --- 第2步:我草,我又抓了一个异常,继续抛出 --- 第3步:catch完调用finally --- 第4步:终于来问这里了方式 --- 第5步:我还得屁股擦一擦 注意:第3步在第4步之前执行我们把main函数改一改如下: public static void main(String args[]) throws SpecialException { try { new ExceptionDemo().methodB3(-1); } finally { System.out.println("---- 屁股擦一擦"); } } 执行结果又是如何呢??? --- 第1步:被methodB 捕获了,继续执行下面的代码 --- 第2步:我草,我又抓了一个异常,继续抛出 --- 第3步:catch完调用finally ---- 屁股擦一擦 Exception in thread "main" Exception.SpecialException: 异常啦~~~ at Exception.ExceptionDemo.methodA(ExceptionDemo.java:12) at Exception.ExceptionDemo.methodB3(ExceptionDemo.java:20) at Exception.ExceptionDemo.main(ExceptionDemo.java:37) at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method) at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:62) at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43) at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:498) at com.intellij.rt.execution.application.AppMain.main(AppMain.java:147) - throws : 用来声明可能出现的异常,可以抛出多个异常,特点:有throw的地方一定有throws
public void method() throws SQLException,IOException{...} - 异常处理 语法规则,这个笔试的时候回碰到
1、try 后面可以跟多个catchtry { methodA(money); } catch (SpecialException e) { System.out.println("--- 被methodB 捕获了,继续执行下面的代码"); e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }2、try后面没有catch,但必须有finally 代码块,catch和finally至少得有一种。public static void main(String args[]) throws SpecialException { try { new ExceptionDemo().methodB1(-1); } finally { System.out.println("---- 屁股擦一擦"); } } - finally 什么时候不会执行呢?这时候出现了一个学渣exit(0),他有背景,看到我你只能立马提裤子走人。
public static void main(String args[]) throws SpecialException { try { System.out.println("----大便的时候学渣来捣乱..."); System.exit(0); new ExceptionDemo().methodB3(-1); } finally { System.out.println("---- 屁股都还没擦...."); } } 结果呢!!! 你没看错,碰到学渣连屁股都没有擦一擦就跑走了,怕被他玩死... ----大便的时候学渣来捣乱... Process finished with exit code 0 tips:如果在执行try代码块中调用了exit(0),则finally代码块以及try...finally 语句后面的代码都不会执行。 - return 语句,在执行try 或 catch 代码块中的return语句时,假如有finally代码块,会先执行finally代码块,然后再return出来
Demo1:先执行 finally代码块,再执行try的return public class ExceptionDemo { public int methodA(int money) { System.out.println("--- methodA"); return -100; } public int methodB5(int money) { try { System.out.println("--- begin"); int result = methodA(money); System.out.println("----执行B"); return result; // 浅黄后执行 } finally { System.out.println("--- final"); // 深黄先执行 } } public static void main(String args[]) { System.out.println("--- result:" + new ExceptionDemo().methodB5(-1)); } } 执行结果: --- begin --- methodA ----执行B --- final --- result:-100Demo2:先执行finally代码块,再执行catch里面的return public class ExceptionDemo { public int methodA(int money) throws SpecialException { if (money < 0) { throw new SpecialException("异常啦~~~"); // return -200; unreachble statement } System.out.println("--- methodA,这里执行不到"); return -100; } public int methodB5(int money) { try { System.out.println("--- begin"); int result = methodA(money); System.out.println("---- 这里不会执行,有异常,已被捕获了呢"); return result; // 浅黄后执行 } catch (SpecialException e) { System.out.println("--- message:" + e.getMessage()); return -200; } finally { System.out.println("--- final"); // 深黄先执行 } } public static void main(String args[]) { System.out.println("--- result:" + new ExceptionDemo().methodB5(-1)); } } 执行结果: --- begin --- message:异常啦~~~ --- final --- result:-200 - 变量:finally 代码块不能通过重新给变量赋值的方式来改变 return 语句的返回值,这个经常笔试会碰到!!!
