从 PostSharp官方网站下载一个试用版,安装
简单示例
PostSharp采用Post-Compile的方式实现AOP,即对已经生成的程序集,按照拦截规则进行修改,对需要拦截的方法注入拦截代码。这种方式与基于动态代理的方式相比,没有过多限制,比如不需要目标方法为virtual类型或者实现了接口等
1. 新建一个PostSharp.Test的Console测试项目添加引用: PostSharp、PostSharp.Laos
2. 程序引用的命名空间
using System;
using System.Reflection;
using PostSharp.Laos;
3. 测试用的代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
private
static
void
SayHello(
string
user,
string
title)
{
Console.WriteLine(
string
.Format(
"Hello {0} {1}"
, title, user));
}
private
static
void
ThrowException()
{
throw
new
Exception(
"I'm a test message."
);
}
static
void
Main(
string
[] args)
{
SayHello(
"Richie"
,
"Mr."
);
try
{
ThrowException();
}
catch
{
}
Console.ReadKey();
return
;
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
[Serializable]
public
class
OnMyExceptionAspect : OnMethodBoundaryAspect
{
public
override
void
OnEntry(MethodExecutionEventArgs eventArgs)
{
base
.OnEntry(eventArgs);
Console.WriteLine(
string
.Format(
"Entering method: {0}"
, eventArgs.Method.Name));
object
[] arguments = eventArgs.GetReadOnlyArgumentArray();
ParameterInfo[] parameters = eventArgs.Method.GetParameters();
for
(
int
i = 0; arguments !=
null
&& i < arguments.Length; i++)
Console.WriteLine(
string
.Format(
" arg{0} {1}: {2}"
, i + 1, parameters[i].Name, arguments[i]));
}
public
override
void
OnExit(MethodExecutionEventArgs eventArgs)
{
base
.OnExit(eventArgs);
Console.WriteLine(
string
.Format(
"Exiting method: {0}"
, eventArgs.Method.Name));
}
public
override
void
OnException(MethodExecutionEventArgs eventArgs)
{
Console.WriteLine(
"There's an error occured:"
+ eventArgs.Exception.Message);
base
.OnException(eventArgs);
}
}
|
5. 接下来的2个步骤就是设置项目,使得PostSharp在编译结束后能够对生成的程序集进行修改,假如拦截处理机制
a). 在项目中添加一个assembly指令,告诉PostSharp对哪些目标实施拦截
[assembly: PostSharp.Test.OnMyExceptionAspect(
AttributeTargetAssemblies = "PostSharp.Test",
AttributeTargetTypes = "PostSharp.Test.Program")]
b). 修改项目文件,让PostSharp在编译完成后能够注入拦截代码:
先通过VS的右键菜单卸载项目
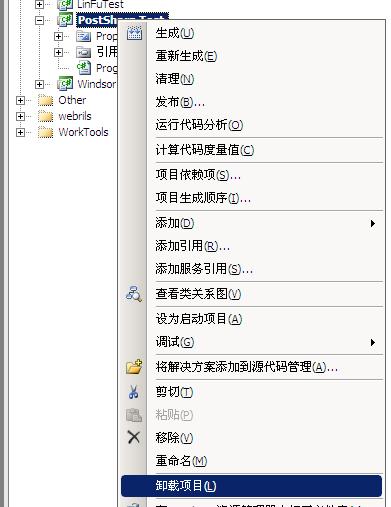
然后通过VS邮件菜单编辑项目文件,添加一个import指令:
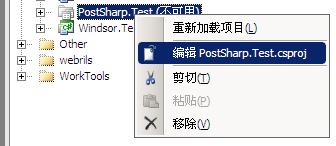
在<Import Project="$(MSBuildToolsPath)\Microsoft.CSharp.targets" />后面添加一条import指令如下:
<Import Project="E:\Program Files\PostSharp 2.0\PostSharp.targets" />
6. 重新加载项目,编译,PostSharp就会在我们指定的位置上使用我们的OnMyExceptionAspect对Program的方法调用注入拦截代码,运行结果如下:
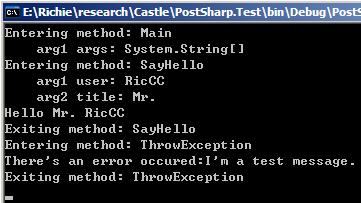
使用Attribute方式
上面使用一个assembly指令告诉PostSharp应该对哪些方法实施拦截,OnMethodBoundaryAspect类已经继承了Attribute,因此我们可以通过给类或者方法添加Attribute的方式来代替assembly指令
下面示例需要引用的命名空间:
using System;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Reflection;
using PostSharp.Extensibility;
using PostSharp.Laos;
我们用下面的PropertyChangedNotificationAttribute来实现对象属性更改通知:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
[Serializable]
[MulticastAttributeUsage(MulticastTargets.Method)]
