一、创建对象并将其初始化
a、使用new创建对象和方法
<<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<mete http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=utf-8"/>
<title>javaScript中的数组和对象</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="./out.js">
var box=new Object;
box.name="张三";
box.age=23;
box.run=running();
function running(){
return "我是中国人";
}
document.write(typeof box+"<br/>");
document.write(box.name +"<br/>");
document.write(box.age +"<br/>");
document.write(box.run);
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
b、字面量表示方法
<<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<mete http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=utf-8"/>
<title>javaScript中的数组和对象</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="./out.js">
var box={
name:"张三",
age:23,
run:function(){
return "我是中国人!!"
}
};
document.write(typeof box);
document.write(box.name);
document.write(box.age);
document.write(box.run());
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
c、综合使用
说白了就是二者结合使用
function box(obj){ if(obj.name!=undefined)document.write(obj.name+"<br/>"); if(obj.age!=undefined)document.write(obj.age+"<br/>"); if(obj.love!=undefined)document.write(obj.love+"<br/>"); } var obj={ name:"张三", age:23 }; box(obj);
二、Array类型
新建数组的三种方法:
var box=new Array(1,2,3,4);
document.write(typeof box);
document.write(box);
var box2=new Array(10);
box2[3]=4;
box2[6]=25;
document.write(typeof box2);
document.write(box2);
var box3=[1,3,4,44,5,5,23];
document.write(typeof box3);
document.write(box3);
(1)转换方法
对象或数组都具有toLocaleString(),toString()和valueOf()方法。其中toString()和valueOf()无论重写了谁,都会返
回相同的值。数组会将每个值进行字符串形式的拼接,以逗号隔开。
默认的情况下,数组字符串都会以逗号隔开。如果使用join()方法可以使用不同的分割符来构建这个字符串
(2)栈方法
ECMAScript数组提供了一种让数组的行为类似于其他数据结构的方法。也就是说,可以让数组像栈一样,可以限
制插入和删除想的数据结构。栈是一种后进先出的数据结构,也就是最新添加的元素最早被移除。而栈元素的插入和
移除,只发生在栈的顶部。ECMAScript为数组专门提供了push()和pop()方法。
栈操作数组元素的图片:
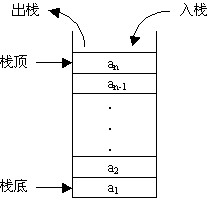
push()方法可以接受任意数量的参数,把它们逐个添加到数组的末尾,并返回修改数组的长度。而pop()方法则从
数组末尾移除最后一个元素,减小数组的length值,然后返回移除的元素。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
var
box=[1,2,3,4];
document.write(box+
"<br/>"
);
box.push(5,6);
//在数组末尾添加元素
document.write(box+
"<br/>"
);
document.write(box.push(7,8)+
"<br/>"
);
//在数组末尾添加元素,并返回添加元素后数组的长度
document.write(box+
"<br/>"
);
box.pop();
//移除数组末尾的元素
document.write(box+
"<br/>"
);
document.write(box.pop()+
"<br/>"
);
//移除数组末尾的元素,并返回移除的元素
document.write(box);
|
输出:

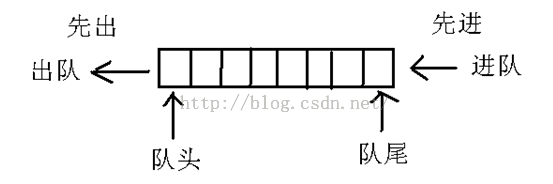
(3)队列方法
栈方法是后进先出,队列方法是先进先出。队列在数组的末端添加元素,从数组的前端移除元素。通过push()向
数组末端添加一个元素,然后通过shift()方法从数组的前端移除一个元素。
队列操作数组元素的图片
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
var
box=[1,2,3,4];
document.write(box+
"<br/>"
);
box.push(5,6);
//在数组末尾添加元素
document.write(box+
"<br/>"
);
document.write(box.push(7,8)+
"<br/>"
);
//在数组末尾添加元素,并返回添加元素后数组的长度
document.write(box+
"<br/>"
);
box.shift();
//移除数组前端的一个元素
document.write(box+
"<br/>"
);
document.write(box.shift()+
"<br/>"
);
//移除数组前端的一个元素,并返回移除的元素
document.write(box);
|
输出:
ECMAScript还为数组提供了一个unshift()方法,它和shift()方法的功能完全相反。unshift()方法为数组的前端添加
一个元素。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
var
box=[1,2,3,4];
document.write(box+
"<br/>"
);
box.unshift(0);
//在数组的前端添加一个元素
document.write(box+
"<br/>"
);
document.write(box.unshift(-1)+
"<br/>"
);
//在数组的前端添加一个元素,并返回添加元素会数组的长度
document.write(box+
"<br/>"
);
box.pop();
//在数组末尾移除元素
document.write(box+
"<br/>"
);
document.write(box.pop()+
"<br/>"
);
//在数组末尾移除元素,并返回移除元素后数组的长度
document.write(box);
|
输出:

(4)重排序方法
数组中已经存在两个直接用来排序的方法:reverse()和sort()。
reverse():逆向排序
|
1
2
3
4
|
var
box=[1,2,3,4,5];
box.reverse();
document.write(box+
"<br/>"
);
//输出54321
document.write(box.reverse());
//再次进行逆序,输出12345
|
sort():从小到大排序
|
1
2
3
4
|
var
box=[3,2,6,4,1,5];
box.sort();
document.write(box+
"<br/>"
);
//输出1,2,3,4,5,6
document.write(box.sort());
//再次从小到大进行排序
|
如果我们实验次数多的话可能回遇到这样的问题,
|
1
2
3
|
var
box=[0,15,10,1,5];
box.sort();
document.write(box);
//输出0,1,10,15,5
|
我们从结果可以看出,这违背了我们想要的结果,解决方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
function
compare(value1,value2){
if
(value1<value2){
return
-1;
}
else
if
(value1>value2){
return
1;
}
else
{
return
0;
}
}
var
box=[0,15,10,1,5];
box.sort(compare);
document.write(box);
//输出0,1,5,10,15
|
(5)操作方法
JS为操作已经包含在数组中的元素提供了许多的方法。concat()方法可以基于当前数组创建一个新数组。slice()方
法可以基于当前数组获取指定区域元素并创建一个新数组。splice()方法主要用途是向数组的中部插入元素。
a
|
1
2
3
4
|
var
box=[1,2,3,4,5];
var
box1=box.concat(6);
//创建新数组,并添加新元素
document.write(box1+
"<br/>"
);
//输出1,2,3,4,5,6,
document.write(box);
//原数组不变化
|
b
|
1
2
3
4
|
var
box=[1,2,3,4,5];
var
box1=box.slice(2);
//取出索引为2以后的元素组成新的数组
document.write(box1+
"<br/>"
);
//输出3,4,5
document.write(box);
//原数组不变化
|
c
|
1
2
3
4
|
var
box=[1,2,3,4,5];
var
box1=box.slice(2,3);
//取出索引为2到3之间的元素组成新的数组
document.write(box1+
"<br/>"
);
//输出3
document.write(box);
//原数组不变化
|
splice中的删除功能
|
1
2
3
4
|
var
box=[1,2,3,4,5];
var
box1=box.splice(0,2);
//截取索引为0开始的两个元素组成新的数组
document.write(box1+
"<br/>"
);
//返回截取的元素1,2
document.write(box);
//当前数组被截取的元素被删除,输出3,4,5
|
splice中的插入功能
|
1
2
3
4
|
var
box=[1,2,3,4,5];
var
box1=box.splice(4,0,6);
//索引为4的位置插入了一个元素
document.write(box1+
"<br/>"
);
//返回新的数组为空,并没有截取元素
document.write(box);
//当前数组索引为4的位置插入一个元素1,2,3,4,6,5
|
splice中的替换功
|
1
2
3
4
|
var
box=[1,2,3,4,5];
var
box1=box.splice(4,1,6);
//索引为4的元素被替换,替换下来的元素组成新数组
document.write(box1+
"<br/>"
);
//返回新的数组5
document.write(box);
//被替换后的原数组1,2,3,4,6
|
以上就是关于JavaScript对象和数组的详细介绍,希望对大家的学习有所帮助。




 本文深入探讨了JavaScript中对象和数组的创建、初始化方法,包括使用new关键字、字面量表示以及结合使用的方式。详细解释了数组的三种创建方法、转换方法、栈方法、队列方法、重排序方法及操作方法。提供了丰富的实例代码,帮助读者理解和实践。
本文深入探讨了JavaScript中对象和数组的创建、初始化方法,包括使用new关键字、字面量表示以及结合使用的方式。详细解释了数组的三种创建方法、转换方法、栈方法、队列方法、重排序方法及操作方法。提供了丰富的实例代码,帮助读者理解和实践。
















 1603
1603

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