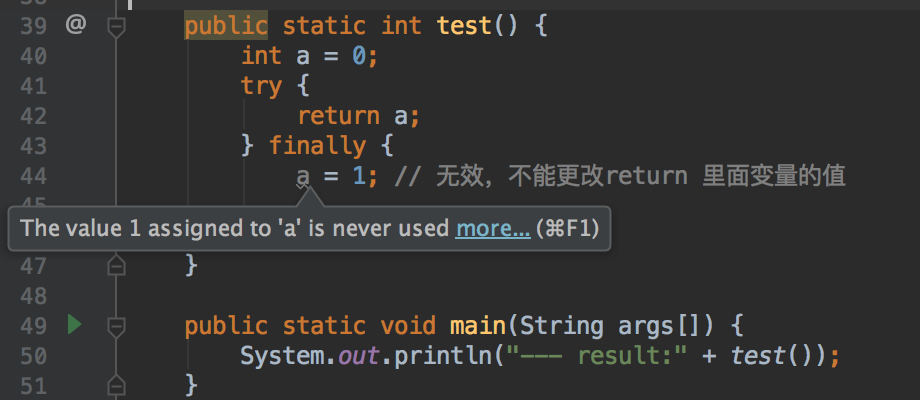
- 如果finally里面直接return呢???
public class ExceptionDemo { public int methodA(int money) throws SpecialException { if (money < 0) { throw new SpecialException("异常啦~~~"); // return -200; unreachble statement } System.out.println("--- methodA,这里执行不到"); return -100; } public int methodB5(int money) { try { System.out.println("--- begin"); int result = methodA(money); System.out.println("---- 这里不执行,有异常,已被捕获了"); return result; // 不执行 } catch (SpecialException e) { System.out.println("--- message:" + e.getMessage()); return -200; // 不执行 } finally { System.out.println("--- final"); return 300; // 这finally里面return 会覆盖try和catch里面的return,以这里面的return为准。 } } public static void main(String args[]) { System.out.println("--- result:" + new ExceptionDemo().methodB5(-1)); } } 结果: --- begin --- message:异常啦~~~ --- final --- result:300 tips:建议不要再finally代码块中使用return,因为会覆盖try、catch里面的return。还有一种情况会导致异常丢失。public int methodB6(int money) { try { methodA(money); } catch (SpecialException e) { throw new SpecialException("----wrong"); 《==== 这个不会执行,没有提示method6 方法要 throws 异常。 } finally { System.out.println("--- 第3步:catch完调用finally"); return 200; } } 可以对比 public void methodB6(int money) throws SpecialException { try { methodA(money); } catch (SpecialException e) { throw new SpecialException("----wrong"); } finally { System.out.println("--- 第3步:catch完调用finally"); 这里没有return,所有catch里面的异常不会被丢弃。 } } - 异常类
public class Exception extends Throwable
获取异常信息的两方法 public void printStackTrace() { printStackTrace(System.err); } public String getMessage() { return detailMessage; }System.out.println("---- message"+e.getMessage()); e.printStackTrace(); 结果: ---- message异常啦~~~ Exception.SpecialException: 异常啦~~~ at Exception.ExceptionDemo.methodA(ExceptionDemo.java:14) at Exception.ExceptionDemo.methodB3(ExceptionDemo.java:26) at Exception.ExceptionDemo.main(ExceptionDemo.java:42) at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method) at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:62) at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43) at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:498) at com.intellij.rt.execution.application.AppMain.main(AppMain.java:147)

- Exception 类,又分为两类
运行时异常,runtimeException,也称uncheckException,编译器不检查它,即使没有try catch 或者throws ,还是会编译通过。
受检查异常,Checked Exception,编译器会自己检查,当程序出现这类异常时,要么try catch,要么throws,不然报错。
- 运行时异常由于不受检查,表示无法让程序恢复运行的异常,一旦出现,建议终止程序。







 本文深入解析Java异常机制,包括异常分类、处理流程及代码示例。探讨如何利用异常类提高程序可读性和灵活性,以及finally关键字的作用。
本文深入解析Java异常机制,包括异常分类、处理流程及代码示例。探讨如何利用异常类提高程序可读性和灵活性,以及finally关键字的作用。

















 814
814

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