public
class
PropertyChangedNotificationAttribute : OnMethodBoundaryAspect
{
private
object
_preValue;
public
override
void
OnExit(MethodExecutionEventArgs eventArgs)
{
base
.OnExit(eventArgs);
if
(!eventArgs.Method.IsSpecialName)
return
;
if
(!eventArgs.Method.Name.StartsWith(
"get_"
)
&& !eventArgs.Method.Name.StartsWith(
"set_"
))
return
;
bool
isSetter = eventArgs.Method.Name.StartsWith(
"set_"
);
string
property = eventArgs.Method.Name.Substring(4);
if
(isSetter)
Console.WriteLine(
string
.Format(
"Property \"{0}\" was changed from \"{1}\" to \"{2}\"."
, property
,
this
._preValue
,
this
.GetPropertyValue(eventArgs.Instance, property)));
else
Console.WriteLine(
string
.Format(
"Property \"{0}\" was read."
, property));
}
public
override
void
OnEntry(MethodExecutionEventArgs eventArgs)
{
base
.OnEntry(eventArgs);
//记录属性更改前的值
if
(!eventArgs.Method.IsSpecialName)
return
;
if
(!eventArgs.Method.Name.StartsWith(
"set_"
))
return
;
string
property = eventArgs.Method.Name.Substring(4);
this
._preValue =
this
.GetPropertyValue(eventArgs.Instance, property);
}
private
object
GetPropertyValue(
object
instance,
string
property)
{
PropertyInfo getter = instance.GetType().GetProperty(property);
return
getter.GetValue(instance,
null
);
}
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
[PropertyChangedNotification]
public
class
Person
{
private
string
firstName;
private
string
lastName;
public
Person(
string
first,
string
last)
{
this
.firstName = first;
this
.lastName = last;
}
public
string
FirstName
{
get
{
return
firstName; }
set
{ firstName = value; }
}
public
string
LastName
{
get
{
return
lastName; }
set
{ lastName = value; }
}
public
string
Name
{
get
{
return
this
.FirstName +
" "
+
this
.LastName; }
}
}
<BR>
static
void
Main(
string
[] args)
{
Person user =
new
Person(
"Richie"
,
"Liu"
);
user.FirstName =
"RicCC"
;
Console.WriteLine(
string
.Format(
"{{ {0} {1} }}"
, user.FirstName, user.LastName));
Console.ReadKey();
}
|
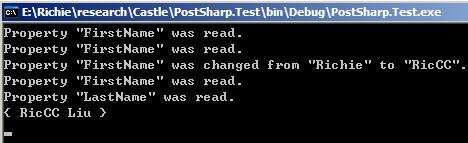
因为我们在Property的setter方法进入(OnEntry)时用反射读取了属性的值,记录修改之前的属性值;然后在setter方法结束(OnExit)时又使用反射去读取了修改之后的属性值,因此在***was changed from *** to ***这条消息之前,有2条属性的读取日志
Cache示例
PostSharp中有个缓存方法调用的示例:第一次调用方法的时候,执行这个方法,并把执行结果缓存起来;后面再调用这个方法时,就直接从缓存中取结果,让方法返回,而不执行方法体
实现这一功能的aspect类如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
|
[Serializable]
public
sealed
class
CacheAttribute : OnMethodBoundaryAspect
{
// 用来生成缓存的key值,key值中包含方法名、参数值等,因此参数不一时方法会被执行
private
MethodFormatStrings formatStrings;
// 用于缓存
private
static
readonly
Dictionary<STRING,
object
=
""
> cache =
new
Dictionary<STRING,
object
=
""
>();
<BR>
// 编译时刻执行的方法
// Cache这个attribute用于方法上,某些方法不允许使用缓存,将在下面进行检查
public
override
bool
CompileTimeValidate(MethodBase method)
{
// Don't apply to constructors.
