最近遇到很多问题都跟Prime有关,于是总结一下:
Prime definition:A prime number (or a prime) is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. A natural number greater than 1 that is not a prime number is called a composite number. So 1 is not a prime, but 2 is a prime.
性质:
先说composite number:Every composite number has at least one prime factor less than or equal to square root of itself. composite又必须含有divisor other than 1 and itself, 所以必须在[2 ,![]() ] inclusive之间有可以整除的prime factor
] inclusive之间有可以整除的prime factor
所以prime number的性质就是:在 [2 ,![]() ] inclusive 之间找不到一个数i 使得 n % i == 0
] inclusive 之间找不到一个数i 使得 n % i == 0
问题1:Efficient program to print all prime factors of a given number
Given a number n, write an efficient function to print all prime factors of n. For example, if the input number is 12, then output should be “2 2 3″. And if the input number is 315, then output should be “3 3 5 7″.
Following are the steps to find all prime factors.
1) While n is divisible by 2, print 2 and divide n by 2.
2) After step 1, n must be odd. Now start a loop from i = 3 to square root of n. While i divides n, print i and divide n by i, increment i by 2 and continue.
3) If n is a prime number and is greater than 2, then n will not become 1 by above two steps. So print n if it is greater than 2.
1 // A function to print all prime factors of a given number n 2 void primeFactors(int n) 3 { 4 // Print the number of 2s that divide n 5 while (n%2 == 0) 6 { 7 printf("%d ", 2); 8 n = n/2; 9 } 10 11 // n must be odd at this point. So we can skip one element (Note i = i +2) 12 for (int i = 3; i <= sqrt(n); i = i+2) 13 { 14 // While i divides n, print i and divide n 15 while (n%i == 0) 16 { 17 printf("%d ", i); 18 n = n/i; 19 } 20 } 21 22 // This condition is to handle the case whien n is a prime number 23 // greater than 2 24 if (n > 2) 25 printf ("%d ", n); 26 }
测试一下上述程序
int main() { int n = 315; primeFactors(n); return 0; }
输出
3 3 5 7
要特别注意12行sqrt(n)中的n是一直随 n = n / i 更新的,而不是始终都是最初始的n。这相当于是在找新的n的prime factor, 而且确定这个新的n的prime factor不包括之前找到过的 i,因为前面已经把小的prime factor全找出来了。反正只要 n 还是 composite number, 那么一定有一个prime factor小于sqrt(n), 那么就一定能找到新的 i 满足条件。找不到就说明 n 不是 composite number了。所以,最后跳出while循环是因为要么n变成了1,要么n变成了质数
当然不这么设置 i 的范围也可以,可以设置 i 从3 到最初的sqrt(n), 或者甚至n,这样可以,但是浪费时间。
How does this work?
The steps 1 and 2 take care of composite numbers and step 3 takes care of prime numbers. To prove that the complete algorithm works, we need to prove that steps 1 and 2 actually take care of composite numbers. This is clear that step 1 takes care of even numbers. And after step 1, all remaining prime factor must be odd (difference of two prime factors must be at least 2), this explains why i is incremented by 2.
Now the main part is, the loop runs till square root of n not till. To prove that this optimization works, let us consider the following property of composite numbers.
Every composite number has at least one prime factor less than or equal to square root of itself.
This property can be proved using counter statement. Let a and b be two factors of n such that a*b = n. If both are greater than ![]() , then a.b >
, then a.b > ![]() which contradicts the expression “a * b = n”.
which contradicts the expression “a * b = n”.
In step 2 of the above algorithm, we run a loop and do following in loop
a) Find the least prime factor i (must be less than ![]() )
)
b) Remove all occurrences i from n by repeatedly dividing n by i.
c) Repeat steps a and b for divided n and i = i + 2. The steps a and b are repeated till n becomes either 1 or a prime number.
问题2: 写一个判断自然数n是不是prime的函数
