C语言实现队列
1.队列的结构及相关概念
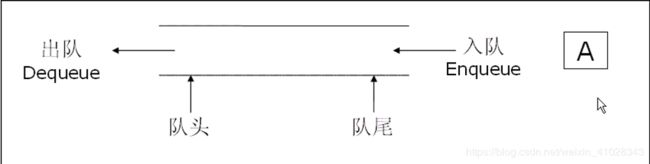
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出 FIFO(First In First Out)的特性。
入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾
出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头
2.队列的实现:
队列也可以数组和链表的结构实现,使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数 组头上出数据,效率会比较低。下面,我们描述如何使用链表实现队列。
QueueNode.h文件:
typedef int DataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* _next;
DataType _data;
}QueueNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QueueNode* _front;//队头
QueueNode* _rear;//队尾
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* p);//初始化队列
void QueueDestory(Queue* p);//销毁队列
void QueuePush(Queue* p,DataType x);//入队
void QueuePop(Queue* p);//出队
DataType QueueFront(Queue* p);//获取队首元素
DataType QueueBack(Queue* p);//获取队尾元素
int QueueEmpty(Queue* p);//判断队列是否为空
int QueueSize(Queue* p);//队列的大小
void Queueprint(Queue* p);//打印队列
void TestQueue();//测试
QueueNode.c文件:
//对队列进行初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* p)
{
assert(p);
p->_front = p->_rear = NULL;
}
//销毁队列
void QueueDestory(Queue* p)
{
assert(p);
QueueNode* cur = p->_front;
while (cur)
{
p->_front = cur->_next;
free(cur);
cur = p->_front;
}
//将队尾置空
p->_rear = NULL;
}
//入队:队尾插入元素
void QueuePush(Queue* p, DataType x)
{
assert(p);
QueueNode* newNode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
newNode->_data = x;
newNode->_next = NULL;
//判断是否为第一个插入的元素
if (p->_front == NULL)
{
p->_front = p->_rear = newNode;
}
else
{
p->_rear->_next = newNode;
p->_rear = p->_rear->_next;
}
}
//出队:队首删除元素
void QueuePop(Queue* p)
{
assert(p);
if (p->_front)
{
QueueNode* next = p->_front->_next;
//删除,出队
free(p->_front);
p->_front = next;
//如果删除的为最后一个元素
if (p->_front == NULL)
{
p->_rear = NULL;
}
}
}
//获取队首元素
DataType QueueFront(Queue* p)
{
assert(p);
return p->_front->_data;
}
DataType QueueBack(Queue* p)
{
assert(p);
return p->_rear->_data;
}
//判断队列是否为空
int QueueEmpty(Queue* p)
{
assert(p);
if (p->_front == NULL)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
//队列的大小
int QueueSize(Queue* p)
{
assert(p);
QueueNode* cur = p->_front;
DataType n = 0;
while (cur)
{
++n;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
//打印队列
void Queueprint(Queue* p)
{
assert(p);
QueueNode* cur = p->_front;
while (cur)
{
printf("%d ", cur->_data);
cur = cur->_next;
}
printf("\n");
}
//测试
void TestQueue()
{
Queue p;
QueueInit(&p);
QueuePush(&p, 1);
QueuePush(&p, 2);
QueuePush(&p, 3);
QueuePush(&p, 4);
QueuePop(&p);
QueuePop(&p);
Queueprint(&p);
}
main.c文件:
int main()
{
TestQueue();
return 0;
}
队列中需特别理解队列的特性——先进先出规则。
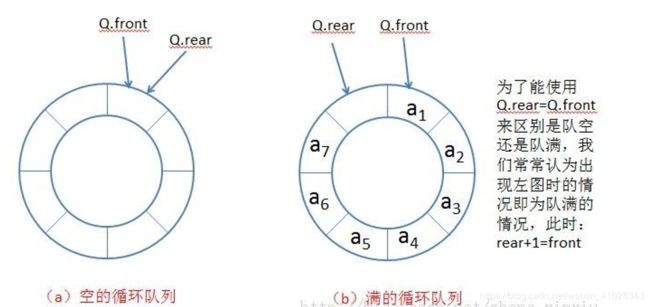
在实际使用中还有一种特殊的队列——循环队列。如操作系统课程讲解生产者消费者模型时可以就会使用循环队列。环形队列可以使用数组实现,也可以使用循环链表实现。
循环队列的实现(leetcode上的原题):
//函数接口说明:
//MyCircularQueue(k) : 构造器,设置队列长度为 k 。
//Front : 从队首获取元素。如果队列为空,返回 - 1 。
//Rear : 获取队尾元素。如果队列为空,返回 - 1 。
//enQueue(value) : 向循环队列插入一个元素。如果成功插入则返回真。
//deQueue() : 从循环队列中删除一个元素。如果成功删除则返回真。
//isEmpty() : 检查循环队列是否为空。
//isFull() : 检查循环队列是否已满。
//free():释放空间
typedef struct
{
int* _a;
int _front;//队首
int _rear;//队尾
int _k;
} MyCircularQueue;
/** Checks whether the circular queue is empty or not. */
//判断为空的条件即是队尾等于队首
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
return obj->_front == obj->_rear;
}
/** Checks whether the circular queue is full or not. */
//判断是否已满的条件是(队尾大小+1)%(容量大小+1)== 队首大小。
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
return ((obj->_rear + 1) % (obj->_k) == (obj->_front));
}
/** Initialize your data structure here. Set the size of the queue to be k. */
MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k)
{
MyCircularQueue* Queue = (MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));
Queue->_a = (int*)malooc(sizeof(int)*(k + 1));
Queue->_front = 0;
Queue->_rear = 0;
Queue->_k = k;
}
/** Insert an element into the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value)
{
assert(obj);
if (myCircularQueueIsFull(obj))
{
return false;
}
obj->_a[obj->_rear] = value;
obj->_rear++;
if (obj->_rear == obj->_k + 1)
{
obj->_rear = 0;
}
return true;
}
** Delete an element from the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
assert(obj);
if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
{
return false;
}
obj->_front++;
if (obj->_front == obj->_k + 1)
{
obj->_front = 0;
}
return true;
}
/** Get the front item from the queue. */
int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
assert(obj);
if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
{
return -1;
}
return obj->_a[obj->_front];
}
/** Get the last item from the queue. */
int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
assert(obj);
if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
{
return -1;
}
if (obj->_rear == 0)
{
return obj->_a[obj->_k];
}
return obj->_a[obj->_rear - 1];
}
void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
free(obj->_a);
free(obj);
}
需注意:循环队列是逻辑上循环,物理上不循环的。







 本文介绍了如何使用C语言实现先进先出(FIFO)队列的数据结构,包括队列的概念、初始化、入队、出队等操作。通过示例代码展示了如何创建链表结构的队列,并提供了测试用例。此外,还提到了循环队列的概念及其在操作系统中的应用。
本文介绍了如何使用C语言实现先进先出(FIFO)队列的数据结构,包括队列的概念、初始化、入队、出队等操作。通过示例代码展示了如何创建链表结构的队列,并提供了测试用例。此外,还提到了循环队列的概念及其在操作系统中的应用。
















 855
855

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