if
(method
is
ConstructorInfo)
{
Message.Write(SeverityType.Error,
"CX0001"
,
"Cannot cache constructors."
);
return
false
;
}
MethodInfo methodInfo = (MethodInfo)method;
// Don't apply to void methods.
if
(methodInfo.ReturnType.Name ==
"Void"
)
{
Message.Write(SeverityType.Error,
"CX0002"
,
"Cannot cache void methods."
);
return
false
;
}
// Does not support out parameters.
ParameterInfo[] parameters = method.GetParameters();
for
(
int
i = 0; i < parameters.Length; i++)
{
if
(parameters[i].IsOut)
{
Message.Write(SeverityType.Error,
"CX0003"
,
"Cannot cache methods with return values."
);
return
false
;
}
}
return
true
;
}
// 编译时刻执行的方法
public
override
void
CompileTimeInitialize(MethodBase method, AspectInfo aspectInfo)
{
this
.formatStrings = Formatter.GetMethodFormatStrings(method);
}
<BR>
public
override
void
OnEntry(MethodExecutionArgs eventArgs)
{
//生成缓存的key值
string
key =
this
.formatStrings.Format(
eventArgs.Instance, eventArgs.Method, eventArgs.Arguments.ToArray());
lock
(cache)
{
object
value;
//查看是否存在缓存
if
(!cache.TryGetValue(key,
out
value))
// 缓存不存在,继续执行这个方法,并将key存在MethodExecutionTag,在执行完毕的
// OnSuccess事件时使用key值将结果放到缓存中
eventArgs.MethodExecutionTag = key;
else
{
// 已经在缓存中存在,则将执行的返回值直接设置为缓存中的值,不执行方法体而立即返回
eventArgs.ReturnValue = value;
eventArgs.FlowBehavior = FlowBehavior.Return;
}
}
}
<BR>
//这个事件只有在方法体被执行了,并且执行成功没有异常发生时才会触发
public
override
void
OnSuccess(MethodExecutionArgs eventArgs)
{
// 取得缓存的key值
string
key = (
string
)eventArgs.MethodExecutionTag;
// 把执行结果放入缓存中
lock
(cache)
{
cache[key] = eventArgs.ReturnValue;
}
}
}</STRING,></STRING,>
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
public
static
void
Main(
string
[] args )
{
Console.WriteLine(
"1 ->"
+ GetDifficultResult( 1 ) );
Console.WriteLine(
"2 ->"
+ GetDifficultResult( 2 ) );
Console.WriteLine(
"1 ->"
+ GetDifficultResult( 1 ) );
Console.WriteLine(
"2 ->"
+ GetDifficultResult( 2 ) );
Console.ReadKey();
}
[Cache]
private
static
int
GetDifficultResult(
int
arg )
{
// 如果方法体被执行了,则会输出下面的消息,否则不会输出,说明使用了缓存
Console.WriteLine(
"Some difficult work!"
