Problem Description
A sequence S
n is defined as:
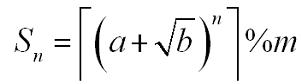
Where a, b, n, m are positive integers.┌x┐is the ceil of x. For example, ┌3.14┐=4. You are to calculate S n.
You, a top coder, say: So easy!

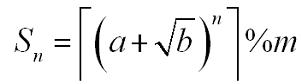
Where a, b, n, m are positive integers.┌x┐is the ceil of x. For example, ┌3.14┐=4. You are to calculate S n.
You, a top coder, say: So easy!

Input
There are several test cases, each test case in one line contains four positive integers: a, b, n, m. Where 0< a, m < 2
15, (a-1)
2< b < a
2, 0 < b, n < 2
31.The input will finish with the end of file.
Output
For each the case, output an integer S
n.
Sample Input
2 3 1 2013 2 3 2 2013 2 2 1 2013
Sample Output
4 14 4
Source


1 /*思路:若(a+√b)n == x + y·√b(x、y为整数),则(a-√b)n == x - y·√b。又因为a-1 < √b < a, 2 所以0 < (a-√b)n < 1,即x-1 < y·√b < x,所以ceil((a+√b)n) == 2x。接下来事情就容易多了, 3 同时对x、y两部分进行快速幂取模即可*/ 4 #include <cstdio> 5 typedef long long LL; 6 LL a,b,n,m; 7 void solve() { 8 LL ans1(1),ans2(0),t1(a),t2(1); 9 LL tmp; 10 while(n) { 11 if(n&1) { 12 tmp = ans1; 13 ans1 = (ans1*t1+ans2*t2*b)%m; 14 ans2 = (tmp*t2+ans2*t1)%m; 15 } 16 tmp = t1; 17 t1 = (t1*t1+t2*t2*b)%m; 18 t2 = 2*tmp*t2%m; 19 n >>= 1; 20 } 21 printf("%lld\n",ans1*2%m); 22 } 23 int main() { 24 while(~scanf("%lld%lld%lld%lld",&a,&b,&n,&m)) 25 solve(); 26 return 0; 27 }




















 3415
3415

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








