reference: Very intuitive example shown in this blog
https://wiseodd.github.io/techblog/2016/12/21/forward-reverse-kl/
Let our true distribution defined as
P
(
X
)
P(X)
P(X), and the approximate distribution as
Q
(
X
)
Q(X)
Q(X).
Forward KL:
∑
x
∈
X
P
(
x
)
log
(
P
(
x
)
Q
(
x
)
)
\sum_{x \in X} P(x) \log(\frac{P(x)}{Q(x)})
∑x∈XP(x)log(Q(x)P(x))
Discussion in different cases:
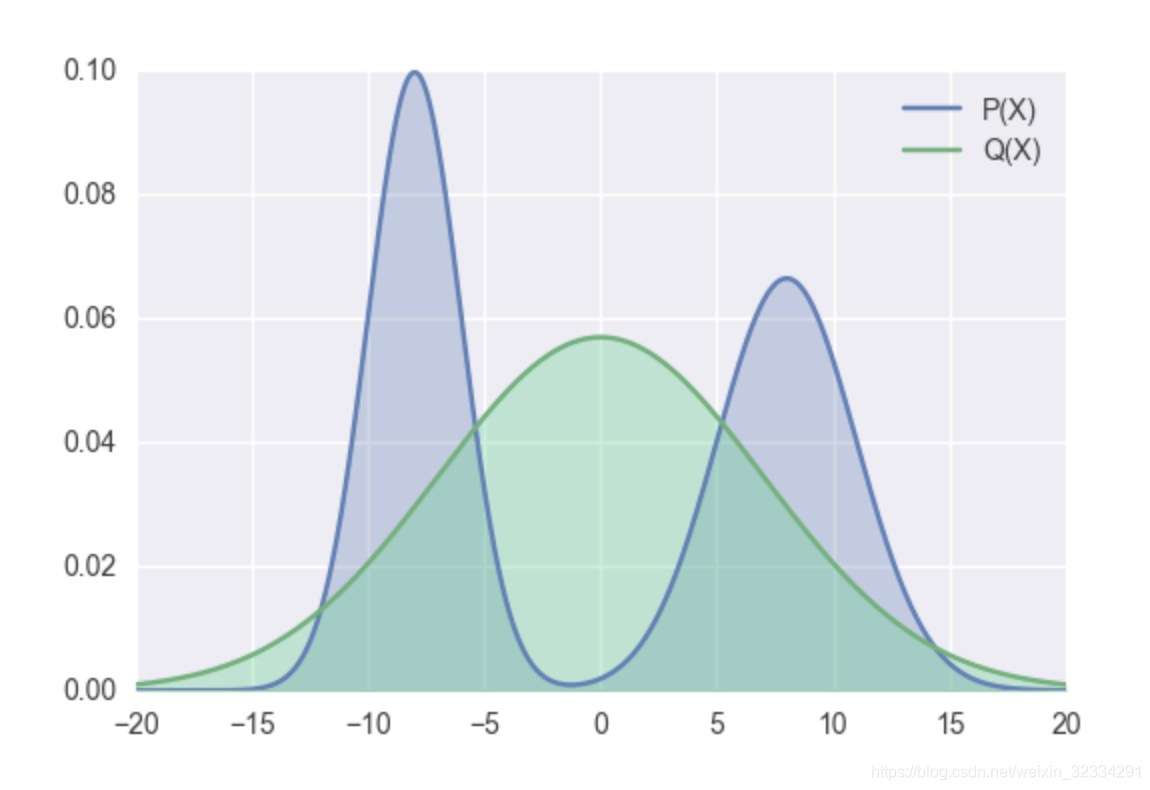
- If P(x)=0, then log term can be igored so that the Q(x) can be any shape when P(x)=0. Q(x) is able to assign any probabilities when P(x)=0)
- If P(x)>0, then the log term have effect during optimization so that Q(x) assign probabilities as close as possible to P(X) when P(x)>0.
- The following graph is a specific optimal optimization for Forward KL.