);
Thread.Sleep( 1000 );
return
arg;
}
|
DbInvoke示例
这也是PostSharp中一个比较有意思的示例,其工作方式大致如下,先使用下面代码声明一些方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
[DbInvoke(
"ConnectionString"
)]
internal
static
class
DataLayer
{
#pragma warning disable 626
extern
static
public
void
CreateCustomer(
string
customerName,
out
int
customerId);
extern
static
public
void
ModifyCustomer(
int
customerId,
string
customerName);
extern
static
public
void
DeleteCustomer(
int
customerId);
extern
static
public
void
ReadCustomer(
int
customerId,
out
string
customerName);
#pragma warning restore 626
}
|
通过这样的方式,将数据库的存储过程声明为.NET中的extern方法,简化对存储过程的调用方式
Aspect的类型
1. OnMethodBoundaryAspect
可以override OnEntry、OnExit、OnSuccess、OnException等方法实施拦截,可以读取入参,修改ref、out类型的入参,决定是否调用被拦截的方法体,以及读取、修改方法的返回值等,一般可以用于自己编写的assembly,进行日志记录等操作
PostSharp对原方法注入一个try{}catch(){}语句,在适当的位置注入各个拦截事件的调用代码
当对同一个方法使用多个该类型的aspect时,可以通过设置或者实现AspectPriority来确定各个拦截器的执行顺序
类似于前面的Cache示例中使用到的,在aspect之间或者拦截的各个方法之间,可以通过MethodExecutionEventArgs的MethodExecutionTag属性来传递必要的状态信息
2. OnExceptionAspect
用于实现异常捕获,可以运用于第三方开发的,没有源代码的assembly上
3. OnFieldAccessAspect
方便对field的读取、设置进行拦截处理,override OnGetValue、OnSetValue方法实施拦截。测试过程中无法读取到FieldInfo属性,不知道是不是只有商业版注册后才可以使用这个功能
对field访问的拦截只能适用于当前程序集,如果其他程序集直接诶访问field无法实现拦截,所以对于public、protected类型的field,PostSharp会将field重命名,然后自动生成一个原field名字的property,这会导致依赖的程序集二进制兼容性被破坏,需要重新编译。这个行为也可以通过选项进行配置,阻止PostSharp这样做
4. OnMethodInvocationAspect
override OnInvocation方法实施拦截,PostSharp不是直接修改注入目标程序集,而是为目标方法生成一个委托,修改当前程序集中的调用,改为调用委托,从而实现拦截(这种方式叫做Call-site weaving,调用方织入,对应的另一种方式叫做Target-site weaving,目标织入)。这种方式可以实现对第三方程序集方法实施拦截
5. ImplementMethodAspect
如前面的DbInvoke示例,这个aspect用于extern方法、abstract类的方法进行拦截,不要求目标方法有具体的实现
Aspect的生命周期
aspect在编译期实例化,PostSharp将aspect的实例序列化存到assembly中,在运行时再反序列化回来
对multicast类型的attribute,PostSharp会为每个匹配到的类型、方法等单独创建一个该attribute的实例对象应用于目标上
multicast概念:本来我们写一个custom attribute,必须在每个需要运用的方法、类型上面使用这个attribute,PostSharp中的multicast指可以指定比较宽的一个范围,或者使用正则表达式以及一些filter等,将这个attribute应用到匹配到的多个目标对象上面去,类似于多播这样的效果。这就是在前面使用过的assembly指令
这个概念导致的一个结果,对于理解PostSharp的行为比较重要,如果某个multicast类型的attribute指定为作用于field,但又将这个attribute设置在了type上面,则PostSharp会为该type的所有field运用这个attribute,从而运用拦截处理
另外,PostSharp的示例Advanced\AssemblyExplorer项目演示了如何使用PostSharp的CodeModel。PostSharp没有使用Mono.Cecil和CCI等开源项目,而是建立了自己的CodeModel来分析和修改assembly的元数据以及IL代码等,通过这个示例可以大致了解如何使用PostSharp的CodeModel来实现某些元数据、IL层面的操作
参考:
Aspect Oriented Programming 101
AOP Implementation of INotifyPropertyChanged







 本文介绍PostSharp AOP框架的使用方法,包括日志记录、属性更改通知、方法调用缓存等功能,并通过示例展示如何实现这些功能。
本文介绍PostSharp AOP框架的使用方法,包括日志记录、属性更改通知、方法调用缓存等功能,并通过示例展示如何实现这些功能。
















 185
185

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








