在C++11中,引入了智能指针。主要有:unique_ptr, shared_ptr, weak_ptr。
这3种指针组件就是采用了boost里的智能指针方案。很多有用过boost智能指针的朋友,很容易地就能发现它们之间的关间:
stdboost功能说明
unique_ptr
scoped_ptr
独占指针对象,并保证指针所指对象生命周期与其一致
shared_ptr
shared_ptr
可共享指针对象,可以赋值给shared_ptr或weak_ptr。
指针所指对象在所有的相关联的shared_ptr生命周期结束时结束,是强引用。
weak_ptr
weak_ptr
它不能决定所指对象的生命周期,引用所指对象时,需要lock()成shared_ptr才能使用。
C++11将boost里的这一套纳入了标准。
如下为示例代码:
//文件 test-1.cpp
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
unique_ptr up1(new int(11));
unique_ptr up2 = up1; //! 编译时会出错 [1]
cout <
unique_ptr up3 = move(up1); //! [2]
cout <
if (up1)
cout <
up3.reset(); //! [3]
up1.reset();
shared_ptr sp1(make_shared("Hello"));
shared_ptr sp2 = sp1;
cout <
cout <
sp1.reset();
cout <
weak_ptr wp = sp2; //! [4]
cout <
sp2.reset();
cout <
return 0;
}
//编译命令: g++ -std=c++11 test-1.cpp
[1]: unique_ptr 是禁止复制赋值的,始终保持一个 unique_ptr 管理一个对象。
[2]: unique_ptr 虽然不能赋值,但可以通过 move() 函数转移对象的所有权。一旦被 move() 了,原来的 up1 则不再有效了。
[3]: reset() 可以让 unique_ptr 提前释放指针。
[4]: 由 shared_ptr 构造一个 weak_ptr。
shared_ptr 与 weak_ptr
如下面的示例:
shared_ptr s1(new string);
shared_ptr s2 = s1;
weak_ptr w1 = s2;
在内存中:
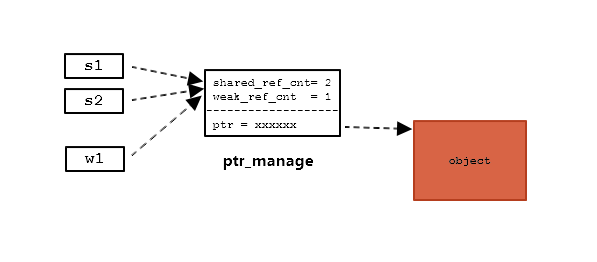
s1, s2, w1 都指向一个 ptr_manage 的对象。
在该对象中有 shared_ref_count 与 weak_ref_count 两个域分别记录引用它的 shared_ptr 与 weak_ptr 的个数。这个很容易办到,只要在复制构造与赋值函数中对相当地引用值进行加1,在析构中减1即可。ptr_manage 中的 ptr 域存放真正的对象指针地址。
当 shared_ref_cnt 被减为0时,自动释放 ptr 指针所指向的对象。当 shared_ref_cnt 与 weak_ref_cnt 都变成0时,才释放 ptr_manage 对象。
如此以来,只要有相关联的 shared_ptr 存在,对象就存在。weak_ptr 不影响对象的生命周期。当用 weak_ptr 访问对象时,对象有可能已被释放了,要先 lock()。
当执行:
s1.reset()
此时:
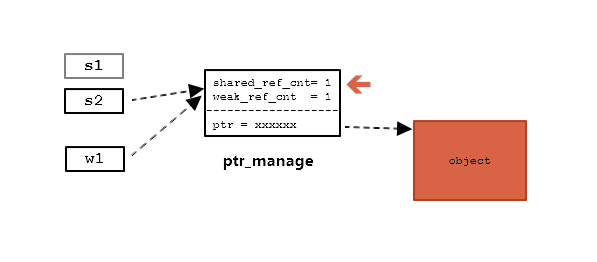
shared_ref_cnt 由2减成了1。
再执行:
s2.reset()
此时:
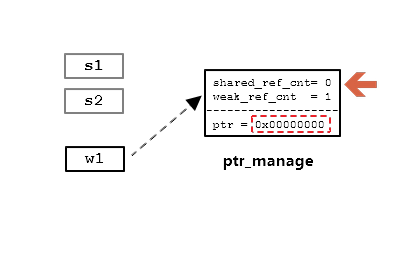
shared_ref_cnt 已被减到0了,ptr 所对应的object已被释放,ptr 被清0。此时,ptr_manage 依旧保留。因为 w1 还需要引用它。
在最后,w1 也析构了的时候:
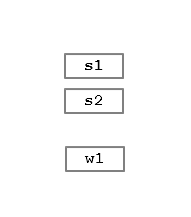
ptr_manage 中的 weak_ref_cnt 被减成0,最后连 ptr_manage 都释放了。








 本文介绍了C++11中的智能指针unique_ptr, shared_ptr和weak_ptr。unique_ptr是独占所有权的,不支持赋值操作;shared_ptr允许多个指针共享对象,对象在所有shared_ptr析构后释放;weak_ptr不控制对象生命周期,需转换为shared_ptr才能访问。示例代码展示了它们的使用和生命周期管理。
本文介绍了C++11中的智能指针unique_ptr, shared_ptr和weak_ptr。unique_ptr是独占所有权的,不支持赋值操作;shared_ptr允许多个指针共享对象,对象在所有shared_ptr析构后释放;weak_ptr不控制对象生命周期,需转换为shared_ptr才能访问。示例代码展示了它们的使用和生命周期管理。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