Reverse KL: ∑ x ∈ X Q ( x ) log ( Q ( x ) P ( x ) ) \sum_{x \in X} Q(x) \log(\frac{Q(x)}{P(x)}) ∑x∈XQ(x)log(P(x)Q(x))
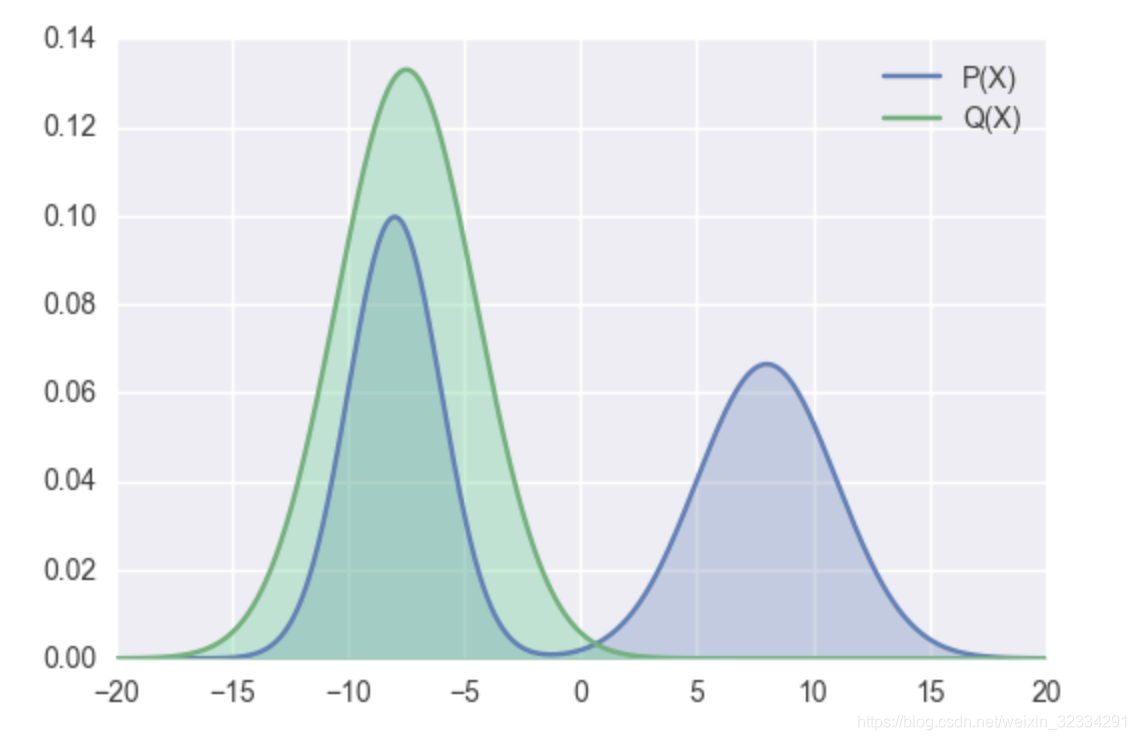
- If Q(x)=0, log term can be ignored so that Q(x) able to assign 0 probabilities to P(x)>=0.
- If Q(x) > 0, log term is taken into account in optimization step so that Q(x) assign probabilites as close as possible to P(X) when P(x)>0
- The following graph is a specific optimal optimization for Reverse KL.





 本文深入探讨了KL散度的两种形式:前向KL与反向KL。通过直观的例子,解释了当真实分布P(X)与近似分布Q(X)不同时,两者在优化过程中的作用与差异。前向KL关注P(X)>0时Q(X)的概率分配,而反向KL则允许Q(X)在P(X)=0时分配概率。
本文深入探讨了KL散度的两种形式:前向KL与反向KL。通过直观的例子,解释了当真实分布P(X)与近似分布Q(X)不同时,两者在优化过程中的作用与差异。前向KL关注P(X)>0时Q(X)的概率分配,而反向KL则允许Q(X)在P(X)=0时分配概率。
















 1006
1006

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