1 public class Solution { 2 public boolean isPrime(int n) { 3 if (n <= 1) return false; 4 if (n == 2) return true; 5 if (n % 2 == 0) return false; 6 for (int i=3; i<=Math.sqrt(n); i=i+2) { 7 if (n % i == 0) return false; 8 } 9 return true; 10 } 11 }
Wiki上也给出了这个算法:The property of being prime (or not) is called primality. A simple but slow method of verifying the primality of a given number n is known as trial division. It consists of testing whether n is a multiple of any integer between 2 and 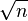 . Algorithms much more efficient than trial division have been devised to test the primality of large numbers. Particularly fast methods are available for numbers of special forms, such as Mersenne numbers. As of April 2014, the largest known prime number has 17,425,170 decimal digits.
. Algorithms much more efficient than trial division have been devised to test the primality of large numbers. Particularly fast methods are available for numbers of special forms, such as Mersenne numbers. As of April 2014, the largest known prime number has 17,425,170 decimal digits.
问题3:
Given a number n, print all primes smaller than or equal to n. It is also given that n is a small number. For example, if n is 10, the output should be “2, 3, 5, 7″. If n is 20, the output should be “2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19″.
The sieve of Eratosthenes is one of the most efficient ways to find all primes smaller than n when n is smaller than 10 million or so (Ref Wiki).
Following is the algorithm to find all the prime numbers less than or equal to a given integer n by Eratosthenes’ method:
- Create a list of consecutive integers from 2 to n: (2, 3, 4, …, n).
- Initially, let p equal 2, the first prime number.
- Starting from p, count up in increments of p and mark each of these numbers greater than p itself in the list. These numbers will be 2p, 3p, 4p, etc.; note that some of them may have already been marked.
- Find the first number greater than p in the list that is not marked. If there was no such number, stop. Otherwise, let p now equal this number (which is the next prime), and repeat from step 3.
When the algorithm terminates, all the numbers in the list that are not marked are prime.
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 4 // marks all mutiples of 'a' ( greater than 'a' but less than equal to 'n') as 1. 5 void markMultiples(bool arr[], int a, int n) 6 { 7 int i = 2, num; 8 while ( (num = i*a) <= n ) 9 { 10 arr[ num-1 ] = 1; // minus 1 because index starts from 0. 11 ++i; 12 } 13 } 14 15 // A function to print all prime numbers smaller than n 16 void SieveOfEratosthenes(int n) 17 { 18 // There are no prime numbers smaller than 2 19 if (n >= 2) 20 { 21 // Create an array of size n and initialize all elements as 0 22 bool arr[n]; 23 memset(arr, 0, sizeof(arr)); 24 25 /* Following property is maintained in the below for loop 26 arr[i] == 0 means i + 1 is prime 27 arr[i] == 1 means i + 1 is not prime */ 28 for (int i=1; i<n; ++i) 29 { 30 if ( arr[i] == 0 ) 31 { 32 //(i+1) is prime, print it and mark its multiples 33 printf("%d ", i+1); 34 markMultiples(arr, i+1, n); 35 } 36 } 37 } 38 } 39 40 // Driver Program to test above function 41 int main() 42 { 43 int n = 30; 44 printf("Following are the prime numbers below %d\n", n); 45 SieveOfEratosthenes(n); 46 return 0; 47 }




 本文总结了关于素数的定义、性质以及如何高效地找出给定数字的所有素因数的方法。此外,还提供了判断自然数是否为素数的函数实现,并介绍了通过埃拉托斯特尼筛法找出小于等于给定整数的所有素数的算法。
本文总结了关于素数的定义、性质以及如何高效地找出给定数字的所有素因数的方法。此外,还提供了判断自然数是否为素数的函数实现,并介绍了通过埃拉托斯特尼筛法找出小于等于给定整数的所有素数的算法。

















 1579
1579

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








